Introduction
Acute esophageal necrosis, more commonly known as the black esophagus, is a rare entity with little clarity in its pathophysiology, reported since 1990, whose diagnosis is made endoscopically. The estimated prevalence of this pathology based on the medical literature is 0%-10.3%, and with the advent of endoscopy, 0.01%-0.28% based on retrospective1-5 and prospective6) studies. Given the rarity of this clinical entity and the lack of understanding of its pathophysiology, we describe the clinical case of a male patient with an endoscopic diagnosis of acute necrotizing esophagitis, treated at a tertiary care university hospital in Popayán, showing its evolution and outcome.
Case presentation
We present the case of a 56-year-old male patient with a history of hypertension, asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, ichthyosis vulgaris, and obesity. He is under pharmacological treatment with amlodipine, carvedilol, indacaterol/glycopyrronium, and montelukast. He has been hospitalized multiple times for exacerbation of underlying lung disease.
He attended the emergency department for a two-week clinical picture consisting of progressive dyspnea associated with cough and purulent expectoration, fever, and chills. On admission, severe bronchospasm and hypotension refractory to fluid therapy were detected.
An admission chest x-ray reveals alveolar opacities in all four quadrants, multiple emphysematous bullae, “ground glass” appearance, and multiple linear images secondary to fibrous tracts in both lung fields. Laboratory tests revealed leukocytosis, neutrophilia, azotemia, severe respiratory acidemia, hypoxemia and hyperlactatemia, and elevation of acute phase reactants.
The septic shock of pulmonary origin was diagnosed, with criteria of severity and mechanical ventilation requirement. The patient was admitted to the intensive care unit (ICU) for comprehensive management with antibiotic coverage based on carbapenem and glycopeptide, bronchodilator therapy, intravenous steroids, and neuromuscular blockade due to poor coupling to invasive mechanical ventilation.
His clinical evolution was torpid; he required high ventilatory parameters and vasoactive support, increased leukocytosis, elevated nitrogen levels, and oliguria. The patient needed renal replacement therapy with hemodialysis from the fifth day of hospitalization.
On the ninth day of his stay in the ICU, the patient presented with hematemesis and sudden anemia. Upper endoscopy (EGD) showed, from 19 cm to the esophagogastric junction, sloughing of the mucosa with necrosis, adherent clots, diffuse bleeding in the layer and some areas, and deep involvement with exposure of the submucosa (Figure 1). He received treatment with a continuous infusion of a proton pump inhibitor, a transfusion of blood products, and antibiotic therapy. Esophageal perforation was ruled out by cervical-thoracic-abdominal computed tomography (CT) scan.
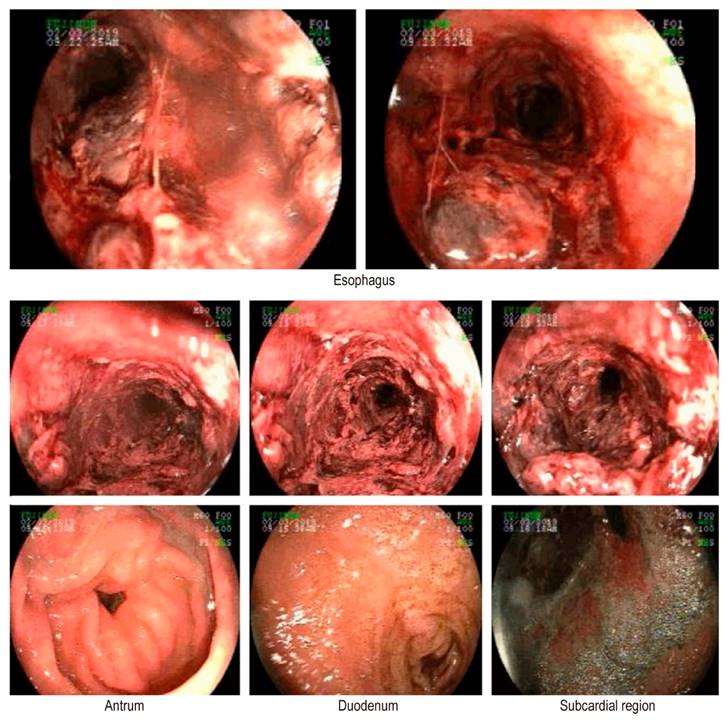
Figure 1 EGD: severe esophagitis, mucosal necrosis, and chronic gastritis of the antrum. Source: Authors’ archive.
The patient exhibits a persistence of prolonged refractory multifactorial shock. It was necessary to perform a tracheostomy and a percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy.
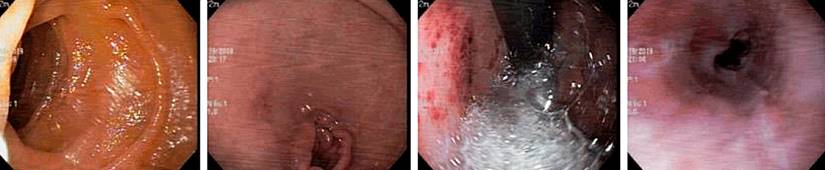
On day 17 of hospitalization, a new follow-up EGD (Figure 2) showed erosions in the lower third of the esophagus with mottled erythema and erosions of the antrum and body.
The patient died on day 34 of hospitalization from worsening of his condition due to an infectious pulmonary event.
Discussion
Acute esophageal necrosis or acute necrotizing esophagitis (AEN), also known as black esophagus syndrome, is a rare pathology that presents with an endoscopically defined alteration in the mucosa of variable severity.
The incidence is four times higher in men than women, and comorbidities are presented as an associated factor in all the cases reported in the literature, including diabetes mellitus, high blood pressure, alcohol abuse, chronic kidney disease, coronary disease, dyslipidemia, among others7.
The pathophysiology of AEN generally involves a combination of multiple mechanisms. The “two hits”8 hypothesis is considered the most widely accepted: the first is a state of hypoperfusion that damages the esophageal mucosa, leading to esophageal ischemia, generally seen in states of hemodynamic compromise and low flow. Subsequently, a second attack is caused by massive gastric acid reflux and impaired mucosal repair mechanisms present in weakened physical conditions9.
There are multiple cases of AEN secondary to septic shock, where generalized vasodilation mediated by cytokines results in hemodynamic compromise and decreased perfusion pressure. Despite aggressive treatment with fluid therapy, vasoconstrictors, proton pump inhibitors, and empiric broad-spectrum antibiotic therapy, the outcome for these patients is commonly sepsis with multiple organ failure and death10,11.
The treatment of this entity is not standardized and is aimed at comorbidities and specific pathologies of the patient. Medical management is based on medication with a proton pump inhibitor or histamine receptor blockers until the clinical condition improves. Antibiotics are recommended in cases of suspected esophageal perforation, clinical deterioration, transplant recipients, cirrhotic patients, and patients on dialysis, reserving surgical intervention for patients with classic indications for it, such as esophageal perforation with subsequent risk of mediastinitis and abscess formation. Once the acute condition has been controlled, the requirement for dilations or stent placement should be defined in cases of poor response12.
Conclusions
AEN is a pathology of rare incidence with a mortality rate of up to 50% whose endoscopic diagnosis is relatively simple due to its characteristic findings. Although such mortality is likely associated with shock or pan-esophageal disease, which conditions early suspicion of this pathology, intensive treatment and management of AEN possibly improve its mortality rate.











 text in
text in