Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Cited by Google
Cited by Google -
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO -
 Similars in Google
Similars in Google
Share
Ensayos sobre POLÍTICA ECONÓMICA
Print version ISSN 0120-4483
Ens. polit. econ. vol.29 no.spe64 Bogotá June 2011
The Risk-Taking Channel and Monetary Transmission Mechanism in Colombia
El canal de toma de riesgo y mecanismo de transmisión monetario en Colombia
O canal de toma de risco e mecanismo de transmissão monetário na Colômbia
Martha López
Fernando Tenjo
Héctor Zárate*
*We wish to thank Hernando Vargas, Andrés González and Enrique López for comments on earlier drafts. We also extend our thanks to Manuel D. Hernández for research assistance and to the participants of the "4th International Workshop on Computational and Financial Econometrics", December 10-12, 2010, London, for comments on earlier drafts. The views expressed in this paper are those of the authors.
The autors are, in orden, Researcher, Department of Macroeconomic Modelling, Banco de la República, Bogotá. Co-Director, Board of Directors, Banco de la República, Bogotá. Chief of Statistics Department, Banco de la República, Professor of Statistics, at Universidad Nacional de Colombia, Bogotá.
e-mail: mlopezpi@banrep.gov.co; ftenjoga@banrep.gov.co; hzaratso@banrep.gov.co.
Document received: 7 October 2010; final version accepted: 30 March 2011.
The recent financial crisis has brought to the forefront the need for a better understanding of the transmission mechanisms of monetary policy. The main step forward on this issue has drawn on work aimed at stressing the role of the financial sector in this transmission. Particular emphasis has been placed on how policy actions impact risk perceptions and attitudes of banks and other financial institutions, leading to shifts in the supply of credit. Along these lines, and based on evidence from Colombia, this paper finds a significant link between low interest rates and banks' risk-taking based on evidence from Colombia. Lower interest rates raise the probability of default on new loans, but reduce that on outstanding loans. Furthermore, this channel of policy transmission depends on some bank, loan and borrower characteristics, as well as on macroeconomic conditions, such as the growth rate of the economy.
JEL classification: E44, G21, L14.
Keywords: monetary policy, lending standards, risk-taking, duration analysis, accelerated failure time models.
La crisis financiera reciente ha advertido la necesidad de un mejor entendimiento del mecanismo de transmisión de la política monetaria. El principal avance en esta dirección destaca la participación del sistema financiero en esta transmisión. En particular, se ha enfatizado en la manera como las acciones de política tienen efecto sobre las percepciones de riesgo y actitudes de los bancos y otras instituciones financieras, las cuales implican un cambio en la oferta de crédito. Con este marco analítico y con base en la evidencia para Colombia, este documento encuentra una relación significativa entre bajos niveles de tasas de interés y toma de riesgo por parte de los bancos. Tasas de interés bajas aumentan la probabilidad de suspender los pagos de los créditos nuevos y reducen la de los créditos vigentes. Más aún, este canal de transmisión depende de las características de los bancos, de los créditos y de los deudores, así como de las condiciones macroeconómicas.
Clasificación JEL: E44, G21, L14.
Palabras clave: política monetaria, estándares de crédito, toma de riesgo, análisis de duración, modelos de tiempo de falla acelerada
A recente crise financeira tem chamado a atenção sobre a necessidade de uma melhor compreensão do mecanismo de transmissão da política monetária. O principal avanço neste sentido salienta a participação do sistema financeiro nesta transmissão. Em particular, faz-se ênfase na maneira como as ações da política têm efeito nas percepções de risco e as atitudes dos bancos e outras instituições financeiras, as quais supõem uma mudança na oferta de crédito. Com este marco analítico e com base na evidência da Colômbia, este documento encontra uma relação significativa entre baixas taxas de juros e toma de risco por parte dos bancos. As baixas taxas de juros incrementam a probabilidade de suspender os pagamentos dos créditos novos e reduzem a dos créditos vigentes. Ainda mais, este canal de transmissão depende das características dos bancos, dos créditos e dos endividados, assim como das condições macroeconômicas.
Classificação JEL: E44, G21, L14.
Palavras chave: política monetária, padrões de crédito, toma de risco, análises de duração, modelos de tempo de falha acelerada.
I. INTRODUCTION
This paper explores a dimension of the monetary policy transmission mechanism that has not been assigned due attention in the theoretical literature and empirical studies; namely, the extent to which policy shocks have real effects through their impact on the behavior of banks towards risk.
To a large extent, the motivation for this work is concern about the role played by the financial sector in general, and credit markets in particular, during the recent financial crisis. Beyond that, however, the role of banks and other financial institutions involved in the monetary transmission mechanism has been underestimated in much of the work conducted by academics and central banks, alike. Recent work has created favorable conditions for a more appropriate approximation on these issues. New conceptual developments have provided a sounder basis for the analysis of how interest rates impact risk perceptions and risk tolerance of banks, and how this translates into lending decisions, including quantities, prices and requirements. The well-known lending channel, with its two key related concepts -the financial accelerator and the external finance premium- has been complemented with the risk-taking channel that explains how the effect of the former channel can be enhanced, creating the possibility of buildup of risk and pro-cyclical or self-accumulating processes in the economy.
The availability of large data sets for banks, borrowers and loans -both at the individual country level and for groups of countries- has also made it possible, coupled with the development of statistical and econometric devices, to conduct comprehensive studies on how monetary policy is transmitted through changes in funding costs of banks and balance sheets, controlling for financial and macroeconomic conditions and bank, borrower and loan caracteristics. Central to these exercises is the possibility of estimating the probability of default of individual loans or of financial institutions that are the dependent variables in empirical works.
This paper draws from these developments and empirically analyzes the link between monetary policy and risk-taking by banks in Colombia. It uses a data base, with quarterly frequency, for more than two million loans, for the period 2000:I to 2008:IV.
This paper concludes that low interest rates affect monetary policy by increasing the probability of default on new loans and by lowering that for outstanding loans. This result is interpreted in terms of shifts in banks´ risk appetite (perception and willingness). It is also found that this effect depends on both the strength of balance sheets as well as on macroeconomic conditions.
The paper is organized as follows. The first section is this brief introduction. Section II presents the conceptual framework that links monetary policy and the supply of credit, overviews the key concepts of the lending and the risk-taking channels of monetary policy, and derives predictions on the impact of monetary policy when these channels are active. Section III elaborates on the empirical approach used to study the occurrence of the above mentioned channels of monetary policy in Colombia, and explains the model and its variables. Section IV summarizes the main findings of the empirical work. Lastly, the conclusions of the papers are presented in Section V.
II. MONETARY POLICY AND THE SUPPLY OF CREDIT
A. FINANCIAL VARIABLES IN THE TRANSMISSION OF MONETARY POLICY
The recent financial crisis has brought out the need for a better understanding of the transmission mechanisms of monetary policy. The main step forward on this issue has drawn on previous work aimed at stressing the role of the financial sector in this transmission. The dominant approach, more in line with the traditional Neo-classical school, has been found wanting. This approach underlines the impact of monetary policy on the relative yields of imperfectly substitutable assets (money versus bonds) Borio and Zhu (2008). These, in turn, affect investment (user cost of capital and Tobin's q) and consumption decisions (wealth and inter-temporal substitution effects), as well as trade flows through real exchange rates, Boivin, Kiley and Mishkin (2009), and Hatzius, Hooper, Mishkin, Schoenbholtz and Watson (2010). Other non-Neo-classical schools stress similar channels (investment and consumption optimization), but add an expectations´ channel in the transmission of monetary policy shocks. For this school, the key elements behind the real effects of monetary policy are the presence of price stickiness and the capacity of the monetary authority to anchor inflation expectations. The real effects of monetary policy are then derived from frictions in goods´ markets. It goes without saying that this neo-Keynesian school´s inclusion of inflation expectations within the policy rule of monetary authorities could be interpreted as a way to allow for the effect of financial variables -in particular, those embedded in the yield curve- on policy decisions.
Looked at more closely, the transmission of monetary policy along these lines really implies, at best, constant interest rate spreads and a passive role for the financial system. In striking contrast with these approaches, there is a growing body of literature that underscores how monetary policy alters the financial conditions of the economy that shape the behavior of economic agents. In particular, this literature focuses on how monetary policy is transmitted to the real economy through its impact on the balance sheets of economic agents and their perception of risk. In turn, this impact depends on the macroeconomic and financial conditions of the economy and on the strength of balance sheets. More concretely, to the extent that these effects converge in the dynamics of the credit market, they make up what is known as the lending channel of the transmission of monetary policy.
B. THE BANK LENDING CHANNEL OF MONETARY POLICY
There are at least two complementary strands in the literature that emphasize different elements of this channel. One strand originates in a re-assessment of the accelerator mechanism and emphasizes the existence of frictions at the level of financial intermediaries derived from asymmetric information in capital and money markets. These frictions are behind the effect of changes in the short-term interest rate set by the Central Bank on the external finance premium, or the cost of funds for banks and other financial intermediaries, Disyatat (2010). In a nutshell, the link between monetary policy shocks and the external finance premium lies in the perceived strength of the balance sheets of financial institutions, which determines their expected probability of default. Changes in banks' cost of funds -in response to such shocks- translate into differing responses in the supply of credit, depending on this probability of default. The risk perceptions of economic agents involved in the previous mechanism are themselves endogenous and unstable. This gives rise to what is known as the risk-taking channel of monetary policy, or the effect that this policy may have on the perception of, and willingness by, agents to bear risk. Disyatat (2010) and Borio and Zhu (2008) have formalized the risk-taking channel by showing how monetary policy may strongly influence the risk in portfolios, the pricing of assets, and the spreads and non-price terms in the extension of credit. These authors underline how this channel operates through the impact of interest rates on valuations, incomes and cash flows, as well as on target rates of return for investors. Furthermore, a Central Bank that reduces uncertainty regarding the future of the economy may exert a downward influence on risk premia.
Adrian and Shin (2009a; 2009b) provides a complementary approach to the bank lending channel, in general, and the risk-taking channel, in particular. For those authors, the latter channel summarizes the set of effects of monetary policy that work through the risk appetite of financial intermediaries: which lies behind shifts in the supply of credit. Along these lines, the origin of the risk-taking channel would be in the agency relationships in the organization of finance in society, where they are made manifestby the way financial intermediaries manage their balance sheets; in particular, by leveraging short- term liabilities to finance longer-term assets. Monetary policy not only determines short-term interest rates, but also strongly affects the financial conditions of the economy.
C. SUMMARY AND PREDICTIONS
A summary of the previous ideas is in order.
Attempts to understand and highlight the active role of banks and financial intermediaries in the transmission of monetary policy have focused attention on the way policy shocks translate into changes in the supply of credit. This can be put together in terms of two complementary channels: lending and risk-taking. The former points to the transmission of monetary policy, as such; the latter refers to how the effects of this policy can be amplified throughout the economy, with important real implications. Firstly, the transmission of monetary policy is highly influenced by: a) the health of the balance sheet of financial intermediaries (leverage and asset quality), and b) the perceptions of risk of economic agents, given c) the macroeconomic and financial conditions of the economy. The key element in this process is the external finance premium, or the cost of funding for these intermediaries, which reflects their perceived probability of default. Secondly, monetary policy decisions impact the perceptions of risk and the behavior of economic agents through their effect on asset valuations, cash flow implications, and risk appetite and tolerance. This means that estimates of default probabilities by banks and other financial institutions are endogenous, and give rise to pro-cyclical and feed-back mechanisms. Lastly, in terms of available policy instruments, the effects of monetary policy derive not only from the level of the short-term interest rate, but also from liquidity and balance sheet management by the Central Bank and communication strategies of the monetary authority.
The level of the policy rate is particularly important as it directly relates to risk-free interest rates and influences the cost of funds for banks and other intermediaries, as well as asset and liability valuations. Based upon the preceding models, it is possible to establish a close relationship among the stance of monetary policy, credit spreads, the growth and strength of balance sheets of financial intermediaries and economic activity. Running through this chain of causation is the idea that the short-term interest rates affect not only a wide set of other rates, but also the risk appetite and/or the risk-taking capacity of financial intermediaries. With this setting in mind, the literature has put forward various testable hypotheses, such as: a) the effect of changes in interest rates on the probability of default on bank loans; b) the role played by some features of banks (size, liquidity, leverage, asset quality, etc.) in their response to monetary policy decisions, or as the determinants of the sensitivity of the external finance premium on these decisions (Disyatat, 2010). Briefly put, three sets of variables would be at the center of the role of the financial system in the transmission mechanism of monetary policy: interest rates, balance sheet characteristics and the external finance premium of banks, or their perceived probability of default.
III. THE RISK-TAKING CHANNEL: EMPIRICAL APPROACHES AND APPLICATION TO COLOMBIA
A. TWO LINES OF RESEARCH
The bulk of the empirical work on the bank lending and the risk-taking channels can be grouped into two categories:
1) The first is centered on the idea of the external finance premium, or perceived probability of default, as influenced by both interest rate decisions of the Central Bank -conditional on a set of bank specific characteristics- and the state of the economy. This line of research follows the intuition that policy rates affect both the willingness and the capacity of agents to bear risks, and includes the estimation of the perceived probability of default in terms of expected default probabilities or loan hazard rates: proxies for the likelihood of a loan not being repaid. Some of the works in this group are: Gambacorta (2009), Jimenez, Ongena, Peydró and Saurina (2009), and Altunbas, Gambacorta and Marques (2009a). Altunbas, Gambacorta and Marques (2010) analyzes determinants of probabilities of default at the bank level.
2) The second group of studies, with a longer tradition, looks for a direct link -also conditioned by bank-specific characteristics- between changes in the policy rate and the supply of credit. The rationale behind this is that the dynamics of some components of the balance sheet of financial intermediaries (the stock of outstanding loans, in this case) is an indication of the risk appetite of these agents as influenced by policy decisions. Some of the papers in this group are: Altunbas, Gambacorta and Marques (2009b), Kashyap and Stein (2000), and Ioannidou, Ongena and Peydró (2009), which is more of a combination of the two approaches.
As already mentioned, research has been carried out on the transmission mechanism of monetary policy at the level of borrowing firms, lending banks, or individual loans, and primarily on the assembling data for sample of countries. The European Central Bank (ECB, 2009) summarizes the main results of a comprehensive survey of papers on the subject for the euro zone, and concludes that "the various credit channels are part of monetary policy transmission in the euro zone, [and that] recent empirical results point to an amplification of monetary policy impulses via the so-called risk-taking channel" (p. 79).
B. A STUDY OF THE RISK-TAKING CHANNEL FOR COLOMBIA
This paper adheres very closely to the research by Jimenez et al. (2009), which can be singled out as a major representative of the first category of works mentioned above. The authors analyze the impact of short-term interest rates on the probability of loan default in Spain. They do this for both before loan origination, and during the life of a loan; and, also include controlling for bank, firm, loan and macroeconomic characteristics. To accomplish this, they have put together a sample of business loans with a quarterly frequency for the period 1985:I to 2006:II. The work in question proposes a measure of credit risk, or a proxy, for a conditional perceived probability of default, which the authors have named ´the hazard rate´ or ´the probability of loan default´ during each period of the life of the loan, given the fact that default did not occur before. The findings derived by Jimenez and his colleagues are interesting, to say the least. They find that "low interest rates increase bank-risk taking, reduce credit risk in banks in the very short run, but worsen it in the medium run…[In addition], higher GDP growth reduces credit risk on both new and outstanding loans". As the authors under discussion have rightly stressed, the basic ingredients of the empirical strategy are: a valid measure of bank credit risk; a methodology that accounts for the dynamic context of the exercise; and exogeneity of monetary policy.
1. A Measure of Bank Risk
The basis for the estimation of a measure of bank risk is a data set for Colombia, consisting of quarterly information on 2,095,755 individual commercial loans for the period 2000:I to 2008:IV, provided by the National Banking Authority (Superfinanciera). The data set also includes information for borrower, lending bank, and some details on the loans such as: amount, collateralization, maturity and payment information (whether in default or not defining default as a situation in which the loan has not been served for more than three months). With this information, it is possible to construct, ex post, a probability of default for each loan. This is a proxy for loan risk, or, as Jimenez et al. (2009) put it, the ´hazard rate of the loan´.
2. Dynamics of the Probability of Default
Monetary policy affects the probability of default of a loan, not only at the time of origination, but also, and differently, during its life time. This is the idea behind the hazard rate defined above, which is derived from a conditional hazard function over the time of maturity of a loan until, and if,default occurs. This function gives the "per-period probability of loan default provided the loan survives to that period" (ibid.). The estimation of this function relies on duration analysis models, which allows for the effect of a set of observable and time-varying explanatory variables, including monetary policy shocks, in the determination of hazard rates for each loan, and in each period in which it is not in default.
3. The Stance of Monetary Policy
It should be taken into account that, in principle, there could be a two-way relation between loan risk and monetary policy. This would be the case when, for example, the monetary authority has an implicit or explicit concern over the stability of the banking sector and translates it into its reaction function. In this case, the policy rate is not exogenous and the econometric exercise would have to deal with identification problems.
Jimenez, et al. (2009) solve this problem in their study for Spain using the German overnight interbank rate of interest for the period 1988-1999, and the euro overnight interbank rate thereafter. In a related study for Bolivia, Ioannidou, et al. (2009) use the Fed target rate, taking into account that the local economy is highly dollarized. Solving probable identification problems in this study for Colombia could, in the first instance, be more complex, since monetary policy in this country is conducted with a greater degree of freedom than in the two aforementioned countries.
It can be argued, however, that during the period of the study, 2000 to 2008, the Central Bank in Colombia did not systematically take into account bank risk considerations in its policy decisions on interest rates. Furthermore, when the Central Bank expressed concern over the dynamics of credit markets and their relation to bank risk, it resorted to other instruments -in particular, changes in reserve requirements- to address this problem.
On the basis of these arguments, it can be contended that, for the purposes of this work -which is to examine the response of banks' willingness to bear risk to changes in interest rates by the Central Bank- the (real) inter-bank rate of interest, closely determined by the policy rate, can be considered exogenously determined.
Nevertheless, we add a robustness exercise in which, instead of directly using the policy interest rate, we use the deviation of the natural interest rate as suggested by Gambacorta (2009). The results of our empirical analysis did not change.
C. THE MODEL
We use a duration or hazard function model to study the time to default of individual bank loans. Duration models applied to this problem can provide answers to questions -after the occurrence of a negative shock- such us: ´What is the probability that a bank loan will default in the following quarter, given the fact that it has survived up to that moment?´. In duration models, the dependent variable is duration, in this case, the time that it takes a loan to change from one state to another.
Let T represent the time that elapses before the occurrence of the default of the loan. The passage of time is often referred to as a spell. According to Jimenez et al. (2009), a simple way to describe the behavior of a spell is through its survivor function, S(t) = P(T ≥ t), which yields the probability that the T spell lasts at least to time t. Alternatively, the hazard function determines the conditional probability that the state ends in a short time after t, provided that it has reached time t, that is:

Where f(t) is the density function associated with the distributions of spells. In this case, the hazard rate provides us with a per-period measure of risk- taking. When λ(t) is increasing in t, the hazard is said to exhibit positive duration dependence.
Usually, when estimating hazard functions it is convenient to assume a proportional hazard specification:

Where X(t) is known as a vector of covariates or explanatory variables, β is a vector of unknown parameters, and λ0 is the baseline hazard function. In our benchmark model, we use a Weibull specification for the baseline hazard rate λ0, where λ0(t) = λαtα-1, which is monotonically increasing if α > 1, and monotonically decreasing if α < 1. Our benchmark model has this specification because after one or two initial quarters overdue, repayments could become conditionally more likely over the life of the loan. However, the scale parameter is a function of some explanatory variables. In other words, the risk of default is not proportional to changes in covariates. However, testing proportional hazard specification was rejected when we used the test proposed by Shoenfeld (1980) and graphical analysis of the residuals. Thus, the accelerated Failure Time Model arises; in this context, the conditional hazard rate is:

This is an acceleration of the baseline hazard λ0(t) if exp(-x'β)>1, and a deceleration if: exp(-x'β)<1
In addition, we performed robustness checks using different probability distributions. The estimation technique used maximum likelihood estimation with a Newton-Raphson algorithm and took into account right- censoring.
The variables included in the model are the following.
D. HAZARD RATE
As explained above, the dependent variable in the model is the hazard rate, which is a proxy for the riskiness of a loan in a given period. It should be interpreted as its time-varying probability of default.
The independent variables can be grouped into different categories.
E. INTEREST RATE
Monetary policy impacts loan risk doubly: prior to the origination of a loan in period ζ[INTERESTRATEζ - 1], and during each of the periods of the life of the loan until it eventually defaults or is due in period T [INTERESTRATEζ+ T - 1]. In other words, changes in the policy rate can have two separate effects on bank risk: as new loans are originated and on existing loans. As mentioned above, the interest rate used in the estimation is the real inter-bank interest rate.
F. BANK-SPECIFIC VARIABLES (MEASURED PRIOR TO THE LOAN ORIGINATION PERIOD)
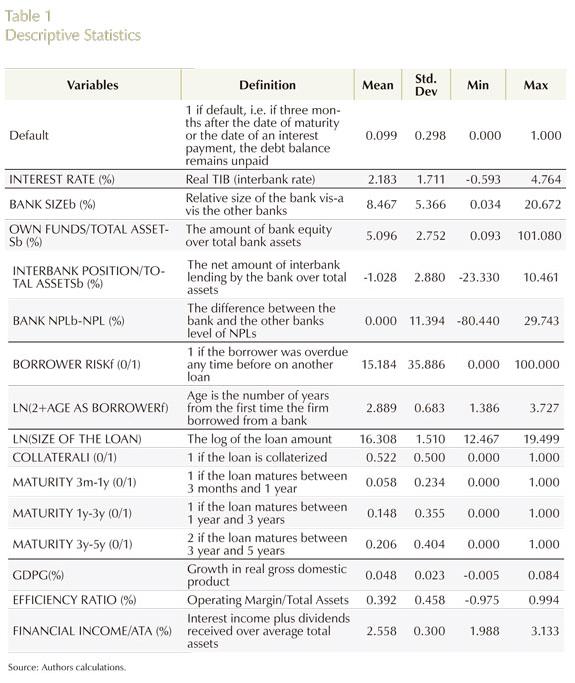
1) Size [BANK SIZEbbζ - 1]: measured in terms of assets and entered as the relative size of the bank (in percentage points) vis-à-vis the other banks in the sample.
2) Own Funds [OWNFUNDS / TOTALASSETSbζ - 1]: measured as the ratio of bank equity to total bank assets. It is also the inverse of the leverage of the bank
3) Interbank position [INTERBANKPOSITION/ TOTALASSETSbζ - 1]: the ratio of net inter-bank lending to the bank to its total assets.
4) Relative non- performing loans position [BANKNPLbζ - 1- NPLζ - 1]: difference between the bank and other banks' level of non-performing loans.
G. LOAN-SPECIFIC VARIABLES (MEASURED AT THE PERIOD OF LOAN ORIGINATION)
1) Size [LN(SIZEOFTHELOAN1ζ]: measured by the natural logarithm of the amount of the loan.
2) COLLATERAL1ζ: a dummy variable equal to "1" if the loan is collateralized and to "0", if it is not collateralized.
3) MATURITY1ζ: dummies for each of three categories, namely, loans of 3 months to one year of maturity, 1 to 3 years, and 3 to 5 years.
H. GDP GROWTH
Annual percentage growth rate of GDP on a quarterly basis. As in the case of interest rates, this variable has two separate effects on hazard rates, one at origination and another effect during the life of the loan [GDPGζ - 1, GDPGT - 1 or GDPGt - 1]. A summary of descriptive statistics is provided in Table 1.
IV. RESULTS
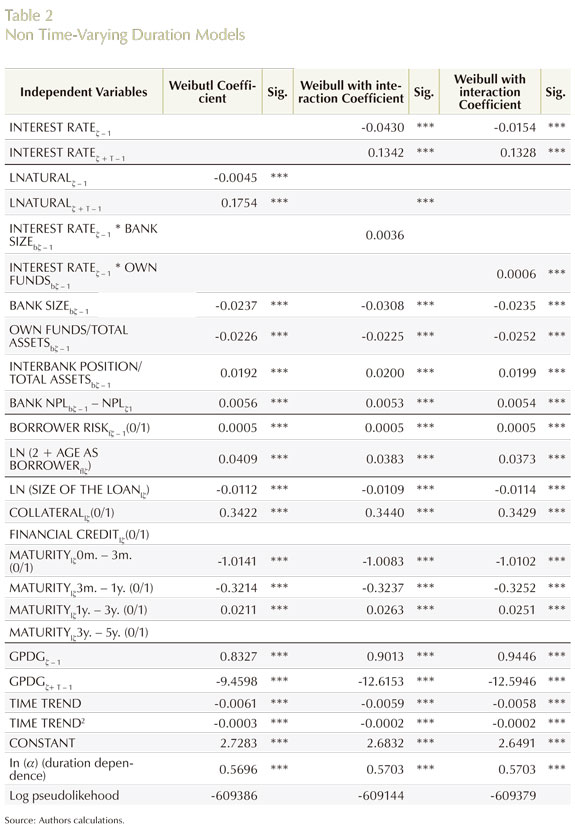
The way the model was specified allows for a wide range of mechanisms through which changes in interest rates affect risk perceptions, risk tolerance and, in general, the behavior or economic agents. The exercise is designed not only to illustrate the impact of lower interest rates on this behavior, but also to make explicit, or to delve into the channels through which this impact takes place. However, the effect of lower interest rates on the balance sheet of lending institutions -one of the central factors that explains how enhancing mechanisms arise and that eventually leads to the overextension of balance sheets- cannot be envisaged from the exercise above. The link from lower interest rates to balance sheets and then to hazard rates is thus not made explicit in the model. In spite of this, the results obtained are promising, and lend interesting support to the conceptual framework presented in the previous sections of this paper. All the regression coefficients analyzed above are statistically significant. In Table 2, we present the results. Our benchmark model, as explained before, is the Weibull specification (column 1).
A. INTEREST RATES AND HAZARD RATES
The main finding of this paper sheds light on how monetary policy is transmitted through the credit market in Colombia. This finding is similar to Jimenez´s et al. (2009) finding for Spain:
1) Lower interest rates raise hazard rates on new loans (-0.013),
2) But reduce the hazard rate on outstanding loans (0.133).
These two results provide evidence in favor of the hypothesis put forward in this, and other papers, that lower interest rates impact the behavior of lending institutions by affecting their attitude towards risk. Banks respond to a more expansive monetary policy in a way that indicates higher tolerance for lower quality loans, and a reduced perceived risk for outstanding loans. As a robustness exercise, we present the results with a different measure of the stance of monetary policy: the deviation of the interest rate with respect to the natural interest rate (part Two in Table 2, column 1), and the basic results remain unchanged.
With these results in mind, it is possible to see how changes in the stance of monetary policy would affect the perceived probability of default of a loan. This is done by calculating an annualized hazard rate for a loan with mean characteristics, but with a maturity of twelve months, and for two paths of monetary policy: a) an increase in the interest rate from its mean at loan origination (2.18%, in real terms) to its maximum level at maturity (4.76%, also, in real terms), and b) a reduction in this rate from the mean level at origination (real, 2.18%) to its minimum level at maturity (real, -0.59%), see Figure 1.
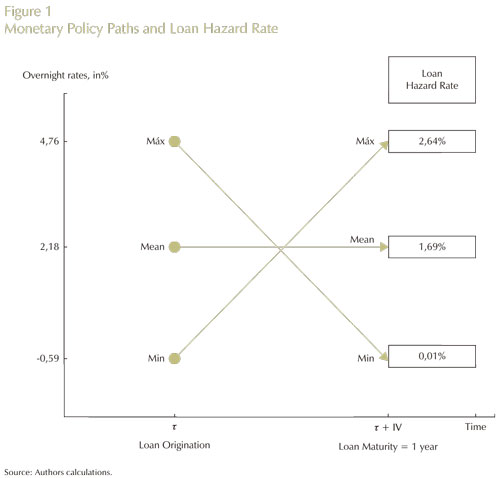
Whereas the first policy path (rate increase) raises the annualized loan hazard rate from 1.69% to 2.64%, the second (rate reduction) lowers the annualized loan hazard rate from 1.69% to 0.01%. These results suggest asymmetric effects of shifts in monetary policy to an expansive or a restrictive stance. Hazard rates of outstanding loans are more sensitive to downward than to upward movements in policy rates.
A new avenue for the analysis of the transmission of monetary policy could be derived from here, more centered on hazard rates than on market rates of interest. In a nutshell, the response by banks to policy shocks "in terms of credit supply", depends, ceteris paribus, not on the magnitude of changes in policy rates, but on how these changes affect banks' perceptions and tolerance towards risk. It follows, that the Central Bank in Colombia is relatively more effective when it tries to stimulate the economy by lowering interest rates than when it tries to slow it down through higher interest rates.
B. CONTROL VARIABLES
The interpretation of the results for control variables contributes to determining if there are features in the behavior of lending institutions that strengthen the persistence mechanisms embedded in the risk-taking channel.
C. AS REGARDS THE BANK-SPECIFIC VARIABLES INCLUDED IN THE MODEL
1) Bank size. Larger banks exhibit lower hazard rates or, in other words, face lower loan risk. The reason for this negative relationship could lie in the direct links that connect bank size with relative power in the market for savings, liquidity and interbank resources. This advantage of larger banks enables them not only to fund their liabilities at lower rates, but also to diversify their funding sources.
2) Own funds. The negative sign of the coefficient indicates that banks with a higher ratio of own funds to total assets exhibit a lower hazard rate. This may be interpreted as a sign of self-discipline on the part of banks: they lend more carefully when there is a larger proportion of their own resources involved in their lending activities.
Alternatively, a more interesting interpretation can be obtained if use is made of concepts more akin to the literature on lending and risk-taking channels. The same result can be read as an indication of a positive relationship between leverage and hazard rates, which would suggest that a build-up of risks accompanies the expansion of banks' balance sheets. This mechanism is, in fact, a key ingredient of the risk-taking channel.
3) Dependence on the interbank market. The results indicate that the more a bank depends on the interbank market for funds, the higher the hazard rate on its loan portfolio. This may be interpreted as a sign that, independent of the level of the interest rate, and of changes in it, the bank with greater reliance on the interbank market faces higher funding costs (a less favorable external finance margin). These higher costs have to be transferred to lending rates -in particular, to lower quality borrowers and loans. There seems to be an element of persistence- enhancing in this mechanism, and even of overextension on the balance sheets of banks.
4) Response to non-performing loans. The finding that banks with a higher incidence of non-performing loans vis-à-vis other banks exhibit worse loan risk may appear counter-intuitive at first sight, since it suggests that the bank with a heavier load of low quality assets consciously persists in risky lending. However, there is room for an alternative interpretation in line with the previous paragraph: relatively lower quality assets imply higher funding costs that are transmitted to lending rates that, in turn, further deteriorate hazard rates.
Again, this result is evidence of the persistence- enhancing mechanisms that characterize the risk-taking channel.
D. FOR LOAN-SPECIFIC CHARACTERISTICS THE RESULTS ARE THE FOLLOWING
It was found that smaller and shorter-maturity loans hold greater risk, which clearly coincides with what can be expected in a credit market with asymmetric information and economics of scale in the lending activity. The positive sign on the coefficient for collateral seems counter-intuitive and difficult to interpret on the basis of existing literature.
E. FOR BORROWER-SPECIFIC CHARACTERISTICS
It was found -in line with what could be expected- that borrowers who have defaulted in the past exhibit a higher probability of worse hazard rates on new loans. This result also confirms that there is persistence in the credit market that is enhanced by the behavior of banks, probably derived from higher interest rates that are charged on loans to "bad" borrowers.
The other result, that "older" borrowers exhibit higher hazard rates, seems counter-intuitive and difficult to interpret on theoretical grounds.
F. GROWTH AND RISK-TAKING
The results on GDP growth reinforce the notion that there is, embedded in the behavior of banks, a mechanism that changes their perception of risk in response, in this case, to macroeconomic conditions. A higher rate of growth of the economy increases the hazard rate of new loans and lowers that of outstanding loans. Higher growth makes banks more optimistic and tolerant to risk, and this, in turn, implies that lower quality loans are originated. On the other hand, the same higher rates of growth positively impact the perception of risk on outstanding loans and reduce their probability of default through, among other things, cash flow implications.
G. OTHER SPECIFICATIONS
In order to check robustness of the results we estimate several models under different distributions. Table 2 (columns 3 to 5) shows that our main results remain unaffected.
In addition, the literature on the bank-lending and risk-taking channels underscores the fact that the transmission of monetary policy depends on some characteristics of banks. This contention has been tested here through the interaction of these characteristics with changes in interest rates by the monetary authority. Columns 6 and 7 from Table 1 present these results. On the one hand, the effect of a reduction in interest rates on the hazard rate for new loans is reinforced in the case of lower-sized banks. On the other hand, banks with a lower ratio of own resources to total assets or, more precisely, more leveraged banks, also strengthen the negative impact of a reduction in policy rates on the hazard rates of new loans. This highlights two amplification mechanisms of monetary policy: one related to the size of banks, and the other to their balance sheet characteristics. The results for interactions with other bank-specific characteristics are not robust.
V. CONCLUSIONS
Based on empirical evidence for Colombia, this paper finds a statistically significant link between interest rates and banks' risk- taking. Lower interest rates increase the probability of default on new loans and reduce that on outstanding loans. This effect of monetary policy is partially attenuated by bank size, but amplified by bank leverage. Such amplification reflects what theory refers to as "persistence enhancing mechanisms" that underlie the pro-cyclical character of financial markets.
The picture depicted in the previous paragraph corresponds to a dimension of the monetary policy transmission mechanism not often sufficiently taken into account. In this dimension, risk perceptions play a central role and banks are not passive conduits for policy shocks.
It can also be concluded that banks' balance sheets are a key element in the transmission of monetary policy. As argued in this paper, the quality of assets and the degree of leverage both affect and are affected by risk considerations. The results of this paper clearly confirm the links that reach from balance sheets to risk perceptions and tolerance, but only hint at those in the opposite direction.
Short-term interest rates are also an important price in the economy. They are an explanatory variable in the determination of loan risk of individual banks, beyond their relationship with longer-term rates and their role in the formation of expectations. Risk-taking channel literature underlines the effect of the level short-term rates on cash flows and asset valuation, elements that have been put forward in this paper that contribute to explaining the positive relationship between policy rates and the probability of default on outstanding loans.
The findings of this paper suggest that, in spite of the prominent role of interest rates in the transmission of monetary policy, the mechanism, as such, has to be understood carefully. In the first place, just as the model in this paper did, interest rates will have to be translated into hazard rates or perceived probabilities of default on loans and of borrowers. Secondly, the relationship between interest rates and hazard rates is essentially non-linear. As argued in Section IV above, banks' response to policy shocks depends not so much on the magnitude of these shocks as on how they affect perceived probabilities of default. And this, in turn, is also a function of some bank-specific characteristics and of macroeconomic and financial conditions. Again, risk perceptions lie at the heart of the transmission of monetary policy.
Interestingly, the implications of this view go back to, and complement, the pioneering work by Stiglitz (1981) on imperfect information and credit rationing. The authors propose a non-linear relationship between interest rates and the "expected return to the bank" on its loans, with the latter being determined by the adverse selection and incentive effects emerging from asymmetric information. Informational imperfections then affect the supply of credit, making it bend backwards at some unspecified level of the interest rate. To a good extent, the bank lending and risk-taking channels represent a more elaborated and modern version of the views expressed by Stiglitz and Weiss almost thirty years ago, with the emphasis placed on agency relations on the side of banks. The findings of their paper may also give rise to implications for the conduct of monetary policy in Colombia. On the one hand, it is clear from what has been shown and said that monetary policy and policies toward financial stability are closely linked. On the other hand, the asymmetric effects of shifts in monetary policy to an expansive or a restrictive stance should serve as guidance on future policy decisions. In particular, the fact that the Central Bank seems to be relatively less effective when it shifts to a more restrictive stance, could be translated into a few guiding points that monetary authorities should take into account in the future: a) the risks involved in delaying a necessary shift to a more restrictive policy stance, and b) the eventual convenience of complementing interest rate increases with other instruments that contribute to accelerate the transmission of higher rates.
REFERENCES
1. Adrian, T.; Shin, H. Financial Intermediaries and Monetary Economics. Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Staff Reports No. 398, October, 2009a [ Links ]
2. Adrian, T.; Shin, H. Prices and Quantities in the Monetary Policy Transmission Mechanism. Federal Reserve Bank of New York, Staff Reports No. 396, October, 2009b. [ Links ]
3. Altunbas, Y.; Gambacorta, L.; Marques, I. D. An Empirical Assessment of the Risk-Taking Channel. Paper presented at the BIS/ECB conference on "Monetary policy and financial stability", 10-11 September, 2009a. [ Links ]
4. Altunbas, Y.; Gambacorta, L.; Marques, I. D. "Bank Risk and Monetary Policy", Working Paper, num. 712, May, Banca D'Italia, 2009b. [ Links ]
5. Altunbas, Y.; Gambacorta, L.; Marques, I. D. "Does Monetary Policy Affect Bank-Risk Taking?", BIS Working Paper, num. 298, 2010. [ Links ]
6. Boivin, J.; Kiley, M.; Mishkin, F. How Has the Monetary Transmission Mechanism Evolved Over Time. Prepared for the third Handbook of Monetary Economics, presented at the Federal Reserve Conference on Key Developments in Monetary Policy, October 9, 2009. [ Links ]
7. Borio, C.; Zhu, H. "Capital Regulation, Risk-Taking and Monetary Policy: A Missing Link in the Transmission Mechanism", BIS Working Paper, num. 268, December, 2008. [ Links ]
8. Disyatat, P. "The Bank Lending Channel Revisited", BIS Working Paper, num. 297, February, 2010. [ Links ]
9. ECB. Monetary Policy and Loan Supply in the Euro Area, ECB Monthly Bulletin, October, 2009. [ Links ]
10. Gambacorta, L., Monetary Policy and the Risk-taking Channel, BIS Quarterly Review, December, 2009. [ Links ]
11. Hatzius, J.; Hooper, P.; Mishkin, F.; Schoenbholtz, K.; Watson, M., Financial Conditions Indexes: A Fresh Look After the Financial Crisis. Mimeo, 2010. [ Links ]
12. Ioannidou, V.; Ongena, S.; Peydró, J. Monetary Policy, Risk-Taking and Pricing: Evidence from A Natural Experiment. Paper presented at the NBER Summer Institute, Cambridge, MA, 2009. [ Links ]
13. Jimenez, G.; Ongena, S.; Peydró, J.; Saurina, J. Hazardous Times for Monetary Policy: What Do Twenty-Three Million Bank Loans Say About the Effects of Monetary Policy on Credit Risk-taking? Paper presented at the American Finance Association Meetings, San Francisco, 2009. [ Links ]
14. Kashyap, A.; Stein, J. "What Do A Million Observations On Banks Say About the Transmission of Monetary Policy?" American Economic Review, vol. 90, num. 3, pp. 407-428, 2000. [ Links ]
15. Shoenfeld, D., 1980. "Chi-squared Goodness-Of-Fit Tests For the Proportional Hazard Regresion Model", Biometrika, num. 67, pp. 145-153. [ Links ]
16. Stiglitz, J.; Weiss, A. "Credit Rationing in Markets With Imperfect Information", The American Economic Review, vol. 71, num. 3, pp. 393-410, 1981. [ Links ]














