Introduction
The amount of genetic variability within a species and, therefore, adaptability of their progeny to the environment, are mostly determined by the breeding system. Autogamous and asexual species produce populations with little evolutionary flexibility and high local specialization (Stebbins 1950), whereas outcrossing species produce more genetically diverse and ecologically variable offspring. Grasses display an extraordinary diversity of breeding systems including outcrossing, selfing or mixed-breeding, and a mixture of asexual and sexual reproduction (Quinn 1998). Many plant species have developed different ecological, morphological and physiological mechanisms that reduce the degree of self-fertilization to promote cross-pollination (Eckert 1994), most likely motivated by the increase in individual and average population fitness caused by heterosis.
The frequency of outcrossing is an important determinant of population genetic structure, affecting both genetic diversity within populations and genetic differentiation among them (Barrett and Harder 1996). Methods commonly employed for assessing the mode of reproduction in forage grasses include cytological and embryological analyses of the mother plant and screening for morphologically aberrant progeny. Molecular marker analysis, in particular, Simple Sequence Repeat (SSR) or microsatellite, is a tool now widely used in a variety of fundamental and applied fields of biology, including the identification of selfed, outcrossed or apomictic progeny in several grass species (Chistiakov et al. 2006; Liu and Wu 2012). SSRs are loci ubiquitously distributed within genomes that show a high level of polymorphism, environmental independence and rapid detection protocols. The reproductive system and the ploidy level of a species determine the transmission of genes across generations, the pattern of inheritance and gene flow, and influence the genetic structure of plant populations and their evolutionary potential. This information is critical when planning and developing conservation and breeding programs.
Panicum coloratum L., a perennial grass native to Africa, is adapted to a wide range of soil and climatic conditions, and has been used as forage in Australia, Japan, USA, Mexico and South America (Cook et al. 2005). This species has been classified into mainly 2 botanical varieties, var. makarikariense Gooss. and var. coloratum, distinguished by morphological traits and environmental preferences (Bogdan 1977; Armando et al. 2013). The var. makarikariense is particularly well adapted to heavy clay soils that fluctuate between drought and waterlogged conditions, whereas var. coloratum develops well in sandy soils, is tolerant of salinity and performs well at higher latitudes or elevations, as it thrives under low temperatures, withstanding some frost (Tischler and Ocumpaugh 2004). In Argentina, a breeding program and research activities involving var. makarikariense were initiated by the National Institute of Agricultural Technology (INTA) in 2006, with the purpose of developing new pasture cultivars adapted to marginal (drought, waterlogging, salinity or thermal stress) and less productive environments where livestock production has been displaced, with expansion of cropping into the most productive paddocks and planting of soybeans.
Panicum coloratum botanical varieties have been described as mainly allogamous (Brown and Emery 1958; Hutchison and Bashaw 1964), although the degree of self-fertilization has not been quantified and apomictic mechanisms have been suggested (Hutchison and Bashaw 1964). Unlike previous reports, which focused on the female parts of flowers and embryo sac development, our main interest is the analysis of the particular effects of different pollination systems on viable seed production and the survival of subsequent progeny. In addition, cytogenetic studies in var. makarikariense showed variable numbers of chromosomes: 2n = 18, 36, 45, 49 and 63 (Hutchison and Bashaw 1964; Pritchard and De Lacy 1974).
In the present work, progeny of P. coloratum var. makarikariense derived from self- and open-pollinated panicles were studied through the stages of seed production, germination and progeny survival. Additional data were obtained from SSR marker analysis, and chromosome number was also determined. This study attempted to provide information regarding the reproductive behavior of P. coloratum var. makarikariense, with utility for conservation and breeding.
Materials and Methods
Plant samples
Panicum coloratum was introduced into Argentina in the 1990s but has not been used widely as forage, although it has been conserved at various locations as collections or in small paddocks. Details of introductions are often limited, with many coming from different parts of the world. A collection of P. coloratum var. makarikariense (Table 1) was established in a common garden at the INTA Rafaela Experiment Station (31°11'41'' S, 61°29'55'' W) in Argentina in 2006, as a breeding population. Pre-breeding studies demonstrated a high level of variability in morphological and molecular markers, both among and within accessions, which justified the initiation of a breeding program (Armando et al. 2013). In fact, a cultivar from the program was released recently: Kapivera INTA (Giordano et al. 2013). The collection comprised 6 accessions of 32 plants each and 15 clonally propagated genotypes (IFF) obtained by selection on agronomic characteristics. The 32 plants of each accession were placed at 0.6 m intervals in an 8 x 4 matrix plot, with plots 15 m apart, while the 15 IFF genotypes were clonally propagated 8 times and arranged linearly in an 8 x 15 matrix plot at a distance of 0.6 m.
Seed production
Seed production of 3 plants (only 2 plants for accession DF), selected at random from each of the UCB, MR, BR, ER and CM accessions and 1 clone of each of the 15 IFF genotypes (Table 1) (a total of 32 plants) of P. coloratum var. makarikariense, was measured in the field from March to May 2009. Unfortunately, 1 plant of the DF accession was damaged and data were unavailable. For each plant, 2 panicles were selected at random: 1 for self-pollination and 1 for open-pollination. Only a single panicle was enclosed in each seed trap, the ones for self-pollination before anthesis and the ones for outcrossing when 2/3 of the panicle was in anthesis. Seed traps were used in order to facilitate seed collection and to prevent losses by seed shattering. Traps were therefore put in place at different stages of development for self- and open-pollinated treatments, but within the same treatment attempts were made to select panicles at the same stage of development. In self-pollinated treatments seed traps were covered with a white cotton bag to prevent pollen arrival from other sources without precluding light interception and photosynthesis of glumes (Figure 1). Self- and open-pollinated seeds were collected simultaneously once a week and manually separated from the glumes and other residuals. Eventually, the total number of seeds per inflorescence was counted, i.e. dark brown seeds (comprising lemma and palea containing a caryopsis). Small light-weight whitish seeds (hereafter referred to as "empty seeds") were also produced and counted as immature florets and/or spikelets with premature shattering from the inflorescences. Empty seeds show poor germination capacity, while dark brown seeds show a high germination percentage (Maina et al. 2017). The final numbers of seeds produced under self- and open-pollinated conditions were compared.
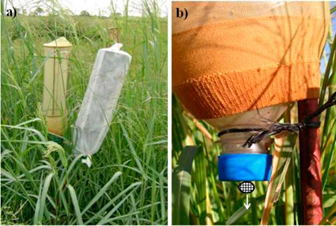
Figure 1 Seed traps enclosing inflorescences consisting of an iron cylindrical structure covered by a nylon stocking (modified from Young 1986). a) Open-pollination trap (left) and self-pollination trap with a white cloth bag (right). b) Detail of the lower part of the trap (water drainage). Seeds (= mature florets) were trapped and funneled into a cap as they shattered from the panicle.
Seed germination and seedling survival
Harvested seeds were naturally air-dried and stored at room temperature in paper bags for 1 year before testing for seed germination to ensure dormancy was already overcome (Tischler and Young 1987). Of the 32 plants evaluated, only 11 produced filled seeds under self-pollination. In each accession, only plants producing a good quantity of filled seeds (UCB3, MR1, BR1, ER1, CM2, IFF10; see Figure 2) were used to evaluate germination and seedling survival (n = 6). Thirty filled seeds per panicle from the same plants in both self- and open-pollinated treatments were placed in 10-cm diameter Petri dishes separately with filter paper at the bottom moistened with distilled water, and incubated in a programmed germination chamber at 42% humidity and 27 °C (Tomás et al. 2015) at a 16-hour photoperiod (light photon flux density: 48 mmol/s/m2). Dishes from different pollination treatments and different plants were randomly arranged in the chamber. The number of germinated seeds per dish was counted daily and seed germination percentage (% G) was recorded on day 7 after the initiation of the germination trial. Studies by Tomás et al. (2015) showed that maximum germination has been reached by day 7. A seed was considered germinated when the radicle emerged through the seed coat. Eight-day-old seedlings were individually transplanted into 0.5 L plastic containers filled with a soil-sand-perlite mix (1:1:1 v/v), placed in a greenhouse at 28 °C and watered as needed, usually every 2 to 3 days. Seedling survival percentage (% Ss) was recorded when seedlings were 15 and 40 days old.
Progeny test
In order to analyze genetic composition of the offspring, a random sample of 12-15 seedling descendants from 3 female parents, UCB3, ER1 and IFF10, was genetically characterized. These plants were selected to represent the observed range in the number of seeds produced within var. makarikariense (see Figure 2). Progeny test was performed only on seeds produced via open pollination as only a limited number of progeny were obtained from selfing. In addition, progeny obtained from open-pollinated traps resembled more natural pollination conditions.
DNA extraction was carried out using a modified SDS method (Edwards et al. 1991). Approximately 150 mg of leaf tissue (from plants >1 year old) was homogenized in liquid nitrogen. A 700 uL volume of extraction buffer containing: 50 mM Tris pH 8, 10 mM EDTA pH 8, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM ^-mercaptoethanol and 10% SDS, was added and incubated at 65 °C for 20 min. After adding 200 uL of 5 M potassium acetate pH 4.8, the sample was incubated on ice for at least 20 min and then centrifuged at 13,000 rpm for 20 min. This was followed by precipitation with 700 uL of iso-propanol incubated at -20 °C for 10 min, and centrifugation at 13,000 rpm for 4 min. The resulting pellet was washed with ethanol 70% and dissolved in 100 uL of 1 x TE buffer. DNA quality was evaluated in agarose gel and the quantity was determined by spectrophotometry.
In previous work, out of 40 heterologous SSR loci evaluated in P. coloratum var. makarikariense, 10 primer pairs were successfully amplified showing polymorphic and clear banding patterns (Armando et al. 2015). From these, the 5 most variable ones were chosen for analysis both of mother plants and offspring (Table 2). Amplification reactions were performed in 20 uL final volume containing: 30 ng of DNA template, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.125 mM of each dNTPs, 10 pmol of each primer and 1 U of Taq DNA polymerase in 1.6x buffer. Negative controls (no DNA template) were also included. Poly-merase chain reactions (PCR) were carried out in an MJ Research Thermal Cycler. The optimum annealing temperature (Tm) was determined for each locus (Table 2). By touchdown PCR (TD), the annealing temperature was decreased to 1 °C starting with 5 °C over the set annealing temperature. Initial denaturation step of 95 °C for 3 min was followed by 10 touchdown cycles of 94 °C for 30 sec, touchdown annealing temperature for 30 sec and 72 °C for 45 sec. PCR products were subsequently amplified for 34 cycles at 94 °C for 30 sec, annealing temperature for 30 sec, and 72 °C for 45 sec with a final extension at 72 °C for 20 min. Amplifications were initially checked on 1% agarose gels. PCR products were analyzed on 6% denaturing polyacrylamide gel, with a TBE 1x electrophoresis buffer at 50W for 1 h and 45 min to 2 h. Bands were visualized by silver staining and scanned.
Table 2 Simple sequence repeat (SSR) loci used for progeny analysis and polymerase chain reactions (PCR) conditions.
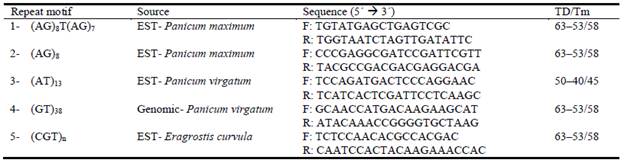
SSR 1 and 2 (Ebina et al. 2007); 3 (Tobias et al. 2006); 4 (Wang et al. 2011); 5 (Cervigni et al. 2008). TD/Tm: Touchdown/Annealing temperature; F: forward primer; R: reverse primer.
Chromosome number
To confirm the chromosome number of P. coloratum var. makarikariense, 8 different plants were evaluated. One plant from each accession was chosen at random and considered representative of each accession (DF, UCB, MR, BR, ER and CM), while 2 plants were selected from IFF.
Root tips of 3-month-old plants were pretreated with 8-hydroxyquinoline (0.002 ml/g) for 5 h. The roots were fixed in a freshly prepared mixture of ethanol:glacial acetic acid (3:1 v/v) for 48 h at room temperature and then placed in 70% ethanol at 4 °C for several weeks. Treated roots were put in 95, 70 and 40% ethanol and distilled water for 15 min each, hydrolyzed in 1 N HC1 at 60 °C for 8 min, transferred to distilled water for 2 min and stained in leuco-basic fuchsin for 1 h at room temperature in the dark. The 3-4 mm deeply stained root tips were removed from the roots, placed in a drop of 2% hema-toxylin with 2% ferric citrate used as mordant, and squashed (modified from Núñez 1968). Cells with fully contracted and well spread metaphase chromosomes were photographed using a digital camera.
Data analyses
Average number of filled and empty seeds, germination percentages at day 7, time at which 50% of seeds had germinated (T50) and survival of 15- and 40-day-old seedlings were recorded for self- and open-pollinated conditions. The mean values obtained for the 2 forms of pollination were compared through one-tailed Student's t-test for paired samples, since a higher number of filled seeds was expected in cross-pollination. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) for the mean number of seeds was performed and accessions were compared by Fisher's LSD tests. Statistical analyses were performed using Infostat software (Di Rienzo et al. 2008).
Based on the number of seeds, germination and survival data per panicle, probability of seed production, and probability of seedling survival for self- or cross-pollinated conditions were estimated by using the conditional probability and Bayes Theorem (Quinn and Keough 2002). The probability of seedling survival (SS) was calculated as: P(SS) = P(SS/SPs)*P(SPs) + P(SS/SPo)*P(SPo), where P(SS/SPs) and P(SS/SPo) are the conditional probabilities of seedling survival from seeds produced under self- and open-pollinated conditions, respectively; P(SPs) and P(SPo) are the probabilities of seed production under self- and open-pollination; and P(SS) is the probability of seedling survival. The conditional probability of finding a plant given that it was produced under self- or open-pollination was calculated as: P(SPs/SS) = P(SS/SPs)*P(SPs)/P(SS) and P(SPo/SS) = P(SS/SPo)*P(SPo)/P(SS), respectively.
In the progeny test, offspring's DNA fingerprints were individually compared with the maternal pattern. The occurrence of a sexual reproduction event was defined as when progeny DNA fingerprints revealed a deviation from the maternal profile. Each band was considered as an independent locus, and polymorphic bands were scored visually as either absent (0) or present (1) for each of the 45 plants. Only those bands consistently scored were considered for analysis. By combining the markers, unique profiles were obtained for each individual. Genetic diversity in the progeny was estimated using the total number of alleles, number of alleles shared with female parents (maternal alleles) or deriving from male parents (paternal alleles), and percentage of polymorphic loci (%P).
The genetic dissimilarity between the maternal parents and their progeny was analyzed using a genetic binary distance (GD) according to Huff et al. (1993). An UPGMA cluster was obtained from GD matrix. Analyses of molecular data were performed using GenAlEx 6, Genetic Analysis in Excel (Peakall and Smouse 2012) and Infostat programs (Di Rienzo et al. 2008).
Results
Effect of pollination method on progeny number and seedling survival
The mean number of filled seeds per panicle under open-pollination was considerably higher than those produced under self-pollination (P<0.001, Table 3). In contrast, the mean number of empty seeds (empty perfect florets and/or caryopses unable to germinate) did not differ significantly between the 2 forms of pollination (P = 0.1518, Table 3). In general, the number of filled seeds per panicle was highly variable among plants, registering values from 0 to 72 (CV = 149%) for self-pollinated panicles and from 14 to 795 (CV = 61%) for open-pollinated panicles (Figure 2). Mean number of filled seeds differed significantly among accessions for both self- and open-pollination methods (Figure 3). According to Fisher's LSD test, the commercial variety (cv. Bambatsi) had the highest mean number of filled seeds under open-pollination, while the lowest number was from accession BR (Figure 3).
Table 3 Comparison of the average number of filled (n° Fs) and empty (n° Es) seeds per panicle, seed germination percentage (% G), time needed for seeds to reach 50% germination (T50) and seedling survival percentage (% SS) of 15- and 40-day-old seedlings, between self-pollinated and open-pollinated panicles, using the student t-test in P. coloratum var. makarikariense.
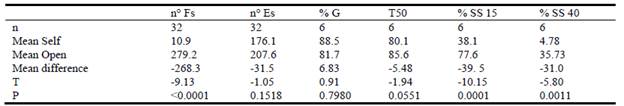
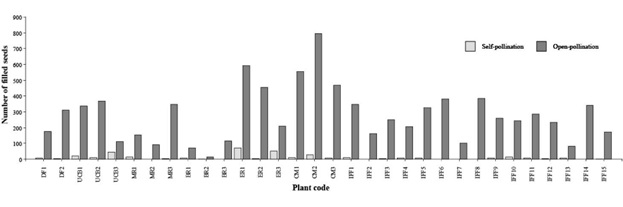
Figure 2 Number of filled seeds produced per panicle under self-pollination and open-pollination in 32 individuals of P. coloratum var. makarikariense.
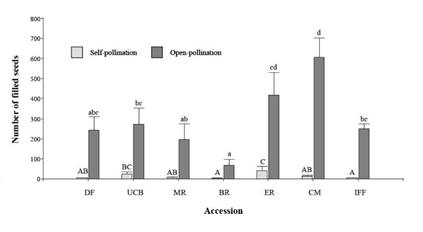
Figure 3 Mean number of filled seeds produced per panicle under self-pollination and open-pollination in accessions of P. coloratum var. makarikariense. In each type of pollination, different letters indicate significant differences between accessions (P<0.001) using Fisher's LSD tests and bars represent standard errors of means (lower case letters refer to open-pollinated and upper case to self-pollinated).
Regarding progeny performance, the seed germination percentages were above 80% and together with T50 no significant differences were observed in filled seeds obtained from both self- and open-pollinated conditions (Table 3). In all the plants evaluated T50 values showed that at least half of the seeds (range 50-97%) had germinated by the 3rd day after the trial started, except for one plant where T50 extended to the 5th day (data not shown). The survival of both self- and open-pollinated seedlings decreased over time, but the survival of seedlings derived from open-pollination was significantly higher (P<0.001) than those obtained from selfing at both 15 and 40 days of age. In particular, survival of 40-day-old seedlings from self-pollinated panicles was much lower than that from out-crossing (4.8 vs. 35.7%) (Table 3).
Estimates of total seed production and seedling survival of plants from accessions of var. makarikariense are shown in Table 4, differentiating those obtained from the different methods of pollination. Of the total number of filled seeds produced per panicle, the probability of them being produced by open-pollination was greater (92%) than by self-pollination (8%). The estimated survival at 40 days of a seedling from a seed obtained by self-pollination was lower (6%) than the survival of a seedling coming from a seed obtained by open-pollination (32%). In addition, the estimated probability of plant survival for this period of time, independently of whether it came from self- or open- pollination, was 30%. Combining data, the estimated probability of finding a plant obtained by open-pollination was significantly higher (97%) than those produced by self-pollination (3%).
Table 4 Probabilities of seed production (SP) under self- (s) or open-pollination (o) and seedling survival (SS) in P. coloratum var. makarikariense.
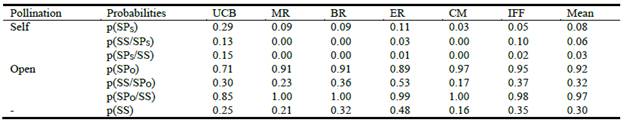
p(SS/SPs) and p(SS/SPo): conditional probability of seedling survival given that seed production was under self- or open-pollination, respectively.
p(SPs/SS) and p(SPO/SS): conditional probability of finding a plant given that it was produced under self- or open-pollination, respectively.
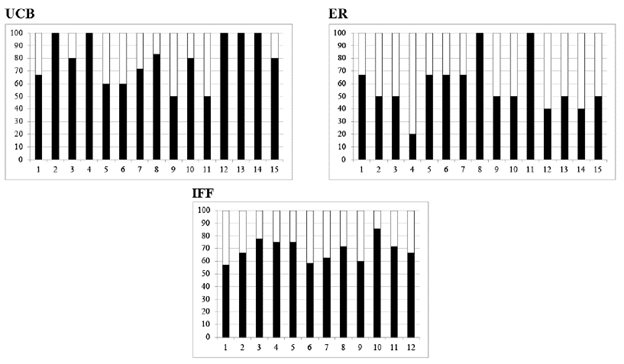
Figure 4 Percentage of SSR alleles attributed to female ( ) and male ( ) parents in progenies of P. coloratum var. makarikariense from 3 accessions (names are detailed in Table 1).
Effects of pollination method on genetic variability and contrast with female parents
Progeny from 3 female parents were analyzed with 5 SSR markers. Offspring plants were classified as identical when patterns were the same as the female parents at all the evaluated SSR loci or distinct when any band differences between female parent and progeny were observed. The SSR analysis showed values of percent polymorphic loci (%P) over 50% in progenies, and maternal and paternal alleles could be recognized in individual progeny (Table 5). On average, 85% (range 67-100%) of individual progeny presented alleles not found in the female parent (Figure 4). Additionally, offspring were not identical with their maternal patterns but they were closely grouped in the dendrogram according to families (Figure 5). Moreover, the 3 female plants were genetically distinct.
Table 5 Genetic diversity in 3 progeny of P. coloratum var. makarikariense assessed by 5 simple sequence repeat markers (SSR).
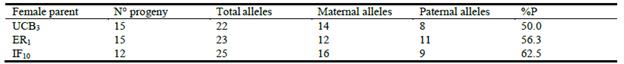
%P: percentage of polymorphic SSR loci in progeny.
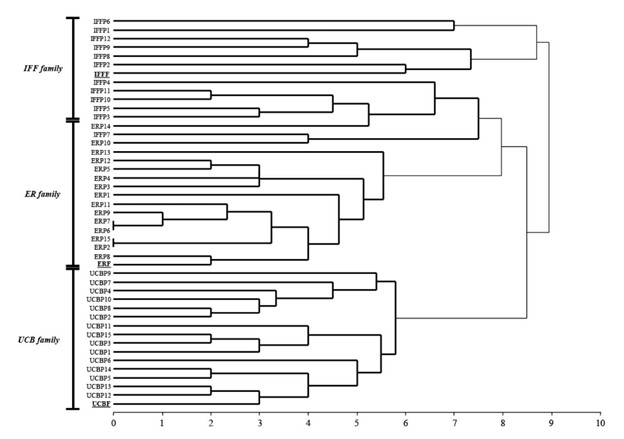
Figure 5 Unweighted pair-group method with arithmetical average (UPGMA) dendrogram based on the GD SSR matrix of 3 female parents (F) and their progeny (P) in families of P. coloratum var. makarikariense. The female plants are underlined.
Chromosome numbers in the P. coloratum var. makarikariense collection
In all mitotic cells observed, 36 chromosomes were counted at metaphase. This number remained stable for all 8 P. coloratum var. makarikariense plants evaluated.
Discussion
There is an increasing need for a better understanding of the reproductive biology in P. coloratum, given that this is an extremely important prerequisite to develop breeding strategies and also for germplasm management and conservation purposes. In this study, we sought to determine the preponderant mode of reproduction of one collection of the var. makarikariense used for breeding purposes both by evaluating seed production in open and forced-to-inbreed panicles and by a progeny test using SSR markers. The evaluated plants in this study were selected to cover the variability present in the germplasm collection at INTA EEA Rafaela, which comprises accessions collected within semi-arid temperate mesic and subtropical zones, both grazed and non-grazed areas, and a commercial variety. Although we analyzed only 3 panicles per accession, our results corroborate previously reported studies pointing out extensive variability in seed production per panicle among genotypes from different accessions in the collection (Barrios et al. 2010). These accessions are also distinctive in other morphological characters, both vegetative and reproductive (Giordano et al. 2013; Armando et al. 2013; 2015). In addition, seed yield is a complex character and additional variability arises as seed set is the culmination of a series of processes at canopy level including radiation interception, bio-mass production and partitioning. Therefore, variability among individuals may be the result of both genetic variation and the integration of these different genetic backgrounds with the multiple environmental influences (Boelt and Studer 2010). The considerable differences in seed production we observed among plants and accessions suggest a promising scenario for selection to increase seed production by means of augmenting the number of seeds per panicle.
The results from seed production, germination and seedling survival assessments in var. makarikariense indicated that open-pollination is by far the most frequent form of pollination in the reproductive biology of this variety. A similar behavior is suggested for var. coloratum based on a small sample of 3 plants (data not shown). Additionally, as only a few panicles produced good quality seeds by self-pollination, a limited number of plants could be analyzed. However, the results from the combined probabilities clearly showed that progeny from selfing make low to no contribution to the population over time since a mean of only 6% of the plants obtained from self-pollinated seeds survived. Although seeds obtained under self-pollination were not weighed, they were visibly much smaller than and had a different color (white vs. brown) from those produced by open-pollination, which could explain the lower vigor of the seedlings (Tomás et al. 2007). The fact that we did obtain seeds from selfing demonstrates the existence of some degree of self-compatibility. Burson and Young (1983), using fluorescence microscopy, demonstrated that, when var. coloratum was self-pollinated, 90% of the pollen germinated within minutes after the pollen grain came in contact with the stigma, but only 2% of the pollen tubes actually grew into the ovary and entered the micropyle within 1 hour after pollination, suggesting active self-incompatibility mechanisms. A gametophytic S-Z incompatibility system has been found in related species (Martinez-Reyna and Vogel 2002) and is common for most of Poaceae (Baumann et al. 2000). In the majority of the grasses this system is not absolute, and some seeds may be obtained from self-fertilization. Further, selfed progeny of highly heterozygous genotypes could result in fitness reduction due to inbreeding (Eckert 1994), a point that we cannot prove with only one generation of selfing.
Brown and Emery (1958) observed typical sexual 8-nucleate embryo sacs in 82 ovules of var. makarikariense and var. coloratum plants indicating both varieties reproduced sexually. Hutchison and Bashaw (1964) also observed 8-nucleate embryo sacs in both varieties but about 2% of the older ovules had large vacuolated cells, which appeared similar to multiple embryo sacs. They considered this as possible evidence of apospory, but developed embryos were not observed in these cells, which dispelled the possibility of apomixis in this species. The high amount of variation expressed in open-pollinated makarikariense progeny rules out the possibility of apomictic reproduction in the species. In our study, molecular progeny tests revealed that an average of 85% of offspring possessed paternal alleles; this is indicative of cross-pollination and 100% of them were genetically distinguishable from the maternal genotype.
Progeny without clear paternal contribution were probably derived from self-pollination or open-pollination involving parents with the same molecular pattern, although this value may be reduced with an increased number of markers. In addition, the level of genomic DNA polymorphism of the analyzed progeny suggests sexuality and genetic recombination, and provides additional evidence that P. coloratum is mainly an allogamous species.
All our analyses accumulated evidence pointing to P. coloratum var. makarikariense as a species with mainly sexual reproduction that depends primarily on open-pollination to obtain viable offspring. All var. makarikariense plants evaluated in this study had 36 chromosomes, and the same number was observed in 3 plants of var. coloratum (data not shown). Considering a basic number of x = 9 (Hamoud et al. 1994), these plants are tetraploids. This ploidy level is one of the most frequently reported for P. coloratum (Hutchison and Bashaw 1964; Pritchard and De Lacy 1974). Apomixis occurs throughout the plant kingdom and is always associated with polyploidy as was reported in Panicum maximum and Paspalum notatum (Warmke 1954; Quarin et al. 2001). However, sexuality also occurs at the 4x and 6x ploidy levels as in Panicum virgatum and Brachiaria humidicola (Barnett and Carver 1967; Pagliarini et al. 2012). The natural distribution of diploid and tetraploid levels in P. coloratum at its center of origin appears to occur throughout central and South Africa, while the hexaploid level was confined to East Africa (Pritchard and De Lacy 1974).
Knowledge of the chromosome number and ploidy level of the germplasm is necessary for developing an efficient strategy of preservation of this promising forage species and is crucial for use in the P. coloratum breeding program. The ploidy level of this species may partially explain the high level of genetic variability in the species and the highly polymorphic progeny. New genetic combinations seem to be obtained relatively easily through segregation and recombination. This fact may represent an interesting means to increase germplasm variability and may be an important factor to consider when releasing new materials resulting from selection and breeding. In addition, the mode of reproduction in a given species must be clear to the plant breeder to accomplish crop improvement. Knowledge about how a plant reproduces naturally helps the breeder to predict the behavior under field conditions and to establish the most appropriate selection method, which markedly differs between self- and cross-pollinated crops. Knowledge of breeding systems is also of benefit for germplasm banks. Based on our results, the number of individuals destined for seed increase should be large enough to include the original variability in genetic diversity. Moreover, isolation distances need to be taken into account in order to prevent gene flow among accessions and thus preserve the genetic identity of each accession.