Serviços Personalizados
Journal
Artigo
Indicadores
 Citado por SciELO
Citado por SciELO  Acessos
Acessos
Links relacionados
 Citado por Google
Citado por Google  Similares em
SciELO
Similares em
SciELO  Similares em Google
Similares em Google
Compartilhar
Colombian Journal of Anestesiology
versão impressa ISSN 0120-3347
Resumo
GARCIA, Mario J e ARDILA, Angel M. Cell volume variation under different concentrations of saline solution (NaCl). Rev. colomb. anestesiol. [online]. 2009, vol.37, n.2, pp.106-109. ISSN 0120-3347.
Background: It is very important to know the volumetric relation between the cellular contraction and the concentration of saline solution (NaCl) used in clinical practice. Methods: Blood samples of healthy volunteers were exposed to different concentrations of NaCl ranging from 0.42% to 11.70% and the resultant variation in the hematocrit was observed. The variation of the cellular volume as a function of the corresponding concentration of NaCl was studied. An equation theoretically predicting the observed behavior was obtained. Results: We studied 53 blood samples of 12 healthy volunteers. The relationship between cellular contraction and the concentration of NaCl shows that the maximum contraction of cellular volume is obtained when NaCl is about 5.85%. The mathematical model derived is summarized in the 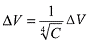 . means the cellular variation to the corresponding NaCl concentration. This model has a linear regression coefficient of 0.996 and applying chi-square goodness of fit test is observed a level of confidence superior to 99.5%. It was also noted that concentrations equal to or higher than 7.02% of NaCl provokes some degree of hemolysis. Conclusions: There is no reason to use concentrations of NaCl higher than 5.85%. Higher concentrations do not induce more contraction of cellular volume, but they do provoke cellular damage.
. means the cellular variation to the corresponding NaCl concentration. This model has a linear regression coefficient of 0.996 and applying chi-square goodness of fit test is observed a level of confidence superior to 99.5%. It was also noted that concentrations equal to or higher than 7.02% of NaCl provokes some degree of hemolysis. Conclusions: There is no reason to use concentrations of NaCl higher than 5.85%. Higher concentrations do not induce more contraction of cellular volume, but they do provoke cellular damage.
Palavras-chave : Cell volume; saline solution; hemolysis; blood cells.













