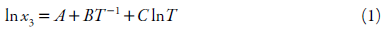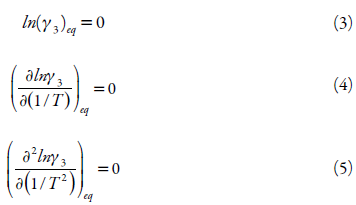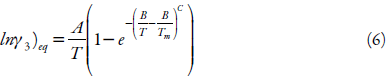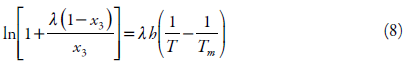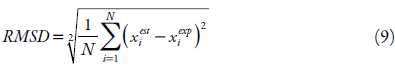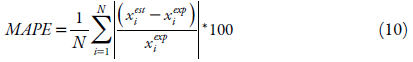INTRODUCTION
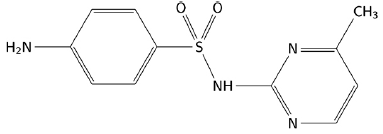
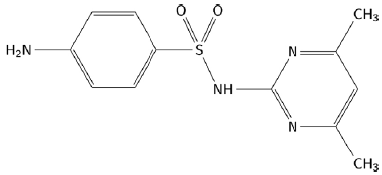
Sulfamerazine (4-amino-N-(4-methylpyrimidin-2-il) benzene-1-sulfonamide) (figure 1) and sulfamethazine (4-amino-N-(4,6-dimethylpyrimidin-2-il) benzene-1-sulfonamide) (figure 2) are members of the sulfonamide family [1]. Sulfonamides are derived from p-amino-benzene-sulfonamide and are characterized by having a benzene nucleus with an amino group (-NH2) and a sulfonamide group (-SO2NH2) [2]. These compounds have been used as chemotherapeutic agents for the prevention of bacterial infections in humans [3]. Additionally, they have been recognized as a starting point for the synthesis of new drugs due to the different pharmacological actions that they can carry out, such as: anti-cancer activity, anti-tumor effect, anti-inflammatory effect, among others [4].
The solubility data of different compounds, especially the ones with pharmaceutical applications, in neat solvents and their mixtures is a very important parameter influencing the design of the drug, its evaluation, as well as its application and future optimization. It is then understandable that many experiments are carried out in order to quantify this solubility in different solvents. Such efforts are undertaken also in the field of sulfonamides and one can include here the works of Delgado et al. [5-9], Cruz et al. [10], Kodide et al. [11], Martínez et al. [12, 13], Romdhani et al. [14], and Blanco et al. [15-17]. Alongside the experimental measurements, many theoretical solubility models have been developed for accurate prediction of solubility and for better understanding of the interactions occurring in solute-solvent systems [18-22].
At present, the development of mathematical models that allow predicting the solubility of bioactive substances in solvents of industrial/pharmaceutical interest is a line of research of great importance [23-26]. Thus, the development of models allows the development of more efficient industrial processes, which in turn reduce the environmental impact [27-29].
Thus, the objective of this work is to challenge the mathematical models of van't Hoff, Apelblat modified, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, van't Hoff-Yaws model and two-parameter Weibull function model, from experimental solubility data, Sulfamethazine and Sulfamethazine using Python programming language.
THEORETICAL
Modified Apelblat Equation
The modified Apelblat equation, which is an empirical model derived from solid-liquid equilibrium [30, 31]:
x 3 refers to measured mole fraction solubility of drug in selected solvent at absolute temperature T, A and B reflect the variation in the solution activity coefficient, and C represents the influence of temperature on enthalpy of fusion [32].
van't Hoff-Yaws
The Yaws model are semi-empirical model included three-parameters extension that allow correlating the solubility with the temperature as follows [33]:
where A, B and C are adjustable parameters [34].
Two-parameter Weibull function model
There is little literature that explains the dependence of temperature on the activity coefficient in equilibrium solutions. The activity coefficient in a solution is a function of T and x, but in the direction of increasing temperature, the saturation concentration approaches unity while converging with the ideal case at the limit of Tm, and the following boundary conditions explain the equilibrium activity coefficient [35, 36]:
At T = Tm
Svärd and Rasmuson [36] identified the necessary boundary conditions for prediction of compound solubilities by extrapolation at higher or lower temperatures to the melting point. They proposed a model that meets these boundary conditions and the mathematical formula used in the probability theory and statistics of the Weibull distribution was adopted. Equation 6 shows the temperature dependence of the activity coefficient of a solution in equilibrium:
where: A and B are adjustable parameters, C is a parameter that has to be above 2 in order to satisfy two boundary conditions in equation 2, Tm refers to the melting point of the substance.
van't Hoff Equation
The van't Hoff equation is also a semi-empirical equation, which reveals the relationship between the mole fraction solubility and the temperature in an ideal solution by taking the solvent effect into account [37].
A and B are parameters, which can be related to thermodynamic parameters such as dissolution enthalpy and dissolution entropy [38].
Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh model
In 1980, based on the generalized relationship, the Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh equation was first proposed, which contains two parameters and is widely used to correlate solubility data:
where λ and h are the two parameters of the λh model, and Tm represents the melting point of drug [18, 39, 40].
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
The solubilities of sulfamerazine and sulfamethazine in mixtures of (methanol + water), (ethanol + water) and (1-propanol + water) were taken from Delgado and Martinez [6, 7, 41, 42].
The experimental solubility data calculations were correlated with Apelblat modified equation (1), Yaws model (2), two-parameter Weibull function model (4), van't Hoff (5), Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh (6) using Python 3.6 version using Pandas and NumPy Library, the parameters of the models were estimated with SciPy Library and plots were made with Plotly Library.
Table 1 and table 3 show the parameters of the equations of Apelblat modified, van't Hoff-Yaws, two-parameter Weibull function model, van't Hoff, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, for the solubility of SMR and SMT in (methanol + water), (ethanol + water) and (1-propanol + water) cosolvents mixtures.
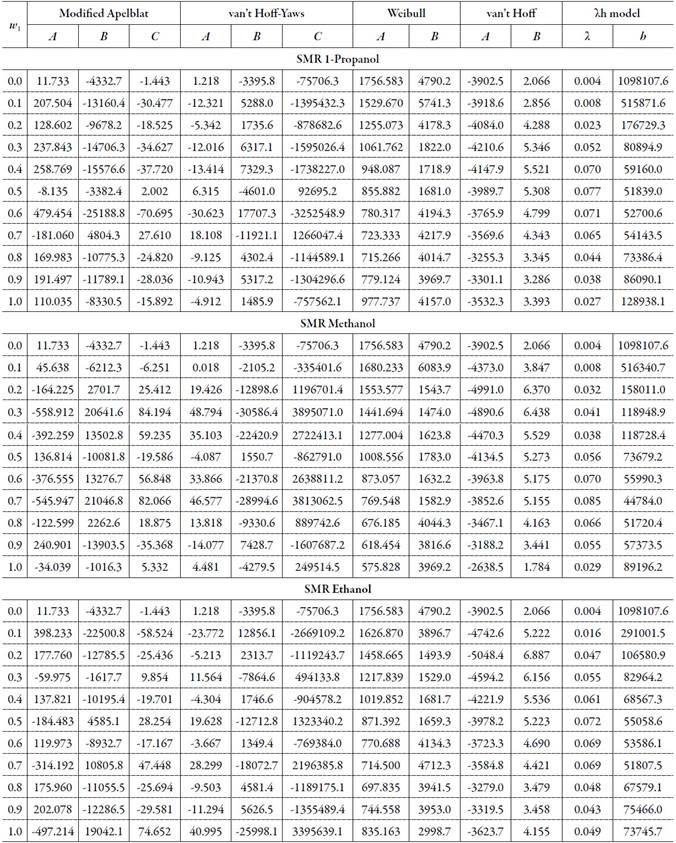
Table 1 The Apelblat modified equation, van’t Hoff-Yaws model, two-parameter Weibull function model, van’t Hoff and Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh equations parameters for sulfamerazine in (methanol + water), (ethanol + water) and (1-propanol + water) cosolvent mixtures.
The figure 3, 4 and 5 show the experimental data vs. the estimated data of sulfamerazine in cosolvent mixtures, linear holdings are obtained. Table 2 shows correlation coefficients equal to 0.99, corroborating that these models show good agreement with the experimental solubility data.
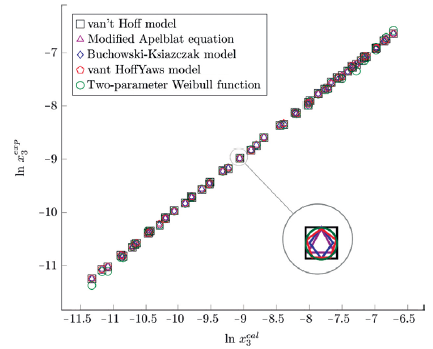
Figure 3 Experimental solubility vs estimated solubility by van't Hoff, Apelblat modified, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, van't Hoff-Yaws model and two-parameter Weibull function model of sulfamerazine in (methanol + water) mixtures.
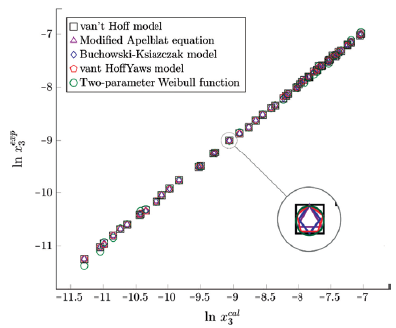
Figure 4 Experimental solubility vs estimated solubility by van't Hoff, Apelblat modified, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, van't Hoff-Yaws model and two-parameter Weibull function model of sulfamerazine in (ethanol + water) mixtures.
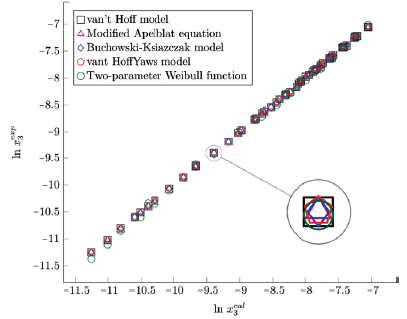
Figure 5 Experimental solubility vs estimated solubility by van't Hoff, Apelblat modified, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, van't Hoff-Yaws model and two-parameter Weibull function model of sulfamerazine in (propanol + water) mixtures.
The values of the obtained equation parameters of the solubility studied were estimated by minimizing the value of the mean squared deviation (RMSD), equation 9, and the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) shown in equation 10, as criteria to assess the quality of the fit and the comparison between the models. The difference between these two parameters is that MAPE express precision as a percentage, it measures the size of the absolute error in percentage. While the RMSD, it is a comparative measure between two sets of data, in this case the experimental and the estimated value.
where: x est i is the estimated mole fraction value, x exp i is the experimental mole fraction value and N is the number of experimental points.
Table 2 shows the statistical measurements of sulfamerazine in cosolvents mixtures, when evaluating the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE) and the mean square deviation (RMSD) it is evidenced that the modified Apelblat and van't Hoff-Yaws model have lowest percentage in the three solvents, 1.1% in methanol and ethanol and 0.6% in propanol, therefore these models are the ones that have the best agreement with the experimental solubility data, in the same way the Buchowski-Ksiazczak model and van't Hoff model have equal MAPE values being a value of 1.5% in methanol, 1.2% in ethanol and 0.8% in 1-propanol. However, these values are very similar for the four models, which shows good agreement with the experimental data of solubility of sulfamerazine. Additionally, Two-parameter Weibull function model shows higher values for absolute percentage error in three solvents, it is the weakest model to correlate the solubility data of the SMR at different temperatures.
Table 2 Statistical measures by van't Hoff, Apelblat modified, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, van't Hoff-Yaws model and two-parameter Weibull function model of sulfamerazine in (methanol + water), (ethanol + water) and (1-propanol + water) mixtures.
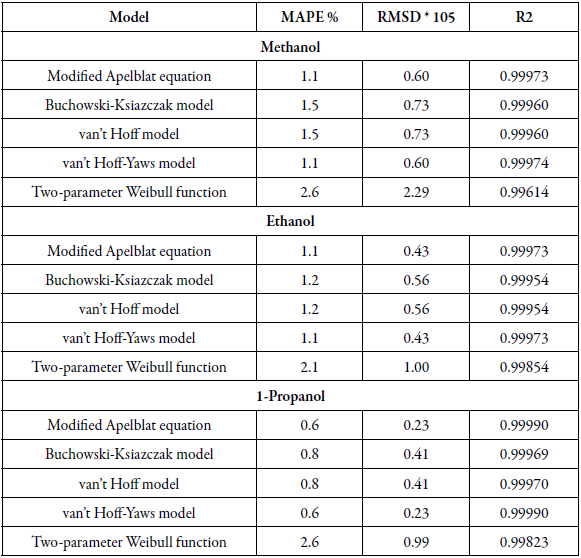
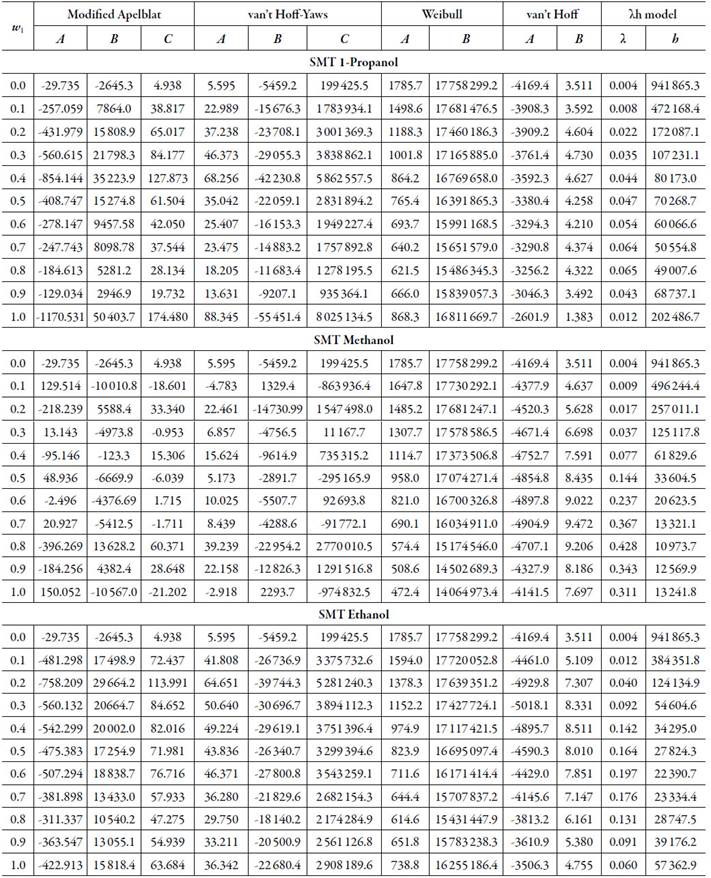
Table 3 The Apelblat modified equation, van’t Hoff-Yaws model, two-parameter Weibull function model, van’t Hoff and Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh equations parameters for sulfamethazine in (methanol + water), (ethanol + water) and (1-propanol + water) cosolvent mixtures.
The figure 6, 7 and 8 show the experimental data vs. the estimated data of sulfamethazine y cosolvent mixtures, linear holdings are obtained. Table 4 shows correlation coefficients equal to 0.99, corroborating that these models show good agreement with the experimental solubility data.
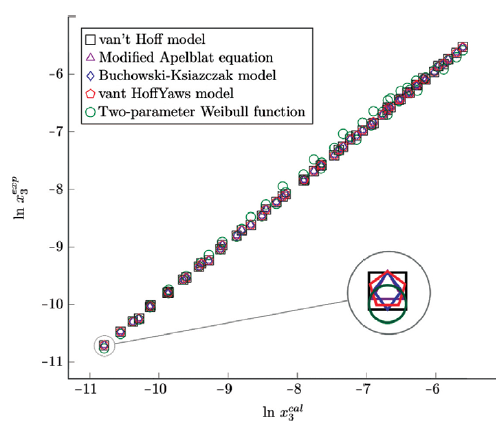
Figure 6 Experimental solubility vs estimated solubility by van't Hoff, Apelblat modified, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, van't Hoff-Yaws model, two-parameter Weibull function model of sulfamethazine in (methanol + water) mixtures.
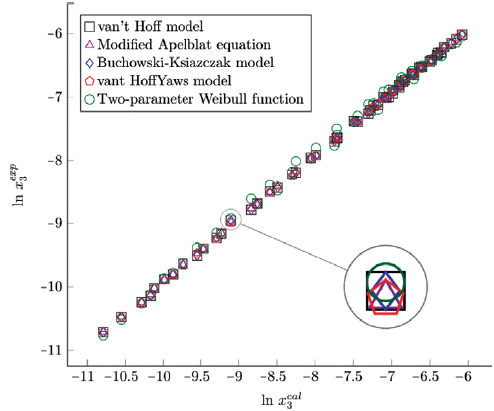
Figure 7 Experimental solubility vs estimated solubility by van't Hoff, Apelblat modified, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, van't Hoff-Yaws model, two-parameter Weibull function model of sulfamethazine in (ethanol + water) mixtures.
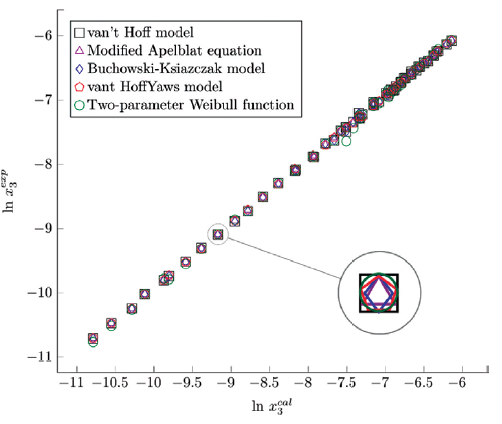
Figure 8 Experimental solubility vs. estimated solubility by van't Hoff, Apelblat modified, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, van't Hoff-Yaws model, two-parameter Weibull function model of sulfamethazine in (1-propanol + water) mixtures.
Table 4 shows the statistical measurements of sulfamethazine in cosolvent mixtures, when evaluating the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), the same behavior as for sulfamerazine is evidenced. The models that show the best relationship are the modified Apelblat model and the van't Hoff-Yaws model. There is a good correlation between the experimental results and those obtained theoretically in this study with these models. Subsequently, a good correlation is found with the data of the Buchowski-Ksiazczak model and van't Hoff model and finally for the Two-parameter Weibull function model the mean absolute percentage error has higher values in the case of the three solvents. For SMR and SMT, it is evident that for most models, the lowest MAPE values are found for the propanol.
Table 4 Statistical measures by van't Hoff, Apelblat modified, Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh, van't Hoff-Yaws model, two-parameter Weibull function model of sulfamethazine in (methanol + water), (ethanol + water) and (1-propanol + water) mixtures.
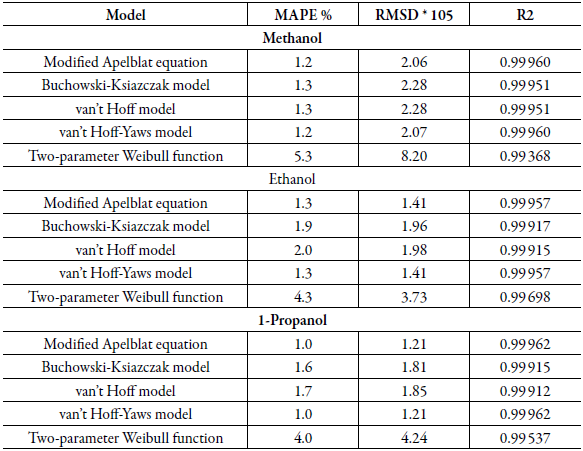
Table 2 and table 4 show that in all cases the same behavior mentioned above was obtained for MAPE when the mean square deviation (RMSD) is analyzed, the following behavior is found: RMSD: Apelblat modified model = van't Hoff-Yaws model < Buchowski-Ksiazaczak λh = van't Hoff model < Two-parameter Weibull function model.
This statistical measure corroborates that the models that have the best fit with the experimental measures are Apelblat modified model and van't Hoff-Yaws model in all co-solvent mixtures.
CONCLUSIONS
The use of the Python programming language has proven to be very useful to determine the parameters of the different models developed in this research. The theoretical results, obtained through each of the mathematical models used, present small deviations with respect to the experimental data, also indicating the relevance of the mathematical models to calculate the solubility data of sulfamerazine and sulfamethazine in co-solvent mixtures.