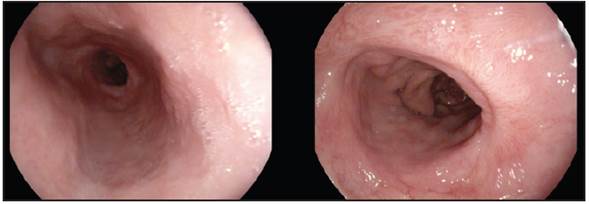
The medications most frequently associated with esophageal ulcers are antibiotics. We report the case of a 71-year-old woman who took ciprofloxacin for a urinary tract infection. Seventy-two hours after taking it she experienced sudden-onset chest pain. On esophagogastroduodenoscopy (Figure 1), ulcers were found in the middle and lower third of the esophagus. When the medication was discontinued and the patient received proton pump inhibitors, she improved. Twelve weeks later, a follow up endoscopy was performed (Figure 2), showing scarring from the ulcers. The most common endoscopic findings of medication-induced esophageal lesions are esophageal ulcers (24.27-87.5%) 1,2 located in the middle third of the esophagus in 80% of cases, even in normal subjects, probably due to compression by the aortic arch and the left atrium, where the peristaltic amplitude is relatively low 1,2.
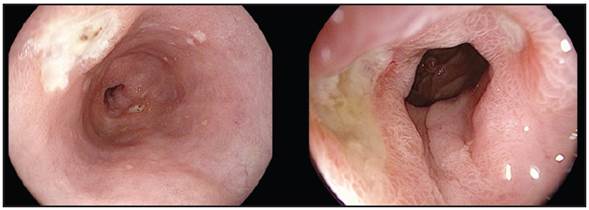
Figure 1 Excavated lesion in the middle third of the esophagus at the site of aortic narrowing. Mirror ulcers in the lower third of the esophagus.











 texto em
texto em