INTRODUCTION
The world recently faced a great economic downturn due to Covid-19 which not only affects the individual's financial conditions, but their mental health owing to fear of death and of losing wealth. Pakistan is one of those countries that gained control on Covid-19 but still Pakistan's economy was seriously affected. According to World Bank, Pakistan may go into recession if the difficult situation continues for more than two months, as Pakistan's GDP has had its lowest record for the first time in 68 years, and the unemployment rate rises to 28%. Due to all this, most of the people lost their jobs and faced a situation of complete uncertainty about their financial flow, which had an impact on their physical health. So, the objective of this study is to investigate the financial threat background and its relationship to the individuals proclivity to change their financial behavior and health. The most novel contribution of this study is the role of social support which significantly moderates the relationship between financial threat and the willingness to change financial behavior.
The core reason of suicides in Pakistan during Covid-19 was severe financial issues as compared to other countries where the suicide attempt was due to fear of infection (Mamun, 2020). The increasing attacks of Covid-19 are not only causing deaths in developing countries, but also herald the great economic loss in the coming days that will amount to 220 billion dollars and the situation may worsen in Africa, where social protection will become a big problem (UNDP, 2020). The inflation rate increased towards 13.25% in january 2020, but due to Covid19, and to support the industry, it was revised and reduced to less than 10% (SBP Pakistan). Pakistan economy growth is now muted and this situation may remain for the coming two years (World Bank). Economic difficulties and their associated shocks in the form of psychological distress and financial threat are not new in Pakistan, they can be traced back to the great economic recession that began in the United States and spread around the world. During the 2008 crisis, many people lost their jobs and faced financial threats to run their businesses and even household expenses. The unemployment rate increased during this period and the world was shocked by the result of this economic recession (Lisa et al., 2017). The horrible effect of this economic crisis was evident in the lives of people who faced economic difficulties and financial threats. This generated multiple obstacles and problems for people, such as psychological anguish and anxiety. Financial anxiety created the financial threat in people's minds. At the same time, people lost their jobs, adding more seriousness to financial anxiety and financial threat. This created a panic situation in people's minds as a result of facing psychological distress. This state of mind forced people to change their financial behavior in terms of income, debt, and expenses.
The condition of any individual who is experiencing uncertainty regarding their current and future financial situation, and that is unable to maintain the necessary finances to meet the needs, is associated with financial threat (Zdravko et al., 2015). Due to this, many other problems arise such as the use of alcohol and the intention to commit suicide. During this period of economic crisis, the suicide rate has increased significantly, as well as the level of insecurity about their future financial situation. The economic downturn had a detrimental impact on small businesses, and for the most part, small investors faced huge losses and went out of business. The large investor also faced many problems, but they made the necessary changes, cut their expenses and fired most of their employees to cover expenses. (Archuleta, 2013).
Economic hardship is a situation in which individuals face difficulties about the finances to run their household or business activities (Ahnquist et al., 2011). When this situation remains constant for a longer period, it becomes a daily problem and the individual becomes unable to meet their daily needs. So we say that the situation is a financial threat. In this case, the individual is insecure about their current and future financial situation, and feels uncertainty and depression. Depression is associated with anxiety, with the two types of anxiety: preparatory and inhibitory. In anxiety, an individual becomes insecure and distrustful about whatever problem they are facing, feeling fear before the problem occurs and sometimes the situation becomes more complicated and the individual experiences a severe level of anxiety and becomes paralyzed when facing uncertainty (Britt, 2015).
In the previous researches it was identify that economic problems have a great impact on human financial behavior and a deleterious impact on the psychological wellbeing of an individual. Those researches only revealed that to avoid this situation there is a need to change the financial behavior, they did not give any other sources to elude this situation of financial panic (Marjanovic et al., 2017).
Financial threat is a stimulus to change the financial behavior and the individual can overcome this situation by altering the financial patron. Searching for a new job, increasing income by doing multiple jobs at the same time, saving money for future bad times, removing luxurious expenses from the current expenses, rent out part of the house if it is possible, selling some costly possession like small investment, cars, etc., and finally getting help from the group of colleagues, business friends and family to eradicate the financial threat and psychological distress situation.
Problem statement: Pakistan is currently facing a financial threat situation due to a major decrease in individuals income as a result of the lockdown and the limited opportunities for business and job, as well as increased psychological distress about finances in small investment holders during the Covid-19 pandemic (Rana, 2020). Another recent study identified that graduating students face an economic recession with many problems, such as lower pay and late job opportunities, and it also found lasting impact of this economic recession in the form of death in middle age due to the economic burden and psychological distress which is very tragic for individual and college students (Crowe et al., 2016).
After all this, an individual investor needs to change their financial behavior in terms of income, expenses and debt to fight against the crisis. So, there is a need to explore the underlying relationship between economic hardships, financial literacy and financial threat. It is important to know the role of social support in this crisis because Pakistan is one country where is common to support to each other.
Research Gap: social support may moderate the economic hardship and the psychological distress. This needs to be explored in further studies (Marjanovic et al., 2017). The available knowledge on financial threat is limited, therefore it is necessary to improve literature on this topic by doing further researches (Marjanovic et al., 2013). That is why this study took social support as a moderator variable for economic hardship. The social support also endorses the idea of reducing psychological distress and increasing individual's wellbeing.
Purpose of the Study:
To assess the meditational role of financial threat between the dependent and independent variables. To know the moderative role of social support on the relationship of financial threat and willingness to change behavior.
To examine the relationship of financial threat with economic hardship and financial anxiety. This study focused to show the relationship between financial threat and willingness to change financial behavior and psychological distress.
Significance of the study: this study is useful for people to know the relationship of economic difficulties with financial threat and the will to change behavior; as well as for individuals to be aware of the importance of their social group and how they can use it for their improvement.
This study helps investor to know about the impact of financial issues on their mental health, and reveals the guidelines to prepare themselves to face financial crisis. What should they possess to avoid these crises?
From the academic point of view, this study is a valuable input for the financial threat literature. There is a limited knowledge on the financial threat concept in the existing literature and this study aims to build a respectable literature regarding to it. This study focuses on identifying the role of social support to reduce the economic hardship pressure.
From the individual point of view, this study helps household individuals and college students how to react in the times of economic hardship and what actions should be taken to remove this financially panic situation.
Research contribution: this study focuses on how the investor schould react in economic bad times and what things can save them from bad decisions. It identifies the impact of economic hardship and anxiety on the investor's willingness to change financial behavior and the arising of psychological distress condition. Besides, it recognizes a financial threat as a stronger stimuli towards willingness to change behavior, and it contributes that the social support has a stronger role to eliminate and controll the financial threat, and lessen the impact of economic hardship and anxiety on the dependent variables: willingness to change behavior and psychological distress.
LITERATURE REVIEW
Economic hardship is a situation where people have problem paying their bills and enjoying the basic things of life, such as food, shelter, medical treatment and others (Pudrovska et al, 2005). Previous researchers define economic hardships as a financial situation of individuals in which they are unable to meet their expenses, and have lower income compared to their expenses, and less cash available to meet their needs (Ahnquist et al., 2011).
Anxiety is defined as a fearful situation with a notable content (Mathew, 2012). Financial anxiety is particularly associated to the uncertainty about future events. It is the unbearable level of uncertainty which is the level where individual reacts emotionally, cognitively and behaviorally in a negative way. There are two types of anxiety that the individual faces: inhibitory and prospective anxiety. Prospective anxiety deals with uncertainty of the future events while inhibitory anxiety deals with the strong negative effect of current situation on individual (Fiksenbaum et al., 2017).
Financial threat is a situation in which for individuals current and future financial condition is unknown, uncertain and unable to meet basic needs (Marjanovic et al., 2017).
The willingness to change behavior is obvious when someone is facing difficulties, and natural intentions are there to change the behavior to avoid these difficulties. Here, faced with the financial threat, the individual intends to change financial behavior in terms of income, debt and expenses (Marjanovic et al., 2017). The individual is more inclined to change behavior when they are seeing any opportunity or subsidy and if they are facing any kind of economic hardship or financial threat (Schaner, 2018). Depression, anxiety and stress are the makers of psychological distress (Denollet, 2010). Different authors defined psychological distress in the context of depression, anxiety and fatigue (Fiksenbaum et al., 2017).
The psychological distress is a wide range of individual's feelings which may cause them stress in daily life events (Rustoen et al., 2010). And social support is defined by researcher as a state in which any individual can get information, material help; in other words, it is the ability of the person to cope up with unfavorable life events with the help or support provided by different groups (Maier, 2015). Social support is a wide concept and it may includes different definitions. At different times, different researchers define it in different ways. For example, some defined it as a form of communication to solve problems and maintain well-being. Another defined it as a state of mind in which someone is there for me, cares for me, and loves me. One researcher defined it as an emotional bond, an instrumental and information exchange (Tang, 2016).
Theoretical Background
Social Support Theory
Social support theory suggests that a person with high social support may face less psychological distress compared to someone with low social support, who may face a high level of depression and health problems. The theory concludes that high levels of depression, eating disorders and health problems are common among those who do not have social support and feel lonely (Lakey & Cronin, 2008).
Theory of Reasoned Action
According to the theory of reasoned action, an individual makes any change in behavior always supported by specific desired results in his mind. The main reason for ToRA is to understand individual voluntary behavior by examining the underlying motivation for a specific action. The willingness to change the behavior or the intention to change the behavior is positively associated with actual behavior changes. The theory revealed that the individual's violation of behavior is always supported by his attitude and subjective norms that force someone to show a behavioral intention (Procter, 2019).
Fear Appeal Theory
Threat to an individual wellbeing is the antecedent for the individual to act in a certain way, this threatened stimulus motivates an individual to exert some specific action. According to this research, fear can be an effective motivator. So here financial threat is the stimulus that compels the individual to change their financial behavior otherwise they will face some horrible consequences (Williams, 2012).
Complete Literature Overview
Different studies showed that during the economic hardships the individual faces anxiety, stress and depression, and due to all this their psychological wellbeing decreases significantly (Viseu et al., 2018). According to the research on psychological distress, the one source of distress is the unemployment in the individual, although sometimes the conditional employment becomes the source of psychological distress (Egan et al., 2015). Literature shows that there is a relationship between economic hardship and willingness to change behavior (Grable et al., 2015). The willingness to change scale was first introduced and used in research by Lisa Fiksenbaum et al., and they attributed it with income, expenses and debt changes, which all related to the economic hardships (Fiksenbaum et al., 2017). In a life cycle individual faces different issues and as a result their psychological situation becomes unstable and their level of satisfaction with life is seriously affected. They feel stress, anxiety, depression and health problems, and in these life events, most of the time, economic hardships and financial issues are common (Marum et al., 2014).
There is a need for financial counseling when a person is faced with anxiety about their financial situation, and the counselor will attempt to eliminate the factors that are causing a financial threat to ultimately avoid the financial anxiety (Grable et al., 2015). In the face of anxiety, the willingness to change behavior is very logical; According to the prevailing literature, anxiety forces a person to obtain financial advice to eradicate it and do financial planning (Lim, 2014). Anxiety is the best system for alerting a person to their upcoming worries and the need to deal with them before they become stronger. (Baruch & Lambert, 2007). Anxiety and psychological distress are strongly associated; According to research, the highest level of individual anxiety will show a higher level of psychological distress. The research shows that the individual who has a low level of anxiety but faces problems will also exhibit a low level of psychological distress compared to people who have fewer problems but who show more anxiety, since the latter will face a higher level of psychological distress (Grable et al, 2015). According to Freud, anxiety is the accumulated negative emotions and physiological changes that occur in individuals. Anxiety is a survival system for human beings which helped individual many times from different kinds of threats (Baruch & Lambert, 2007). Anxiety is a reaction which is real, and we cannot overlook it when some danger or risk approaches to us. Theory of reasoned action (ToRA) supports this hypothesis that any behavioral change always has some stimulus which compels an individual to show behavioral change.
H1. Economic hardship and anxiety have significant impact on willingness to change behavior and psychological distress.
According to different studies most of the time financial problems lead towards economic crisis (Karanikolos et al, 2013). Anxiety is the result of poor performance; the unsatisfied result of your efforts leads to financial trouble and causes anxiety (Coetzer et al., 2011). The feeling of being helpless, according to Hobson's choice, is like feeling anxiety (Bujisic et al., 2017).
There is a relationship between anxiety and financial threat, and according to the literature there is a positive relationship between both, because if someone faces anxiety, then the financial threat will be there (Archuleta, 2013). The individual who faces financial anxiety most of the time uses financially threaten words in their communication (Shapiro & Burchell, 2012).
H2. Economic hardship and anxiety have significant relationship with financial threat.
An individual faces many phases of success and failure in life, and during bad financial times all individuals suffer from stress, depression, bad health, and all of these are symptoms of psychological distress (Marum et al., 2014).
Different studies cited the severe negative effect of health and economic hardships; they also revealed the categorical relationship between financial threat and psychological distress (Pudrovska et al., 2005). Fear appeal theory is a backbone of this hypothesis formulation which suggests that any sudden unexpected behavioral shift indicates there is some kind of fear behind it, which forces an individual to change their behavior to eliminate or lessen this threat.
H3. Financial threat has significant impact on willingness to change behavior and psychological distress.
The economic hardships and financial threat are mostly the main factors for individual psychological distress, health issues, fatigue, depression and reduction in life satisfaction level (Viseu et al., 2018). Previous studies have shown that there is an association between low income, financial difficulties, financial stress, and different health problems. (Ahnquist et al., 2012). Financial stressors are associated with increased anxiety and depression in people, financial threat boosted in those facing increased debt (Fiksenbaum et al., 2017).
During the period of unemployment or underemployment all the people face financial issues which also cause stress to the individual about present and future situation and in the same way produce psychological distress and decreasing of life satisfaction (Ajdukovic, 2018). An individual which is facing economic hardship and financial threat in their daily life events, suffers a severe impact on their health (Rios, 2011).
H4. Financial threat mediates the relationship between dependent (economic hardship, anxiety) and independent (willingness to change behavior, psychological distress) variables.
The person who has strong social support from family and friends and a strong social network will experience less psychological stress and health issues. According to recent research, social support does not only refer to poor health, but to all aspects of life, such as choosing better future plans, financial assistance and also in construction of behaviors. Different investigations show the components as psychological, hedonic, physical and social well-being (Feeney & Collins, 2015). From the previous researches it is evident that there is a categorical relationship between economic hardships and financial threat. A person facing financial difficulties tends to take measures to eliminate this financial threat through strategies such as socializing more, saving or reducing expenses (Lemoine et al., 2016). The social support theory presented by Don Drennon-Gala and Francis Cullen helps to build this particular hypothesis to know the impact of social support on the proposed relationship.
H5. Social support moderates the relationship between financial threat and willingness to change.
Research Methodology
Study Population
The population of the present study is made up of small individual investors in life insurance policies, because they are who save throughout the year to pay the annual fee of the policy and, sometimes, cannot even pay it due to weak financial conditions. It was also found that some people could not complete the expiration period of the policy and had to withdraw it. Most people who want to ensure the future of their children try to get a life insurance policy, so they save for a lifetime to protect their children with a safe future.
Sample Size
Primary data was collected from 360 life insurance policy holders by using simple random sampling technique. Only 326 responses were included in the analysis, the rest of them were incomplete or misplaced.
Data Collection Procedure
Current research uses the cross-sectional study, as here the data collection occurs for one time. This data collection was carried out using a structured questionnaire.
Five-point Likert scale was used in this study and 60 questions were included in this research. In this study, the probability sampling technique and the simple random sampling technique were used, as well as convenient sampling to facilitate the choice of respondents. SmartPLS3 was applied for data analysis which is suitable for social science research and for the analysis of cause and effect relationship variables (Mohd & Fadilah, 2017).
Instrument Measurement
The first financial hardship was measured through the Economic Hardship Questionnaire (EHQ scale) created by Lampers, Clark-Lempers and Simmon in 1989. The questionnaire has 10 questions that measure the inability of the individual to meet their needs due to the reduced availability of money for basic needs, as well as the inability of the individual to make changes in their daily routines due to lessened finances. In this, each item was measured on a 4-point Likert scale ranging from never to very often.
Anxiety is measured through the 12-item uncertainty intolerance scale. Originally there were 27 questions, but it was updated and nowadays it has only 12 questions, which were created by Carleton et al. in 2007. This is a 5-item Likert scale that goes from 1 to 5. Where 1 = not at all characteristic of me, and 5 = completely characteristic of me.
The FTS scale is used here to measure the financial threat variable which was recently created. It is a 5-item scale which measures the individual fearful condition about their current financial worries. This scale is a 5 item Likert scale ranging from 1-5, where 1 = not at all and 5 = extremely.
In this study, a 15-item Likert scale has been used to measure the willingness to change financial behavior in the next year, such as increasing income, reducing expenses and the debt level. It is a 5-point Likert scale that goes from 1 to 5, where 1 = strongly disagree, and 5 = strongly agree.
To measure psychological distress, the K10 psychological distress measurement scale was used, which consists of 10 items, where each item is measured through a 5-point Likert scale, ranging from all the time to never.
Social support variable was measured through 6 item questionnaires where each question has 5 item Likert scale. This is the short version of the original social support scale (Fiksenbaum et al., 2017; Carleton et al., 2007; Marjanovic et al., 2013; Andrews & Slade, 2001; Rascle et al., 2015)
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
Table 1 Demographics of the study
| Gender | Frequency | Percentage % |
|---|---|---|
| Male | 274 | 84 |
| Female | 52 | 16 |
| Age | ||
| 16-19 years | 5 | 1.5 |
| 20-35 years | 176 | 54 |
| 36-55 years | 137 | 42 |
| Above 55 years | 8 | 2.5 |
| Qualification | ||
| High school and Lower | 20 | 6.1 |
| Under-graduate | 37 | 11.3 |
| Graduate | 50 | 15.3 |
| Master | 187 | 57.4 |
| Others | 32 | 9.8 |
| Employment | ||
| Businessman | 150 | 46 |
| Employee | 176 | 54 |
| Income | ||
| Under 20000 | 13 | 4 |
| 20000-40000 | 109 | 33.4 |
| 41000-60000 | 95 | 29.1 |
| Above 60000 | 83 | 25.5 |
| Refused | 26 | 8 |
Reliability of Instruments
Cronbach 's Alpha
The Cronbach's Alpha test is a famous and reliable test to know the internal consistency of the instrument, as it tells whether or not all the elements of the instrument measure the same concept. Cronbach's alpha is used primarily in behavioral and social science research. So here we use this test to know the reliability of the instrument used in this research.
Tabla 2
| Cronbach’s Alpha | rho_A | Composite Reliability | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Economic hardship | 0.706 | 0.719 | 0.756 |
| Financial Threat | 0.745 | 0.747 | 0.828 |
| Financial anxiety | 0.754 | 0.733 | 0.807 |
| Psychological Distress | 0.812 | 0.782 | 0.844 |
| Social support | 0.803 | 0.845 | 0.860 |
| Willingness to change behavior | 0.706 | 0.730 | 0.761 |
The value 0.70 for Cronbach’s Alpha is considered as highly reliable, more than 0.60 indicates a good level (table 2) of reliability, and less than0.5 a not reliable level. In this research all the instruments have more than 0.70 values which makes them strong (Pallant, 2007).
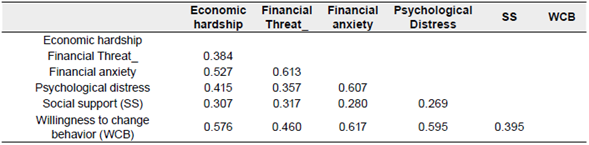
Nowadays, the best discriminant validity measurement tool is HMTM, which is reliable and efficient compared to other tools. The HMTM threshold valueis below .85 and some researchers say it is below 0.9. If it is higher, the instrument is invalid (Henseler et al., 2015).
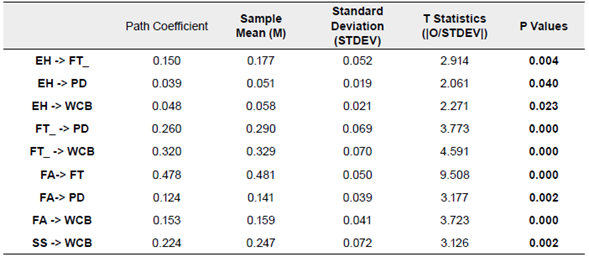
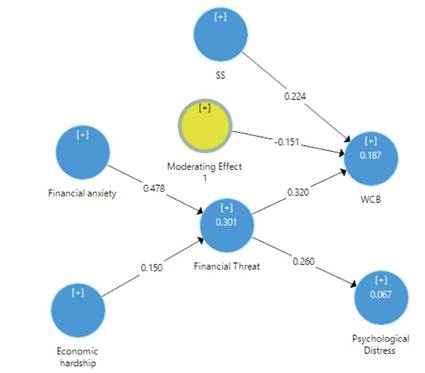
The table 4 indicates the trajectory coefficient, SD, SM, T statistics and P value of all the proposed relationships, and in all relationships the T statistic is greater than 1.96 and P <0.05, which is the level of acceptance. of any relationship. It means that all hypothesized relationships are accepted and that there is a positive relationship between all relationships. According to Ishtiaq et al. (2020), economic hardships are not significantly associated with financial threat, but the respondents in that study were students, they were receiving support from parents, but here in our study the population consists of holders of the insurance policy, who are not only students but the parents themselves, so they do not receive any reasonable support. Another research by Fiksenbaum (2017) also approved the result of this study.
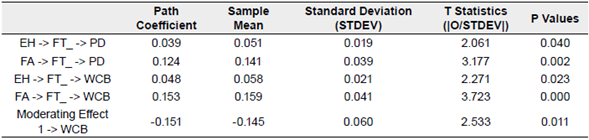
The table 5 shows the total indirect effect, and financial threat significantly mediates between financial distress and psychological distress, economic hardships and the will to change, financial anxiety and psychological distress, and financial anxiety and the will to change. In all statistical findings the T statistics is higher than 1.96 and P<0.05 which is standard for accepting any hypothetical relationship. According to one study (Ishtiaq et al., 2020), economic difficulties do not indirectly affect the will to change. But in another study carried out by Fiksenbaum et al. (2017), they also identify the mediating relationship. Moderation is approved by statistical analysis due to T statistics higher than 1.96 and P <0.05. The result shows that social support moderates the financial threat and the willingness to change financial behavior in a negative way, because the trajectory coefficient is -0.151, which indicates that if the financial threat has a positive relationship with WCB, then, in presence of social support, the direction of the relationship is reversed and becomes negative.
Discussion
The hypotheses H1, H2 and H3 state that the direct relationship between the independent and dependent variables is tested from the data, and the direct categorical relationship exists if economic difficulties increase, since definitely the willingness of investors to change financial behavior is more likely to increase and also psychological distress will grow significantly. In addition, it has been proven that financial anxiety is also directly related to the will to change behavior and psychological distress, both independent variables change if financial anxiety increases. It will affect the psychological condition of the investor and will participate as a stimulus for the investor to change his intention on financial behavior. The financial threat is significantly related to the dependent variables. These results are supported by existing studies (Fiksenbaum et al., 2017; Marjanovic et al, 2013).
All the mediation hypotheses were also approved based on the findings of this research and the result shows that the financial threat has a stronger mediation impact on the dependent variables (H4). Existing studies also confirm the result of this research (Fiksenbaum et al., 2017).
The hypotheses H5 is also supported by this research, moderator social support has stronger impact on the relationship of financial threat and willingness to change behavior The moderator can change the direction of the impact of independent variable on dependent variable.
CONCLUSIONS
The independent variables in this study (financial hardships and anxiety) have a positive relationship with the dependent variables (willingness to change behavior and psychological distress). Which means that if the investor's financial problems increase, he will be more inclined to change his financial behavior in order to find new sources of income and new ways to reduce debts and expenses. The investor will face more health issues and stress if his economic hardships increase, so he must worry and take strong actions to cope up with this situation. Also the findings show that if investor's financial anxiety increases, then he will be more disposed to change his financial behavior and will try to increase his income and reduce debts and expenses. Similarly the investor experiences more psychological disorder and health issues due to financial anxiety.
It means that financial threat is a serious matter that has a stronger and more horrible effect than financial hardship. If the investor faces economic difficulties for a long time, this situation becomes a financial threat and will have a dangerous effect on his health and his behavior towards finances. The investor will be more inclined to increase income and reduce debt and expenses at the same time. The moderator in this study is the social support which has a stronger impact on the dependent variable, and this moderator can change the impact of independent variables on the dependent variables. This is the major finding of this study which guides the investor on how to handle this tragic economic hardship condition and the severe disorder that arises from this in the form of financial threat. Certainly getting social support from family and friends circle will help him physically, mentally and financially, as well as manage psychological distress. Likewise, this circle will support him to maintain his financial behavior without having to worry about it.
Research Implications
This research uses the fundamentals of behavioral finance to address this important phenomenon. The study is of great importance for individual investors and for knowledge of behavioral finance. When these investors feel psychological distress, a physician must identify the underlying financial anxiety, which could be job loss. This study helps the general practitioner to better understand the reason for stress and to suggest some valuable comments. All of them can understand the role of social support in decision-making in times of economic crisis.
Research Limitation and Future Recommendations
This study only presents the impact of social support in the face of financial threat and willingness to change financial behavior, but there are many other variables such as personality traits, coping skills that can lessen the effects of these factors. In Pakistan there is a need to work objectively on the financial threat to SMEs because most of the Pakistani economy is based on these companies and as researchers it is our duty to identify the possible reason for the financial threat in these small companies. It is also the State's duty to do research to improve these small businesses.