Indexing of scientific journals in Web of Science (WoS)
Web of Science (WoS) is a platform based on web technology that collects the references of the main scientific publications of any discipline of knowledge since 1945, either scientific and technological, or humanistic and sociological, essential for supporting research and for the recognition of the efforts and progress made by the scientific and technological community. Its purpose is not to provide complete manuscripts, but rather to provide analysis tools that allow the performance and scientific quality of the research to be assessed and evaluated. It allows access to different Databases through a single query interface, being able to access a single Database or several simultaneously. WoS was founded by Eugene Garfield and belongs to Clarivate Analytics, formerly Thomson Reuters [1-3].
The process of selecting journals for indexing in the Web of Science Core Collection™ is through editorial decisions made by expert in-house editors who are not affiliated with publishers or research institutes, excluding potential bias or conflict of interest. Each publisher focuses on specific subject categories, allowing in-depth knowledge of journals in their respective fields. The basic selection principles for journal indexing in the Web of Science are: objectivity, selectivity, and collection dynamics [4].
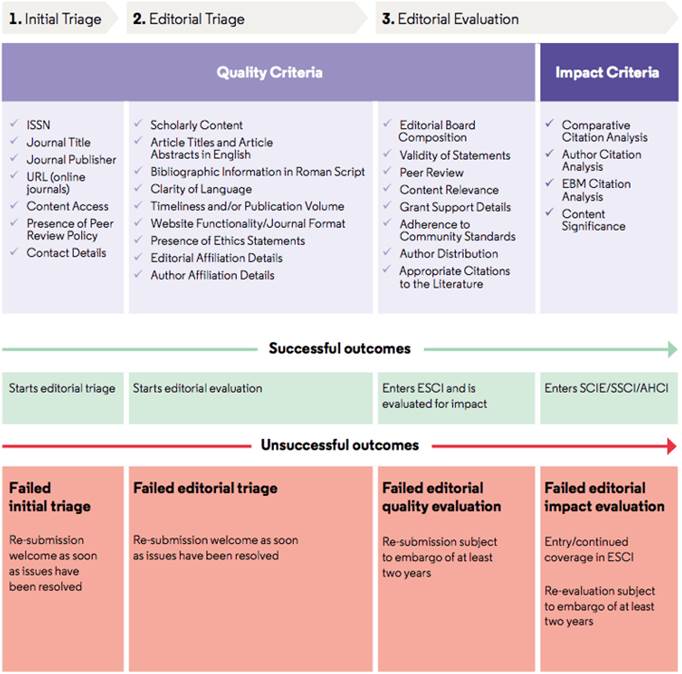
The Web of Science selection process is based upon both quality and impact criteria; a journal must pass a set of 28 quality criteria, 24 quality criteria to select for editorial rigor and 4 related to the impact of the journal. Journals that meet the 24 quality criteria enter the Emerging Sources Citation Index (ESCI). If the 4 additional impact criteria are also met, they become part of the Science Citation Index Expanded™ (SCIE), Social Sciences Citation Index™ (SSCI) or Arts & Humanities Citation Index (AHCI) depending on their subject area. It is a dynamic process, in constant evaluation, so that the ESCI journals that show an increase in impact can be part of the other indices and vice versa, if the journal loses impact, it can be removed from these indices (SCIE, SSCI or AHCI) to enter ESCI [5]. In addition, the Web of Science Core Collection has the Conference Proceedings Citation Index (CPCI) created in 2008 that indexes conference proceedings and the Book Citation Index (BKCI) created in 2011 and indexes books [3]. Revista Facultad de Ingenieria-redin- is currently listed in ESCI complying with the 24 quality criteria, but we still need to meet the 4 remaining criteria related to the impact of the Journal. Figure 1 lists these 28 quality and impact criteria that WoS takes into account for indexing journals in this database.
WoS's current strategy is to reassess ESCI journals that have an estimated Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF) that places them in Q1 or Q2 on the JIF ranking for their category. They use each journal's JIF-not its Journal Citation Indicator (JCI)-as a metric to assess journal-level citation activity by applying their own impact criteria. Typically, the Web of Science editorial team focuses on retests during the first half of the year and prioritizes retests in the second half of the year. If doubts are raised about an indexed journal, either by users or through the supervision of the WoS editors themselves, the journal will be re-evaluated according to the WoS selection criteria. In the event that significant doubts are raised about the quality of the content published by a journal, no new content will be indexed during the course of the reassessment [4].
Below, we will review in more detail the 4 criteria related to the impact of the Journal. The criteria in this step are designed to select the most influential journals in a given field of research, using citation activity as a primary indicator of impact. If a journal does not pass this step, its performance will be monitored. The journal will be re-evaluated when citation activity indicates that the impact criteria may be met [4].
Comparative Citation Analysis
Following the curation process for the Web of Science [4], the previously mentioned indices SCIE, SSCI, and AHCI include the most impactful journals in the corresponding discipline. There are different factors considered in this comparative analysis, such as the number, the sources of the citations, and the stability of citation activity, placing emphasis not only on the influence of a journal in a specific period of time but also on the sustainability of that influence.
Author Citation Analysis
Citation analysis is also conducted at the Author level. This criterion indicates that Authors must have a publication history and a history of adequate citations.
Editorial Board Citation Analysis
Likewise, Editorial Board Members should have a discernible publication history on the Web of Science. This criterion indicates that Editorial Board Members must have a publication history and a history of adequate citations.
Content Significance
The related content in the journal should be significant and appropriate to its intended readership and to Web of Science subscribers. The attributes considered are not reflected in journal-level citation activity but are relevant to selectivity. They are: level of specialization, novel perspective, regional focus, unusual and unique content, or content particularly focused on the Web of Science dynamics.
Relationship between Web of Science Core Collection and Journal Citation Reports
The Journal Citation Reports™ (JCR) is updated annually. Journals that are accepted into SCIE, SSCI, AHCI or ESCI before January 1st, and that remain covered in one of these collections when JCR production is started in March, are eligible to appear in the June release of the JCR data and receive a Web of Science Journal Citation Indicator (JCI). SCIE and SSCI journals that meet these requirements are also eligible to receive a Journal Impact Factor™ (JIF).