Services on Demand
Journal
Article
Indicators
-
 Cited by SciELO
Cited by SciELO -
 Access statistics
Access statistics
Related links
-
 Cited by Google
Cited by Google -
 Similars in
SciELO
Similars in
SciELO -
 Similars in Google
Similars in Google
Share
Colombia Internacional
Print version ISSN 0121-5612
colomb.int. no.70 Bogotá July/Dec. 2009
NATURAL RESOURCE TYPES AND CONFLICT TERMINATION INITIATIVES
Philippe Le Billon
profesor asociado de Geografía en el Instituto Liu de Asuntos Globales de la Universidad de Columbia Británica, Vancouver, Canadá. philippe.lebillon@geog.ubc.ca
ABSTRACT
There is mounting evidence that natural resources can influence the likelihood, course and outcome of armed conflicts. Much of these relationships depend on the institutional setting in which the conflict and resource exploitation occurs, and the specific characteristics of resources involved. This paper examines the relevance of two broad resource characteristicslootability and legalityfor conflict termination initiatives. Observing revenue sharing, economic sanction and military interventions in a total of 26 conflicts between 1989 and 2006, the paper suggests that resource characteristics can affect the effectiveness of resource-related conflict termination instruments.
KEYWORDS
war - natural resources - sanctions - revenue sharing - military interventions.
TIPOS DE RECURSOS NATURALES E INICIATIVAS PARA LA FINALIZACIÓN DE CONFLICTOS
RESUMEN
Existe creciente evidencia de que los recursos naturales pueden influenciar las probabilidades, la trayectoria y el resultado de los conflictos armados. Muchas de estas relaciones dependen del marco institucional en el cual el conflicto y la explotación de recursos ocurren, y de las características específicas de los recursos implicados. Este documento examina la relevancia de dos grandes características de un recurso saqueabilidad (lootability) y legalidad (legality) para las iniciativas de finalización de conflictos. Observando la repartición de ingresos, las sanciones económicas y las intervenciones militares en 26 conflictos entre el año 1989 y el año 2006, este documento sugiere que las características de un recurso pueden afectar la effectividad de los instrumentos de finalización de un conflicto relacionado con los recursos naturales.
PALABRAS CLAVE
guerra - recursos naturales - sanciones - repartición de ingresos - intervenciones militares.
Recibido el 5 de Mayo de 2009 y aceptado el 13 de Octubre de 2009
INTRODUCTION
Much attention has been devoted to the relationships between natural resource wealth and armed conflicts since the mid-1990s (Bannon and Collier 2003; Ballentine and Nitzschke 2004; Nitzschke and Studdard 2005). The United Nations Security Council (unsc) has taken an unprecedented number of measures to curtail access to revenues by targeted groups and help foster a durable transition to peace (Cortright and López 2002). Natural resources do not have the monopoly of war financing, but this priority reffected an upward trend of resource-funded hostilities since the 1980s until the mid-2000s, and a consensus that insurgent access to resource revenues tends to prolong conflicts (Ross 2006). This paper reviews the potential importance of the type of resources involved in hostilities for conflict termination. If specific instruments are more effective for some resources than others, matching them may improve the chance of ending a conflict. The success or failure of resource-focused instruments may also inform arguments about the role of different types of resources in the prolongation of conflicts.
The paper first provides a brief overview of large-n and medium-n studies on natural resources and conflict duration, making no general claims about small-n studies. It then discusses potential linkages between resource types and conflict termination, before reviewing the record of the three main types of resource-focused instruments used for 26 conflicts between 1989 and 2006. Following a discussion of their relative effectiveness, the paper concludes with a discussion of findings, policy implications and avenues for future studies.
HOW DO RESOURCES INFLUENCE (OR NOT) WARS?
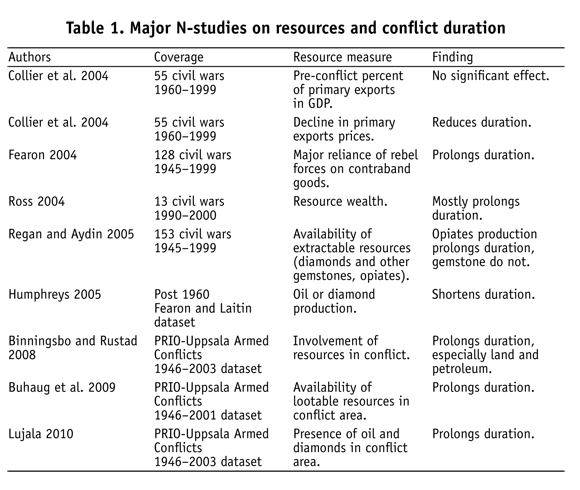
Studies linking natural resources and armed conflicts until the late 1990s have generally sought to examine resource scarcity or environmental degradation effects, mostly through using comparative case studies (Dalby 2002). Using re-source dependence as proxy, Collier and Hoefer (1998; 2004) initially argued that greed was a widespread motivation amongst belligerents, before suggesting that resources constituted a favorable opportunity, setting the context for violence to escalate into armed rebellion. These arguments received widespread attention, including in the public media and international policy circles. The findings and their interpretation, however, have been challengednotably in terms of the interpretation of relationship (e.g. resource dependence being also a possible proxy for grievances), of the characteristic of the variable (e.g. being too broad, not accounting for some resources such as diamonds, or reffecting dependence and its institutional causes rather than resource wealth), and of the unit of analyses (e.g. not disaggregating the location of resources and conflict), see (Buhaug and Gates 2002; de Soysa, 2002). Several studies have re-examined this relationship by checking for robustness (Fearon 2005), using alternative resource variables (Humphreys 2005; Ross 2006), disaggregating types of resources (Lujala et al. 2005; Rustad et al. 2008) and conflict levels (Buhaug and Rød 2006).
The picture emerging from these recent studies is that the relationship is generally less robust than was initially found, except in the case of oil. Both oil dependence (oil exports as a percentage of gdp) and oil abundance (rent per capita) are positively correlated with the risk of war (Fearon 2005; Ross 2006). Humphreys (2005) finds this relationship afected by the level of oil dependence and abundance (medium dependence and abundance present higher risk), the phase of the oil cycle (production is riskier than discovery), and the strength of institutions (oil increasing risk for weak states but reducing it for strong states). Basedau and Lacher (2006) find that the increased risk of high oil dependence is counterbalanced by high abundance. The location of oil and type of conflict also matter, with overlapping conflict and oil areas being associated with longer governmental conflicts (over central government), but not with territorial (i.e. secessionist) ones (Lujala et al. 2007). The presence of oil in conflict areas would also increase the number of deaths resulting directly from hostilities, whereas the presence of oil within the country but outside the conflict area tends to decrease it (Lujala 2008). Besides oil, Lujala et al. (2005) find that secondary diamonds (surface or alluvial diamonds) have some effect on ethnic conflicts. Snyder (2006) stresses in this regard that the type of resource exploitation institutions plays a major role for building political order challenged by the particularities of lootable resourceswith joint private/public exploitation offering the best outcomes. Le Billon (2008) suggests that high diamonds abundance and industrial exploitation seem to reduce armed conflict occurrence. No staThistically significant relationship was found for timber (Rustad et al. 2008), while Humphreys (2005) suggests that agricultural commodities are under-examined and would be positively correlated with a higher risk of conflict; Dube and Vargas. (2006) qualifying this relationship as they find that higher coffee prices reduce the likeli-hood of conflict in Colombiawith the opportunity cost effect (leaving coffee production employment for rebellion) trumping the rapacity effect (increasing prices exacerbating incentives to illegally appropriate coffee rents through rebellion). Narcotics tend to strengthen rebel groups in terms of capacity compared to states, thereby prolonging conflicts (Cornell 2007).
RESOURCES AND CONFLICT TERMINATION
Of most relevance to this study are analyses of conflict duration, risk of renewed conflict, and conflict termination processes. Several empirical studies have suggested that the availability of valuable resources in a conflict area tends to prolong hostilities and undermine conflict termination eforts (Doyle and Sambanis 2000; Stedman 2001; Fearon 2004; Ross 2004; Lujala et al. 2005). Humphreys (2005) finds, in contrast, that oil or diamond productions are associated with shorter conflicts (for a critique, see Collier and Hoefer 2005), and highlights the diversity of mechanisms possibly at play:
- Feasibility mechanism, with resources providing a fow of revenues enabling belligerents to continue fighting;
- Balance of power mechanism, with resources prolonging wars when easily accessible to the weaker party, or shortening them when more exclusively accessible to the stronger party;
- Conflict premium mechanism, with belligerents opportunistically pursing economic agendas in a rewarding resource context;
- Fragmentation mechanism, with economic inTherests and distrust over resource revenue sharing within armed groups fostering a breakdown of discipline, allegiance switching, or the crowding out of ideologically driven belligerents by opportunistic ones (see Weinstein 2007). Hostilities may be prolonged through more diffuse economically-driven violence and undermining peace negotiations, but also shortened by militarily weakening fragmented groups if they face a more capable military force;
- Peace-buying mechanism, whereby resource revenues can provide an incentive to participate in and abide by a peace process. Such redistribution may, however, provide an incentive for further fragmentation among armed groups and difusion of armed violence;
- International stakes (or international conflict premium) mechanism, whereby resources can influence the inTherests and capacity of regional or international actors. InTherest groups in neighbouring states in particular can economically benefit from a conflict and seek to prolong it, while major commercial inTherests can also seek to end a conflict to protect or access resources; and
- Resource enclave (or sparse economic networks) mechanism argues that, since economic sectors with dense economic linkages across divided communities would promote conflict termination, the enclave nature or sparse economic linkages of many resource sectors would tend to prolong conflicts.
These mechanisms may have divergent effects on conflict duration. Ross (2005) finds only weak support for the conflict premium mechanism and its negative effect on the success of negotiated settlement. Humphreys (2005) finds support for the balance of power, fragmentation (through military weakening) and the international stakes mechanisms, but no support for the conflict premium and peace-buying mechanisms. Finding a positive staThistical association between oil discovery in conflict areas and increased conflict duration, Lujala (2010) argues in support of the conflict premium mechanism. Assessing the likely impact of different initiatives on the various mechanisms may assist to confirm this argument: some initiatives may be more suited to the types of mechanism at play in a conflict, and help realize their potential contribution to conflict termination.
Examining the effect of resource dependence on peacebuilding success, Doyle and Sambanis (2000, 789) find that these are significantly and negatively associated, and suggest that "easily looted resources provide incentives for new wars, which would reduce the probability of [peace-building] success." Collier, Hoefer et al. (2004) do not find that primary commodity export dependence has significant effect on the duration of civil wars; yet they find that lower commodity prices reduce conflict durationsanctions able to lower prices through closing 'open' markets should thus help shorten conflicts. Beyond such contradictory findings, several studies examine the sensitivity of conflict duration to the characteristics of the resources, their location with regard to the conflict, as well as the type of conflict involved and initiative deployed (see Table 1). Using a large-n analysis that spatially disaggregates resources and conflict areas, Buhaug et al. (2009) find that the presence of resources within a conflict zone increases the duration of conflictending hostilities around resource areas should thus be a priority. Examining the specific case of 'lootable' or 'contraband' goods, Fearon (2004) finds that, compared to a total sample of 128 civil wars between 1945 and 1999, those in which rebels had access and relied heavily on contraband goods such as narcotics or gems lasted about five times longercutting access to such resources should thus also contribute to hastening peace. Based on thirteen case studies of civil wars involving natural resources in the 1990s, Ross (2004) finds that access to resource wealth by rebel groups lengthened eight of them, but shortened two conflicts as a result of military interventions by regional powers and had a mixed effect on two others as rebel groups defected to the government, in part to maintain access to resource revenues in the face of mounting military pressure. Ross' findings seem to confirm that access to resource revenues by the weaker party prolongs conflicts; they offer weak support, however, for the argument that resources offer a financial incentive to oppose a peace settlement through current gains on present or future control of resources. Given these studies, one would expect that resource-related peacebuilding initiativessuch as wealth sharing, military interventions and economic sanctionswould contribute to conflict termination and post-conflict stability. As discussed below, these initiatives are not likely to have the same effect within all conflict environmentsnotably with respect to resource type.
Many studies have examined relationships between conflict termination initiatives in general and conflict settlement. Licklider (1995) finds for a sample of 91 civil wars between 1945 and 1993 that the risk of renewed conflict is higher for negotiated settlement than a military victory, thereby suggesting that interventions should aim at facilitating military victory rather than negotiations. Using a sample of 55 civil wars between 1960 and 1999, Collier, Hoefer et al. (2004) points out that only military interventions on the rebel side shorten civil war. Several studies have found that foreign interventions tend to increase the duration of civil wars (Regan 2002); although towards negotiated but not military settlement (Balch-Lindsay et al. 2008). Regan, Frank et al. (2009) qualify these findings by arguing that well-timed diplomacy conducted by some international actors, alone or combined with other initiatives, can help reduce conflict duration. Besides these general studies, at least four studies have examined conflict termination initiatives either targeting resources or deployed in a specific resource context. Using a selection of 16 cases, Stedman (2001, 11) finds that no peace agreement in which international actors were assigned a prominent role on the ground has been successfully implemented where there are "valuable, easily marketable commodities such as gems or timber," and suggests that such resources "not only provide armies with the means for continued fighting, they also become the reward against which they weight the benefts of peace."1 In his study of conflict duration and mode of termination, Fearon (2004) notes that conflicts are about four times longer in cases where ethnic minorities took up arms to protect their access to land, fuel or mineral resources against migrants or the state. Fearon (2004) suggests that negotiated settlements would be more problematic in such contexts by increasing the stakes of one party and suspicions about reneging by the other.2 Therritorial conflicts may not be the only ones prolonged by the availability of resources.
Arguably, if resource revenues are only available to the stronger party, then resources should not prolong but shorten conflicts by providing the stronger party more economic leverage to achieve a military victory or to 'buy peace' (Le Billon 2003). Humphreys (2005) finds that both oil and diamond export dependence is associated with shorter wars by making military victory easier, but not by obstructing negotiated settlements. Oil revenues are generally much more accessible to governments than to rebels, even if rebel forces can steal oil or extort protection rents or kidnapping ransoms from oil companies. Diamond revenues may be as much accessible to rebels than governments, but Le Billon (2005) find that military victory over diamond-funded rebels is also easier, suggesting that deriving revenues from diamonds could have a deleterious effect on rebel organizational structure (see also Weinstein 2005; 2007; Le Billon 2008).
Overall, recent studies on resources and conflict termination underline the relevance of commodity-related instruments for ending conflicts. They also point to the importance of distinguishing between diferent type of resources and conflicts involved, their relative location, as well as the parties accessing resources and the mechanisms prolonging or shortening the conflict. Finally, they tend to suggest that conflicts involving resources are more likely to be successfully settled through military victory than negotiated settlements resource, and that policy initiatives should in general seek to deny resource access to the weaker party rather than accommodate its demands.
RESOURCE TYPE AND CONFLICT TERMINATION INITIATIVES
The literature on conflicts and natural resources identifies several resource type dimensions potentially influencing their relationship, including those affecting conflict duration and preferred mode of conflict termination (Le Billon 2001; Lujala 2003; Ross 2003). The most classic dimension in resource and war studies is that of 'scarcity,' measuring the imbalance between 'supply' and 'demand,' and thus the motivational element in a 'struggle' over 'strategic' or 'vital' resources. This imbalance is not set only by the supply and demand for the resource itself, but by the broader economic and livelihood context (e.g. conditions of poverty). Scarcity is often interpreted through the categories of renewable and non-renewable, with much of the literature emphasizing more robust links between large-scale violence and non-renewable resources than for renewable ones (de Soysa 2002; Binningsbo et al. 2007; Theisen 2008). The argument that 'abundant' resource would motivate conflicts, although apparently contrary, builds on some of the same assumptions, but shifts scale from local to global scarcity (hence a locally abundant but still highly valuable resource), and often adds the dimension of dependence.
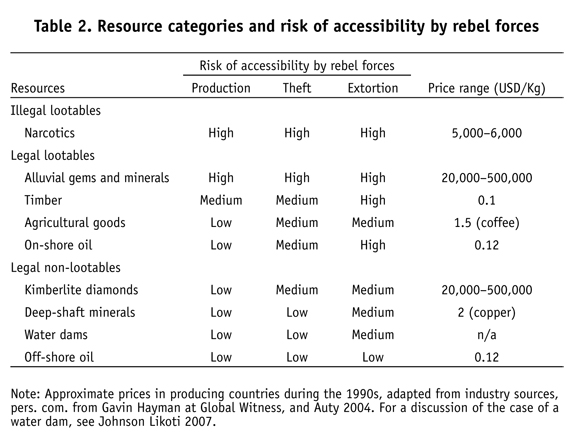
The most well known dimension in the current literature is the idea of 'loot-ability,' measuring the ease with which a rebel group could access revenue from this resource. This aspect has been declined through terms such as accessibility and appropriability, as well as variations on this theme such as obstructability (i.e. ability to racket through threats of obstructionsee Ross 2003). All of these relate to the 'opportunity' effect according to which a rebel group operating in a more 'opportune' environment would be more viable. There are many components to this lootability: the materiality of the resources, its mode of exploration and production, its spatial spread and accessibility to its revenues, and (il)legal and (il)licit character along its value/commodity chain.
- Materiality of the resource influences for example its ease of extraction and transportation, and its price/weight ratio. The easier to extract and transport, and the more valuable per weight, the more 'lootable' the resource.
- Mode of exploration, production, and consumption influences its accessibility, notably through labour, technical, and capital input, but also the social relations and financial fows that take place around resources along the (global) commodity chain.
- Location, spatial spread and accessibility to its revenues are defined by the components presented above, as well as the geographical spread of resources (either in the form of placer/reserves or suitable socio-ecosystems in the case of cash crops for example). Depending on the relative capacity of the belligerents to capture revenues, point source or diffuse resources can provide advantages to some belligerents over otherswith diffuse resources generally favoring rebellions over governments.
- Livelihood impact of the resource reffects its importance for the survival of individuals or groups. This can relate to 'vital' resources such as water, not only in terms of access but also of quality (e.g. mining related pollution).
- Legal and licit character is defined, respectively, in judicial and moral terms. What is illegal by law can be considered licit by the population, such as narcotics at some production sites, and thereby further advantage an 'illegal' actor such as a rebellion vis à vis a government.
- Identity and divisibility characters defined by how much a resource is identified by a social group as its own and by the divisible character of resource ownership and benefts, both of which relate in large part to its territoriality, mode of production, and revenue fows. These dimensions are less often examined, notably by quantitative studies due to its 'qualitative' character (although not always impossible to measure). Beyond simple dimensions of 'property rights,' this can extend for example to cultural rights. The particularity of this dimension is the indivisible character it can give to resources, especially with respect to land. This notion of identity is, of course, socially constructed and historically contingent. It can help explain, as discussed above, the longer duration of many secessionist or 'sons of soil' conflicts.
Most of the contemporary resource and conflict literature has focused on the financial opportunities aforded by resources to belligerents in conflict situations: the legality of a resource, and its accessibility or 'lootability.'3 The legality of a resource refers to its legal status in domestic and international markets. This legal character shapes specific opportunities for belligerents. In the case of an illegal resource, a rebel group is advantaged compared to a government that risks losing its international legitimacy and associated sources of support if it engages in trafficking. In the case of a legal resource, a government is advantaged since the market should offer higher prices to a recognized authority rather than an illegal one.
The accessibility of a resource is defined by the ease with which an armed group can generate revenues from it, through exploitation, theft, as well as taxation or extortion (see Table 2). Several factors influence this accessibility. Some relate to the production and commercial characteristics of a resource: a resource is more accessible when its exploitation requires less financial, technological or labour inputs, and when the high price per volume ratio facilitates transportation. Other factors relate to the geographical context and mode of exploitation of a resource: a resource is more accessible when it is spread over a vast territory, in a terrain propitious to insurgency, and along an international border, as well as when it is exploited by high number of businesses vulnerable to protection rackets and protected by ineffective or corrupt security forces (Le Billon 2005).4
Together, the legality and accessibility criteria may be used to define four categories of resources: illegal lootables (e.g. narcotics), legal lootables (e.g. alluvial diamonds, on-shore oil), legal nonlootables (e.g. of-shore oil), and illegal nonlootables. Illegal nonlootables could include uranium, which exploitation is mostly conducted by tightly controlled industrial mines and which trade comes under regulation through the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty and the national legislation of Nuclear Suppliers Group members (akin to the voluntary agreement of participants to the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme). Uranium from the Democratic Republic of Congo, however, was identifed by a un group of experts as both 'lootable' through arThisanal exploitation, and somewhat 'legal' given the total absence of control on the site and the porous borders of the country.5 Some commodity-focused instruments may better address specific resources given these distinctions; I review each type of instrument in turn.
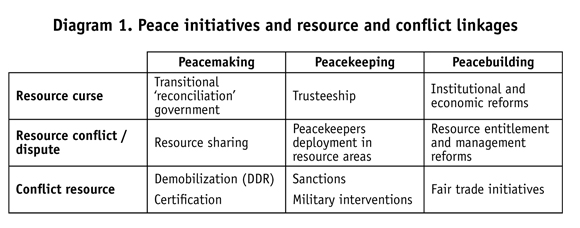
Conflict termination is often presented in three stages that are frequently over-lapping each other: peacemaking consists of initiatives seeking to settle a conflict through negotiations (and possibly military intervention), peacekeeping consists in preventing further hostilities through a military interposition between contending parties, and peacebuilding consists in normalizing relations and reconciling contending parties. Diagram 1 matches these three stages with the three main arguments relating natural resources and armed conflicts (see Le Billon 2008): the resource curse argument suggesting that resource dependence negatively affects economic performances and the quality of institutionsthereby supposedly increasing the vulnerability of countries to armed conflicts;6 the resource conflict (resource dispute) hypothesis positing that the resource itself, its discovery and its exploitation can increase the likelihood of conflicts and various forms of violence, notably through disputes over rent allocation as well as the social and environmental impacts of exploitation; and the conflict resource (looting or resource financing) argument for which resources shape the opportunities and behavior of belligerents by financing their activities, dissociating them from a popular base and securing the support of external actors.7 The resulting framework can help situate initiatives targeting potential resource and conflict linkages.
MILITARY INTERVENTIONS, SANCTIONS, AND REVENUE SHARING
Tree main types of conflict termination instruments targeting resources have been used: military interventions taking over the control of resource production areas from belligerents, economic sanctions against targeted belligerents, and revenue sharing agreements between belligerents.
These three types of instruments are not the only ones deployed to address the role of resources in prolonging conflicts, as indicated in Diagram 1. Some of these instruments have been used to implement or complement the three main types of instruments examined in this study, such as the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme seeking to enable more effective sanctions against 'conflict diamonds' (Le Billon 2008). Some have also been deployed according to conflict prevention or human rights abuse accountability objectives, rather than conflict termination per se. Although rare, litigation against resource companies or individuals suspected of trading in conflict commodities has occurred, in order to implement and give future credibility to un sanctions. Dutch timber merchant Guus Van Kouwenhoven, for example, received an eight-year prison sentence for violating a un arms embargo imposed on the Liberian government.8 Several transparency instruments, most notably the Extractive Industries Transparency Initiative, have also been deployed to curb the likelihood of corruption and revenue embezzlement.
Curtailing wartime access to resource revenues can take two main forms: military interventions to capture resource production areas; or economic sanctions preventing investments, technical inputs or the trading of resources. The three main categories of military interventions relevant to this discussion are: those conducted by domestic forces as part of the general conduct of war; those conducted by external mercenary forces (or private military companies, pmcs) working under contract from one of the belligerents; and those conducted by external military forces under a mandate from the un, a regional organization, or in the form of a 'coalition of the willing'. These divisions are not always clear, especially when external governments intervene outside of a un mandate using foreign mercenaries.
Economic sanctions, or 'commodity sanctions,' seek to prohibit the import of resources under the control of the sanctioned party, an alternative being restricting investment for, or export of production technology to, the sanctioned party. Sanctioned parties have included governments (often through a country-wide sanction regime) or non-state groups (mostly rebel movements). Sanctions aiming at particular commodities (commodity sanctions) can be applied to a country but in effect only target the actor most benefiting from that commodity. Commodity sanction regimes have also been applied to a country, but provide for the exemption of commodities certified by the government, once a credible system is in place. Sanctions targeting resources have been imposed by the Security Council, regional associations of states such as the Economic Community of West African States (ecowas), or individual governments such as the us, as well as business associations and non-governmental organizations (ngos)through market access restrictions through sectoral reforms or consumer boycotts, as in the case of the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme for 'conflict diamonds,' or industry guidelines for coltan in relation to the conflict in the Democratic Republic of Congo. Sanctions have been the most studied among the three types of initiatives examined in this essay and, as reviewed by Cortright and López (2000), findings generally suggest that un sanctions most often fail to change the behaviour of their targets. Mack and Khan (2000) argue that, nevertheless, many un sanctions had positive impacts in terms of stigmatizing and containing targets, notably in terms of funding opportunities. Furthermore, the use of sanctions has much evolved since the end of the Cold War, with a greater use of un sanctions that are better targeted and implemented (Cortright and López 2002; Le Billon 2003).
Although sanctions have been imposed to alter the behaviour of their targets, they have increasingly been used with the objective of curtailing the financial means available to rebel groups. The growing use of so-called 'smart sanctions' has allowed for selective targeting to maximize the impact on the selected group, while lowering it on the general population. Measures such as the public 'naming and shaming' of sanction busters by un expert panels and the threat or implementation of 'secondary sanctions' on sanction busting states have strengthened their implementation. The National Union for the Total Independence of Angola (unita), for example, lost logistical and diplomatic support in 2000 and 2001, following exposure by un expert panel reports. The imposition of sanctions against the government of Liberia progressively eroded its support for the Revolutionary United Front in Sierra Leone. Resource smuggling, however, remained widespread under most sanction regimes, in part because of a lack of enforcement on the ground and effective judicial action against sanction busters. The characteristics of resources have also played a role, in terms of ease of transport, concealment, or low traceability. Yet the smuggling in the 1990s of vast quantities of petroleum from Iraq or logs from Cambodia illustrate that, with the collusion of local authorities on both sides of an international border, the bulkiness of a resource is less of a major factor.
Positive incentives can address the linkages between resources and wars. Rather than seeking to curtail revenue access to belligerents, revenue can be made accessible to 'former' belligerents. Sharing resource revenues, in other words, can 'buy peace.' This type of positive incentive encompasses a broad range of options. Resources constitute divisible goods, especially in terms of revenues and to a lesser degree in terms of ownership (especially if considering state sovereignty), and are thus amenable to self-enforcing sharing agreements. Divisibility can be arranged according to territorial, organizational, or commercial criteria. A first option is to simply leave the armed group inat least partialcontrol of the territory and resources it is holding, for example as part of a local autonomy or secession agreement or even as part of a sanction regime as in the case of the oil-for-food program in Iraq. A second option is to offer the armed group new resource concessions, the control of resource businesses, or lucrative government positions overseeing resource sectors. A third option is to establish a broad sharing agreement for resources through fiscal legislation. In this regard, any conflict settlement could be considered as involving a sharing of resource revenues as long as opposing parties are allowed to have an input into governing. However, in this analysis I only consider the cases in which natural resources constituted a major financial stake in the conflict and in which agreements had an important resource dimension (although not always incorporated into formal documents, see below). These agreements can take place at various levels, concerning an entire rebel movement as part of a comprehensive peace agreement, or only regional units as part of a local ceasefre or defection process.
As with military interventions and economic sanctions, there are ethical dimensions to the use of sharing agreements, since those benefiting from these agreements (or at least negotiating them) include individuals or groups bearing responsibility for war crimes and occupying positions of power through force rather than consent and popular representation. Buying peace, in other words, could be perceived as rewarding violence (Le Billon 2003). The trade-of is of course curbing further abuses that could result from the absence of such agreements. Although sanctions and military interventions should have the ethical advantage of punishing rather than rewarding war criminals, in practice both also often bring about sufering for the general population.
As the cases of Sudan (1997 Khartoum Agreement), Liberia (1995 Abuja Accord), Sierra Leone (1999 Lomé Agreement), or Angola (1994 Lusaka Protocol) illustrate, sharing revenue initiatives face in practice many risks of failure. The parties to the sharing agreement may not encompass all actors with a capacity to prolong the conflict. The incapacity of a party to enforce the agreement within its own ranks can lead to a resumption of the conflict by new factions rejecting the agreement. Such agreement can also motivate rebellion in other aggrieved regions (e.g. in Darfur). Finally, a party can be duplicitous and use such agreement for tactical use to rearm, reorganize or relocate troops to achieve its objectives by military means.
There remains much debate about the effectiveness of these strategies, and more generally about the use of force, sanctions or negotiations. In the following section I present an assessment of initiatives conducted since 1989, before discussing possible factors influencing the relative effectiveness of these initiatives.
MEDIUM-N STUDY (26 CONFLICTS BETWEEN 1989 AND 2006)
Resource revenues did finance belligerents before the end of the Cold War, but in most cases their relative importance was much lower given the financial and military involvement of foreign powers. Furthermore, the number of international commodity-focused initiatives only sharply increased from the early 1990s onwards. I thus select commodity-focused international initiatives taken between 1989 and 2006, identifying 26 armed conflicts in which at least one resource-focused initiative was used. In total, 45 resource-focused initiatives are surveyed (see also Le Billon and Nicholls 2007). A number of caveats and limitations to this dataset need mentioning.
First, with regard to sharing initiatives, I only consider in this analysis the cases in which a reference to the control of a key resource by the opposing party is included in a publicly available settlement agreement, as in the options outlined above. Yet revenues are generally fungible and other types of economic incentives may be offered in addition to, or as a substitute for, resource revenues in a sharing agreement. Furthermore, not all financial deals appear publicly and any confidential agreement would not appear in this dataset. The selection criterion thus effects the difficulty of identifying other types of agreements, either be-cause they are clandestine or because they occur at a smaller scale and fail to be reported. The 14 sharing initiatives identified were concluded between opposing armed groups, with the exception of three cases that were set up unilaterally by central governments, in part to address secessionist agendas (in Angola for Frente de Libertação do Estado de Cabinda (flec) and in Indonesia for both the Free Aceh Movement (gam) and the Free Papau Movement (opm)). Finally, I assess the effectiveness of these initiatives through only three main criteria: successful implementation, conflict outcome after one year and peace stability after five years.
Second, I limit analysis of economic sanctions to those mandated by the Security Council. This selection is motivated by the fact that un sanctions are currently the sole means of legally and internationally imposing a market access denial, with the exception of the prohibition of specific commodities through international agreements, as in the case of narcotics, or voluntary agreements and peer monitoring as in the case of the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme. un sanctions can thus be considered more comprehensive than other types of sanctions and related initiatives, even if they have often been less strictly implemented than sanctions originating from individual states (for example us sanctions); and ngo advocacy was often key in bringing about a more effective implementation of un sanctions, as in the case of 'conflict diamonds.' Of the seven sanction initiatives identified, only one involves a ban on the export of production material to the targeted groupthe Taliban in Afghanistansince narcotics were already illegal on the international market. Third, I only consider external military interventions, including major mercenary interventions and foreign government-mandated interventions that were publicly reported. Of the 17 selected military interventions, five involved international mercenaries groups (or private military companies).
Among the initiatives examined, external military interventions were the most frequent, followed by revenue sharing, and un sanctions. Four conflicts were addressed through all three types of instruments, and eight through two types of initiatives. To assess their potential effectiveness in terms of conflict settlement in general, I use three criteria: effective implementation and status of the conflict after one and five years. Implementation success represents the achievement of operational objectives, specifically: the institutionalization of the agreement in the case of sharing; curtailment of trade in the case of sanctions; and control of resource production area in the case of military interventions. Effectiveness has been assessed through a review of un situation reports and expert panel investigations, as well as think tank, civil society and press reports. As such, these assessments remain tentative and at times subjective. The one and five year lags assess the immediacy and sustainability of a potential effect on conflict termination. I do not argue that peace is the result of the implementation of instruments, but simply assess the occurrence of both events.
I find that among the different types of instruments, those most successfully implemented were military interventions and revenue sharing mechanisms, while sanctions were lagging.9 This result is not surprising since sharing involves willingif sometimes duplicitousparties; military intervention is generally used when there are reasonable chances of success, especially in the case of military interventions by western powers; and sanctions represent a limited instrument of coercion which has furthermore been criticized for being poorly enforced and used as a default policy option. When examining the potential effect of instruments on a resolution of a conflict, however, peace was achieved within a year for about half of the successfully implemented revenue sharing agreements, sanctions, and military interventions. This proportion increases for all instruments after five years, but sanctions were associated more frequently with durable peace than revenue sharing, and military interventions. This suggests that, whereas military interventions are the most frequently used and success-fully implemented, their potential contribution to peace seems lower than that of the two other instruments when these are also successfully implemented. Military interventions were more successfully implemented against states than non-state groups, but these successes were more frequently followed by war than for non-state armed groups. Sanctions seem to have been more successfully implemented and followed by peace in the cases where they targeted whole countries or governments, rather than non-state groups. Sharing agreements all involved state and non-state groups (or the separaThist government).
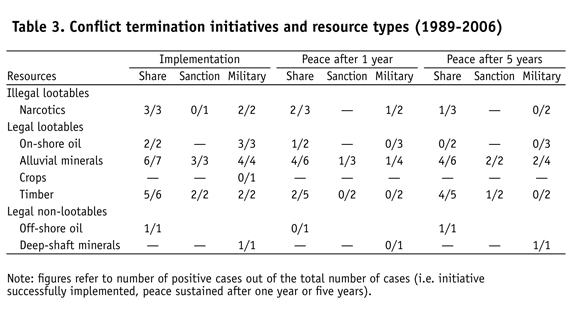
Turning to the criteria of resource type, Table 3 provides an assessment for the major different resources. Regrouping resources further into three major types, I note that revenue sharing agreements have been used for all three types. The implementation success rate of revenue sharing agreements is highest for illegal lootables and non-lootables, but their association with a stable peace is strong only in the case of illegal lootables. Sanctions have also been used for all three types of resources, but mostly for lootable goods. Sanctions failed to be implemented in the only case of illegal lootable resource, have a low implementation success rate for other lootables and a medium one for non-lootables. Association with peace stability is also nil for illegal lootables, but medium for the other two categories. Military interventions were used for all three types of resource categories. Military interventions were successfully implemented in most cases, but most strongly for non-lootable resource, a result that also appears to be associated with peace stability.
Overall, this survey of instruments indicates that illegal lootable resources have been most successfully dealt with through revenue sharing mechanisms.10 There are several reasons for such a finding. First, a high level of implication of state officials in the narcotics sector and the influence of drug cartels in the affairs of the state are relatively common within producing countriesas suggested by the extensive literature on 'narcostates'some of these relations providing (in the eyes of some protagonists) a degree of 'political stability' (McCormack 1999; Le Pichon 2008). Second, clandestine operations by state agents have been financed through illegal but lucrative sectors, some of which have involved alliances with insurgent groupsas alleged in the case of the ciaoccasionally leading in the entrenchment of narcotics inTherests through continued support for (former) allies (Dale-Scott and Marshall 1999; McCoy 2003). Third, narcotics income can play a significant economic role, especially during economic downturns, thus leading to acquiescence or even complicity on the part of authorities to sustain the economy (for the case of Mexico in the late 1990s, see Block 2001); an argument that also applies during 'reconstruction.' Empirically, this finding is mostly driven by cases of cease-fire agreements taking place between the government of Burma/Myanmar and several insurgencies involved in drug production and trafficking (Sherman 2003; see also Snyder, this volume). The case of Afghanistan is also relevant here. The us-led military campaign against the Taliban in 2001 seemed to match a drop in poppy production, suggesting an apparently successful case of military intervention. Yet the intervention occurred after the Taliban had imposed a ban, and the us military were not tasked with military cracking down on drug production, trafficking, and revenue flows before 2005 (Felbab-Brown 2005).11 Since 2001, opium production sharply increased, partly a result of a sharing agreement between former warlords now in the Afghan government, withat the timethe tacit knowledge (if not agreement) of the us government.
In the case of legal lootable resources, sanctions appear to be the most successful with regard to peace stability, despite a low implementation success rate. Although sharing appears as a second best option, with a higher rate of implementation success, all successful cases were only part of broader negotiated peace agreements, rather than prior to a settlement of the conflict. Revenue sharing in Papua New Guinea, for example, was part of a comprehensive agreement signed after a three-year truce between belligerents. Military interventions to control legal and lootable resources, while highly successful in terms of implementation, were very often followed by a resumption of the conflict within the next five years. In the case of non-lootable resources, military intervention was most successful, followed by sanctions. This could be explained by the fact that these resources were controlled by central governments unwilling to respond to sanctions (e.g. Iraq), or facing politically motivated secessionist groups with which sharing agreements were not respected or proved unsaThisfactory (e.g. Aceh in 1999, Chechnya in 1996 and Sudan in 1997).
As discussed in Le Billon and Nicholls 2007, the choice of instruments should thus not only be dictated by the type of resources, but also by the type of conflicts involved and the mechanisms at play. In turn, the selected instruments could be articulated with other conflict resolution measures so as to sustain or amplify the positive impacts of instruments on a possible return to peace. Furthermore, organizations seeking to curtail revenue access for belligerents should also consider the structure of the industry as well as the capacity and motivations of intermediaries and authorities along the resource supply chainas demonstrated in the case of 'conflict diamonds' and the creation of the Kimberley Process (Smillie 2004).
CONCLUSION
This analysis suggests three preliminary findings of relevance to conflict termination. First, and mostly based on a review of the literature and anecdotal evidence from the case studies reviewed, the analysis provides qualified support to the argument that access to resource revenues by belligerents generally prolongs armed conflicts, thereby justifying that conflict settlement initiatives should ad-dress this relationship. This argument is supported by the relatively short delay within which a number of conflicts are settled after resource-focused initiatives are implemented. Yet renewed hostilities after many of these 'successful' interventions indicate that curtailing financial opportunities is not a panacea. It suggests, rather, that the importance of resource revenues for the viability and motivation of rebellion in these conflicts may be overemphasized. In this regard, resources are rarely the only source of revenues and motivation for belligerents who often find ways to adapt their struggle to more difficult economic conditions resulting from effective resource-focused initiatives (Jean and Rufn 1996).
Second, resource-focused initiatives have different levels of successful implementation and potential association with stable peace. Military interventions appear to be a deceptive 'quick-fx': often successfully implemented, these appear to force the targeted party into a settlement, but fail to be followed by a stable peace. Military intervention would thus require significant follow-up to avoid the recurrence of hostilities. In the light of the Angolan and Sierra Leonean cases, the deployment of peacekeeping forces with weak mandates following interventions by external mercenary groups targeting rebel-controlled resource production areas warrants attention in this regardin particular stronger mandating of un peacekeepers to militarily intervene in resource control (as in the case of unsc resolution 1856 for the monuc in the Democratic Republic of Congo, see Le Billon 2009). Revenue sharing seems as successful as military intervention in terms of implementation and is more rapidly followed by conflict settlement, but is also rarely followed by a stable peace. This finding, however, may reffect a timing issue since agreement on revenue sharing is often concluded as part of a settlement of a conflict. Given the asymmetry between belligerents and the risks of duplicity characterizing many of these sharing agreements, third parties may have a role in guaranteeing these arrangements. Adequately mandated peacekeeping forces and an international supervising mechanism for the resource sector can help provide such guarantees. The un Secretary General recently stressed the importance of supporting mediation, notably for wealth sharing agreements, a task assigned to the un Mediation Support Unit (unsg 2009). Sanctions have a poor overall record in terms of implementation for the period examined, but major improvements have been noted since the late 1990s in terms of monitoring and enforcement. Sanctions are furthermore generally lifted only once a conflict is comprehensively settled, possibly contributing to a lasting peace.
Third, the characteristics of the resource sectors targeted seem to affect the effectiveness of these instruments. This finding does not only argue in favour of contextualising responses, but also points to some of the dilemmas and limits of resource-focused instruments. Conflicts involving primarily illegal lootable resources seem best addressed by sharing arrangements; legal lootable resources by sanctions; and non-lootable resources by military intervention. Responding to conflicts related to narcotics poses a dilemma: sharing arrangements are rarely an official option for governments and even less so for conflict responding countries. As noted earlier, however, a number of governments or government officials have nevertheless taken this option to secure a conflict settlement, to support local allies, or to reduce levels of violence (see Snyder, this issue)not to mention benefiting from narcotics revenues at the individual level or to sustain the economy. There is a greater chance that at least some government officials will be amenable to such wealth sharing if narcotics are deeply entrenched in the political economy of the area, support numerous livelihoods (with few alternatives) as well as local revenue reinvestments, politicized and portrayed as 'emancipatory' (from poverty or specific elites), and if the state is too 'weak' to impose anti-drugs policies through coercive means or incentives, and the state is isolated from major donors and sources of capital investment.
The above analysis is admittedly tentative, as it does not address the many other conditions that affect the settlement of a conflict and the likelihood of war recurrence. In the absence of a multivariate analysis that controls for these other factors, the findings of this article should be treated as hypotheses for further investigation, rather than a demonstration of causal links between conflict resolution mechanisms and outcomes. Tree further specific studies could be conducted. The frst is a large-n study encompassing all conflicts involving resources since 1946. Such a study is currently being undertaken by Rustad et al. (2009) using the prio/Uppsala conflict datasetwith preliminary results suggesting that the type of resource (lootable and non-lootable) does affect sta-Thistically the duration of 'post-conflict' peace. Wealth sharing appears to be an effective peacebuilding tool when applied to conflicts involving lootable resource. So far, results have not reproduced findings from (Le Billon and Nicholls 2007) and more work is needed to consider the impact of sanctions and the legality of resources. The second study would consist of a more detailed comparative analysis of individual case studies, so as to determine more precisely the relative impact of resource-focused instruments. Whereas sanctions have been the object of much attention, this has not been the case for military interventions and wealth sharing initiatives. Such study could be extended to other instruments, such as certification schemes, judicial measures, and corporate social responsibility measures. The last study would be a comparative analysis of both international and domestic conflict resolution initiatives across a variety of sectors within one or several countries. The instruments examined here represent only some of the initiatives taken to address connections between resources and conflicts, and such a detailed study would broaden scope and depth.
More generally, a more precise analysis would result from a standardization of the assessment of instrument effectiveness (e.g. standard questionnaires sent to conflict specialists). A more comprehensive approach would require an examination of the effectiveness of military interventions by domestic groups; a more detailed differentiation of the types of economic sharing agreements, including at different scales; as well as an examination of regional and unilateral sanction regimes. Future analyses could also examine the influence of the timing and complementary of these various initiatives, as well as the influence of resources on the capacity and will of external interveners, including the question of commercial inTherests among interveners (Balch-Lindsay and Enterline 2000). Finally, further research could focus on the means by which to establish a credible and enforceable sharing agreement, and examine how credibility and enforceability might vary according to the type of resources involved. Learning more about the context in which conflict termination instruments are deployed may improve their effectiveness and reduce the risk of renewed conflicts.
Comentarios
1 This finding should be qualified, however. Stedman (2001) assesses that two peace agreements were partial successes (Cambodia and Liberia) and that there were as nearly many peace agreements that were partial successes or failures in the case of available and valuable 'lootable' resources than in their absence (Cambodia, Lebanon, Liberia, Sierra Leone, Angola I and II, versus Bosnia, Sri Lanka, Rwanda, and Somalia).
2 Fearon (2004: 284) notes, however, that 'the business synergies between rebel groups and drug traffickers are so strong that any rebel group that can avoid destruction long enough will eventually move into this area.'
3 On the potential importance of the specific characteristics and modes of production of different types of resources on the likelihood, type, or duration of armed conflicts, see (Le Billon 2001; Ross 2003; Snyder 2006).
4 The low traceability of resources can also facilitate trading and the collaboration of business intermediaries with rebel groups. Difficulties over the identification of the origin of diamonds, for example, delayed the effective application of sanctions and required significant reforms in rough diamond trading, notably through the Kimberley Certification Process Scheme.
5 Letter dated 18 July 2006 from the Chairman of the Security Council Committee established pursuant to resolution 1533 (2004) concerning the Democratic Republic of the Congo ad-dressed to the President of the Security Council, S/2006/525, accessed at http://daccess-dds.un.org/doc/UNDOC/GEN/N06/391/16/PDF/N0639116.pdf?OpenElement.
6 The resource curse argument remains debated, with Mehlum et al. (2006) finding that the resource curse result disappears in a cross-section of countries once the quality of institutions is accounted for.
7 Conflict resources are defined by Global Witness, a UK-based NGO, as "natural resources whose systematic exploitation and trade in a context of conflict contribute to, benefit from or result in the commission of serious violations of human rights, violations of international humanitarian law or violations amounting to crimes under international law," see http://www.globalwitness.org/pages/en/defnition_of_conflict_resources.html.
8 The sentence was subsequently overturned by a Dutch court of appeal. 'Profle: Liberia's 'Mister Gus'', BBC News, 7 June 2006, accessed at http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/africa/5055442.stm.
9 As noted above, these results are tentative since they derive from somewhat subjective and non-standardized measures. Furthermore, in part because of the small number of cases, I do not control for the influence of one initiative on the implementation effectiveness of the other. Arguably military interventions can be more effective following sanctions that have weakened a party. Such military intervention, in turn, can affect the likelihood of a successful sharing agreement. In 14 cases only one instrument was used; in 8 cases two were used; in four cases three instruments were used (Angola-UNITA, Cambodia, Liberia, and Sierra Leone).
10 Although sanctions move a commodity from a legal to an illegal category, for the purpose of analysis I maintain the pre-sanction legal status of the commodity. This allows to measure the effect of the sanctions on commodities with pre-existing systems of trade controls (i.e. against illegal commodities), from systems specifically established against legal commodities under sanctions. Since the Kimberley Process Certification Scheme was established in 2003, conflict diamonds are in effect illegal commodities. I have nevertheless maintained conflict diamonds, even after 2003, in the 'legal' category for this analysis.
11 Nor was major US funding provided for counterdrug activities, contrasting with the USD 750 million dollars allocated in 2003 for the Andean region (see White House 2003 National Drug Control Update).
Referenes
Auty, Richard. 2004. Natural resources and civil strife: A two-stage process. Geopolitics 9 (1): 29–49. [ Links ]
Balch-Lindsay, Dylan, and Andrew J. Enterline. 2000. Killing time: The world politics of civil war duration, 1820–1992. International Studies Quarterly 44 (4): 615–642. [ Links ]
Balch-Lindsay, Dylan, Andrew J. Enterline, and Kyle A. Joyce. 2008. Third-party intervention and the civil war process. Journal of Peace Research 45 (3): 345–363. [ Links ]
Ballentine, Karen, and Heiko Nitzschke. 2004. Profting from peace: Managing the resource dimensions of civil war. Boulder: Lynne Rienner. [ Links ]
Bannon, Ian, and Paul Collier 2003. Natural resources and violent conflict: Options and actions. Washington: World Bank. [ Links ]
Basedau, Matthias, and Wolfram Lacher 2006. A Paradox of Plenty? Rent Distribution and Political Stability in Oil States. German Institute of Global and Area Studies Working Paper Series 21. [ Links ]
Binningsbo, Helga M., Indra de Soysa, and Nils Peter Gleditsch. 2007. Green giant, or straw man? Environmental pressure and civil conflict, 1961-1999. Population and Environment 28 (6): 337–353. [ Links ]
Block, Alan A. 2001. On the inestimable value of the ogd. Crime, Law and Social Change 36: 1–20. [ Links ]
Buhaug, Halvard, and Scott Gates. 2002. The geography of civil war. Journal of Peace Research 39(4): 417–433. [ Links ]
Buhaug, Halvard, Scott Gates, and Päivi Lujala. 2009. Geography, Rebel Capacity, and the Duration of Civil Conflict. Unpublished manuscript. [ Links ]
Buhaug, Halvard, and Jan Ketil Rød. 2006. Local determinants of African civil wars, 1970–2001. Political Geography 25 (3): 315–335. [ Links ]
Collier, Paul and Anke Hoefer. 1998. On economic causes of civil war. Oxford Economic Papers 50: 563–573. [ Links ]
. 2004. Greed and grievance in civil war. Oxford Economic Papers 56 (4): 563–595. [ Links ]
. 2005. Resource rents, governance and conflict. Journal of Conflict Resolution 49 (4): 451–482. [ Links ]
Collier, Paul, Anke Hoefer, and Måns Söderbom. 2004. On the duration of civil war. Journal of Peace Research 41 (3): 253–273. [ Links ]
Cornell, Svante. 2007. Narcotics and armed conflict: interaction and implications. Studies in Conflict and Therrorism 30 (3): 207–227. [ Links ]
Cortright, David, and George A. López. 2000. The sanctions decade: Assessing un strategies in the 1990s. Boulder: Lynne Rienner. [ Links ]
. 2002. Sanctions and the search for security: Challenges to un action. Boulder: Lynne Rienner. [ Links ]
Dalby, Simon. 2002. Environmental Security. Minneapolis: Minnesota University Press. [ Links ]
Dale-Scott, Peter, and Jonathan Marshall. 1998. Cocaine politics: Drugs, armies, and the cia in Central America. Berkeley: University of California Press. [ Links ]
Dube, Oeindrila. and Juan F. Vargas. 2006. Commodity price shocks and civil conflict: Evidence from Colombia. Documentos de cerac 2. [ Links ]
Doyle, Michael W., and Nicholas Sambanis. 2000. International peacebuilding: A theoretical and quantitative analysis. American Political Science Review 94 (4): 779–801. [ Links ]
Fearon, James D. 2004. Why do some civil wars last so much longer than others? Journal of Peace Research 41 (3): 275–302. [ Links ]
. 2005. Primary commodities exports and civil war. Journal of Conflict Resolution 49 (4): 483–507. [ Links ]
Felbab-Brown, Vanda. 2005. Afghanistan: When counternarcotics undermines counterterrorism. Washington Quarterly 28 (4): 55–72. [ Links ]
Humphreys, Macartan. 2005. Natural resources, conflict, and conflict resolution: Uncovering the mechanisms. Journal of Conflict Resolution 49 (4): 508–537. [ Links ]
Jean, François, and Jean-Christophe. Rufin, eds.1996. Économie des guerres civiles. Paris: Hachette. [ Links ]
Johnson Likoti, Fako. 2007. The 1998 military intervention in Lesotho: sadc peace mission or resource war? International Peacekeeping 14 (2): 251–263. [ Links ]
Le Billon, Philippe. 2001. The political ecology of war: Natural resources and armed conflicts. Political Geography 20 (5): 561–584. [ Links ]
. 2003. Fueling war or buying peace: The role of corruption in conflicts. Journal of International Development 15 (4): 413–426. [ Links ]
. 2003. Getting It Done: Instruments of Enforcement. In Natural Resources and Violent Conflict: Options and Actions, ed. Ian Bannon and Paul Collier, 1–72. Washington: World Bank. [ Links ]
. 2005. Fuelling war: Natural resources and armed conflicts. London: Routledge. [ Links ]
. 2008. Diamond wars? Conflict diamonds and geographies of resource wars. Annals of the Association of American Geographers 98(2): 345–372. [ Links ]
. 2009. Natural resources, peacekeepers and contracts: improving resource control and management in 'post-conflict' situations. Working Paper, Liu Institute for Global Issues, ubc. [ Links ]
Le Billon, Philippe, and Eric Nicholls 2007. Ending 'resource wars': Revenue sharing, economic sanction or military Intervention? International Peacekeeping 14 (5): 613–632. [ Links ]
Le Pichon, Tibault. 2008. Drug Trafcking as a Security Treat in West Africa. Vienna: United Nations Ofce on Drugs and Crime. [ Links ]
Licklider, Roy. 1995. The consequences of negotiated settlements in civil wars, 1945–1993. American Political Science Review 89 (3): 681–690. [ Links ]
Lujala, Päivi. 2003. Classifcation of natural resources. Edinburgh: ecpr Joint Session of Workshops. [ Links ]
. 2008. Deadly combat over natural resources: Gems, petroleum, drugs, and the severity of armed civil conflict. Journal of Conflict Resolution 53 (1): 50–71. [ Links ]
Lujala, Päivi, Nils Peter Gleditsch, and Elisabeth Gilmore. 2005. A diamond curse?: Civil war and a lootable resource. Journal of Conflict Resolution 49 (4): 538–562. [ Links ]
Lujala, Päivi, Jan Ketil Rød, and Nadja Tieme. 2007. Fighting over oil: Introducing a new dataset. Conflict Management and Peace Science 24 (3): 239–256. [ Links ]
Mack, Andrew, and Asif Khan. 2000. The eficacy of un sanctions. Security Dialogue 31 (3): 279–292. [ Links ]
McCormack, Robert J. 1999. Caribbean sovereignty and the war on drugs: Historical factors and current perspectives. Caribbean Journal of Criminology and Social Psychology 4 (1/2): 71–84. [ Links ]
McCoy, Aalfred.W. 2003. The Politics of Heroin: cia Complicity in the Global Drug Trade. Chicago: Lawrence Hill & Co. [ Links ]
Mehlum, Halvo, Karl Moene, and Ragnar Torvik. 2006. Institutions and the resource curse. Economic Journal 116: 1–20. [ Links ]
Nitzschke, Heiko, and Kaysie Studdard. 2005. The legacies of war economies: challenges and options for peacemaking and peacebuilding. International Peacekeeping 12 (2): 222–239. [ Links ]
Regan, Patrick. M. 2002. Third party interventions and the duration of intrastate conflicts. Journal of Conflict Resolution 46 (1): 55–73. [ Links ]
Regan, Patrick. M., and Aysegul. Aydin. 2005. Diplomacy and other forms of interventions in civil wars. Journal of Conflict Resolution 50 (5): 736–756. [ Links ]
Regan, Patrick M., Richard Frank, and Aysegul Aydin. 2009. Diplomatic interventions and civil wars: A new dataset. Journal of Peace Research 46 (1): 135–146. [ Links ]
Ross, Michael. 2003. Oil, drugs, and diamonds: How do natural resources vary in their impact on civil war? In The political economy of armed conflict: Beyond greed and grievance, ed, Karen Ballentine, and Jake Sherman, 47–67. Boulder: Lynne Rienner. [ Links ]
. 2004. How do natural resources infuence civil war? Evidence from thirteen cases. International Organization 58 (1): 35–67. [ Links ]
. 2006. A closer look at oil, diamonds, and civil war. Annual Review of Political Science 9: 265–300. [ Links ]
Rustad, Siri, Helga Binningsbo, and Philippe. Le Billon. 2009. Do resource-related peacebuilding initiatives build peace? Paper presented at the annual conference of the International Studies Association, February 15, in New York, United States. [ Links ]
Rustad, Siri, Jan Ketil Rød, Wenche Larsen and Nils Petrer Gleditsch. 2008.Foliage and fighting: Forest resources and the onset, duration, and location of civil war. Political Geography 27 (7): 761–782. [ Links ]
Sherman, Jake. 2003. Burma: Lessons from the cease-fries. In Beyond greed and grievance: The political economy of armed conflict, ed, Karen Ballentine and Jake Sherman, 225–255. Boulder: Lynne Rienner. [ Links ]
Smillie, Ian. 2004. What lessons from the Kimberley process certifcation scheme? In Profting from peace: Managing the resource dimensions of civil war, ed. Karen Ballentine and Heiko Nitzschke, 47–67. Boulder: Lynne Rienner. [ Links ]
Snyder, Richard. 2006. Does lootable wealth breed disorder? A political economy of extraction framework. Comparative Political Studies 39 (8): 943–968. [ Links ]
de Soysa, Indra. 2002. Ecoviolence: Shrinking pie, or honey pot? Global Environmental Politics 2 (4): 1–27. [ Links ]
Stedman, Stephen John. 2001. Implementing peace agreements in civil wars: Lessons and recommendations for policymakers. ipa Policy Paper Series on Peace Implementation. [ Links ]
Theisen, Ole Magnus. 2008. Blood and soil? Resource scarcity and internal armed conflict revisited. Journal of Peace Research 45 (6): 801–818. [ Links ]
unSG. 2009. Report of the Secretary-General on enhancing mediation and its support activities. unsc s/2009/189, 8 April 2009. [ Links ]
Weinstein, Jeremy. 2005. Resources and the information problem in rebel recruitment. Journal of Conflict Resolution 49(4): 598–624. [ Links ]
. 2007. Inside rebellion: The politics of insurgent violence. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. [ Links ]