Introducción
Uncontrolled deforestation and increasing greenhouse gas emissions are anthropogenic activities responsible for triggering environmental disequilibrium that affects the Earth’s complex climate dynamism (Menezes-Silva et al., 2019). The carbon dioxide (CO2) concentration in the atmosphere has risen at a rate of 2.16 ± 0.09 ppm year-1 in recent decades as a result of human activity (Le Quéré et al., 2018), and its increase is expected to continue until emissions are reduced (Anderson et al., 2019). Kumar et al. (2017) reported that CO2 levels had reached concentrations above 400 µmol/mol, and a record increase of 415 ppm has been reported recently (Brito et al., 2020). By the end of this century, the prediction of 600 to 700 ppm will increase the mean surface temperature from 4.5 to 5.0 °C (Leung et al., 2014) and CO2 concentration by 1 to 3 ppm per year (Taiz et al., 2017). The increase in global temperature has a direct impact on the structure and function of ecosystems, including its effects on the physiology and growth of trees (Ceulemans et al., 1999), with CO2 being the critical substrate for photosynthesis and, therefore, the main contributor to world food production (Mishra et al., 2019).
Of the CO2 entering the atmosphere each year due to human activity, 45% remains there, while oceans sequester 25%, and terrestrial ecosystems the rest at 30% on average (Henson, 2011). However, there are significant variations from one year to the next due to climatic cycles and changes in land use (Henson, 2011).
Apart from CO2, emissions associated with greenhouse gases (GHG) mainly include methane (CH4) and nitrous oxide (N2O). The three add up to 80% of the GHG (IPCC, 2013). Furthermore, GHGs are associated with fluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons, and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) (López-Bellido, 2015). These GHGs have increased dramatically in recent decades (Al-Mamoori et al., 2017; Ouda et al., 2016) caused mainly by the combustion of fossil materials (coal, oil, and natural gas), industrial emissions, deforestation, and soil degradation (Henson, 2011; IPCC, 2013).
According to the IPCC (2019), climate change affects food security due to warming, altered rain patterns, and a greater frequency of extreme weather events. Furthermore, the impact and consequences of climate change for agriculture tend to be more severe for countries with higher initial temperatures, areas with marginal or already degraded lands, and lower levels of development with little adaptive capacity (Yohannes, 2016). Mishra et al. (2019) stated that in the long term, the exposure of plants to high CO2 (e-CO2), high temperatures, and droughts would considerably affect the balance of ecosystem processes at the local and global levels.
The e-CO2 in trees markedly improves productivity due to increased efficiency in water use, a high rate of photosynthesis, more sugar accumulation in fruits, and higher biomass production (Rajan et al., 2020) (figure 1). However, Ebi et al. (2021) lessen this enthusiasm because e-CO2 can also alter the nutritional quality of C3 plants. Fruit plantations can contribute positively to sustainable development in the climate change scenario in the tropics, considering that the current expansion of agriculture and poverty level continues reducing forest resources (Patil & Kumar, 2017). Wu et al. (2012) estimate that apple orchards in China, the largest producer of this fruit globally, can offset between 1.6% and 3.0% of CO2 emissions from burning fossil fuels in China, highlighting the importance of these orchards for carbon sequestration.
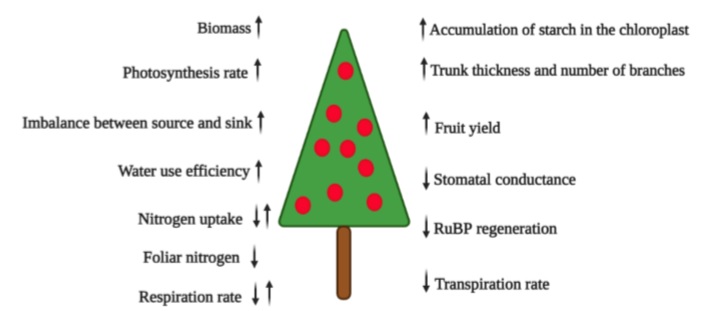
Source: Modified based on Mishra et al. (2019) and Ramírez and Kallarackal (2015)
Figure 1 Diagram of the increase (↑) and decrease (↓) of growth parameters and physiology of the fruit plant under increased atmospheric CO2.
There is enough research that indicates that atmospheric e-CO2 increases net photosynthesis, biomass accumulation, seed and fruit yield, water use efficiency (figure 1), light interception, nutrient uptake, and the water potential of plants (Tognetti et al., 2005). Overall, e-CO2 is expected to improve the fruit nutrient content (Balasooriya et al., 2019). Nevertheless, the studies that find interactions with other environmental and genetic factors that modify these results in e-CO2 events should not be underestimated (Mishra et al., 2019).
Thus, plant responses to e-CO2 and the resulting changes in species can be strongly affected by interactions with other environmental factors and climate change, including tropospheric ozone, temperature, water, and nitrogen (Bradley & Pregitzer, 2007). For this reason, Allen and Vu (2009) warned that global e-CO2 does not have the same effects on all plant species and all environments, so it is unwise to extend predictions from research in well-irrigated systems to those cultivated in hot and arid environments or milder climatic zones.
In many cases, the effects of climate change are examined through each factor involved, but it must be considered that the response of plants to climate change is not the sum of the reactions to the different phenomena but results from the interaction between all these (Pérez- Jiménez et al., 2017). According to the concept of multidimensionality by Zandalinas et al. (2021), all climatic factors occur at the same time, which is why studies in open areas such as the FACE system (Free Air CO2 Enrichment) (Ramírez & Kallarackal, 2015; Sánchez et al., 2015) or also semi-open (open-top chambers) have gained much importance in research into climate change in our crops. Studies of an e-CO2 in the FACE system, which usually runs for several years, have shown effects on photosynthesis and stomata, kept closed longer to directly reduce transpiration (figure 1). However, mitochondrial respiration increases due to increased leaf temperature (Nobel, 1999; Taiz et al., 2017).
Nobel (1991) stated that many C3 plants (all fruit trees except pineapple and cacti such as pitaya and prickly pear, which are CAM plants) need an optimal CO2 concentration of about 1,000 ppm to fix carbon during photosynthesis since no saturation has been observed at the current levels of ambient CO2 (Mishra et al., 2019). Taiz et al. (2017) reported that with e-CO2 up to 600-750 ppm, most C3 plants would grow 30% faster, but the growth rate may become limited by the availability of nutrients for the plant (figure 1).
Because the current concentration of CO2 barely exceeds 400 ppm (Kumar et al., 2017), CO2 deficiency is one of the limiting factors for photosynthesis and crop production (Fischer et al., 2016; Song et al., 2020). An atmospheric e-CO2 would increase plant photosynthesis through a “CO2 fertilizer effect” (Mishra et al., 2019). This effect is generated by biomass production (figure 1) derived from photosynthesis, defined by Larcher (2003) as 85 % to 92 % of dry matter. Due to the more significant accumulation of carbohydrates by plants, e-CO2 will also increase its availability for symbiotic organisms such as mycorrhizal fungi and associated rhizospheric bacteria (Bhargava & Mitra, 2021).
The e-CO2 up to 1,000 µmol/mol used inside greenhouses to increase crop production (mostly of vegetables and strawberries) is a technology that has been applied for several years (Becker & Kläring, 2016). However, in greenhouses, especially for reasons of the indoor climate, ventilation cannot be opened. Therefore, the concentrations of CO2 in the air can decrease to 150 µmol/mol during the day due to plants, as found by Kläring et al. (2007) for cucumber.
Nitrogen availability and cycling play a crucial role in regulating responses to e-CO2, especially in temperate ecosystems (Reich et al., 2006) but also in the tropics (DaMatta et al., 2010) because low N levels do not stimulate increased production in systems with CO2 enrichment (figure 1) (Leakey et al., 2012). Thus, they alter the relationship between nutrient demand and crop growth (Cruz et al., 2016). In this context, it is essential to consider that more significant applications of nitrogen fertilizers can increase the release of N2O into the atmosphere, which is a potent greenhouse gas. Therefore, efforts should increase efficiency in using nitrogen from plants (Jackson et al., 2011). It is also true that moderate CO2 enrichment can improve N absorption efficiency and decrease N loss from the soil associated with a decrease in nitrification and denitrification under a high application of N (Dong et al., 2020).
Experiments in temperate zones showed that e-CO2 could alleviate drought stress (Leakey, 2009) and the drying effects of warming (Morgan et al., 2011). In general, it is assumed that water use in the plant canopy is lower under e-CO2 conditions because, although the leaf area index may increase, there is a lower stomatal conductance on average (Ainsworth & Lemonnier, 2018) that compensates by a larger evaporation surface (Ainsworth & Rogers, 2007). In tomato, Wei et al. (2018) found that an e-CO2 of 800 ppm attenuated the effects of water-deficit stress on performance.
It is well known that high temperatures reduce the net gain of carbon in C3 species by increasing photorespiration (Nobel, 1999). Therefore, e-CO2 can decrease photorespiration and increase photosynthesis, mainly under high-temperature conditions rather than low temperatures (DaMatta et al., 2010), partially offsetting the effects of supra-optimal temperatures on yield (Polley, 2002). DaMatta et al. (2010) concluded that e-CO2 would have the most positive effects on the growth of crops with temperatures close to the optimum. In regions highly affected by high temperatures, such as low latitudes, a progressive increase in heat decreases crop yield independently of e-CO2 (Polley, 2002).
Usually, the e-CO2 applied by horticulturists generates higher yields (Gruda et al., 2019). However, ambient CO2 can reduce input costs for CO2 enrichment. Gruda et al. (2019) reported it as unlikely that these applications will be unnecessary in the future. Crops benefit from even higher levels with this gas, considering the most pessimistic scenario of the IPCC (2013) for 2100 with about 935 ppm of CO2. On the other hand, CO2 applications in greenhouses are restricted by the ambient temperature. If it is high, the vents must be opened, making the e-CO2 ineffective due to losses to the outside (De Zwart, 2012). This effect may still be aggravated by heat waves generated by climate change (Bisbis et al., 2018).
There are few publications on fruit trees with e-CO2 than other crops (Ramírez & Kallarackal, 2015; Wohlfahrt et al., 2018). Studies, especially on vegetables, showed that with e-CO2, the concentrations of calcium, glucose, fructose, total soluble solids, total flavonoids, total phenols, ascorbic acid, and the total antioxidant capacity could increase in the edible part of vegetables. However, e-CO2 can also decrease the concentrations of nitrate, magnesium, zinc, iron, and protein (Dong et al., 2018).
Becker and Kläring (2016) found that e-CO2 in greenhouses or plant factories for species such as lettuce increases the availability of precursors for the biosynthesis of phenolic compounds that are health promoters. Increased e-CO2 can also increase the nutritional quality of fruits (Fischer et al., 2016). Moretti et al. (2010) reported that e-CO2 increased ascorbic acid levels in postharvest strawberries and oranges. Therefore, this review article aims to report the effects of the increase in atmospheric CO2 on the physiology, growth, and production of fruit species. This knowledge can be used to decide on species selection, management, and the mechanisms to mitigate these effects.
Materials and methods
The information from different databases, including ScienceDirect, Scopus, SciELO, Google Academic, and ResearchGate, was assessed for this literature review. The search was made using keywords (in English and Spanish) such as “CO2,” “carbon dioxide,” “CO2 fertilization”, “carbon fertilization,” “climate change,” “fruits,” “fruit trees,” “fruit plants.” From the mentioned databases, we obtained 88 sources that include scientific national and international articles, books, and book chapters from the last 30 years, in English and Spanish.
The different fruit trees were chosen according to the research with CO2 in the last three decades. From these, the studies of species important in Colombia, such as different citrus fruits, grape, papaya, strawberry, and pitaya, are described in more detail in table 1.
Effect of high CO2 on the physiology and production of fruit trees
The effects of e-CO2 in the air near the leaf blade are well-known and reported. They include decreased stomatal opening, stomatal conductance, and transpiration. In response, photosynthesis and plant growth increase. Additionally, the plants show greater efficiency in the use of water (Pritchard & Amthor, 2005; Stöckle et al., 2011) and light (Drake & González- Meler, 1997). The key reason for this enriched photosynthesis is the increased carboxylation efficiency of RuBisCO, which is relatively low in the concentration of ambient atmospheric CO2 (Mishra et al., 2019).
If the environmental level of CO2 increases from 350 to 550 ppm (at 25 °C), with time, the rates of photosynthesis will be reduced in some species, compared to plants grown at ambient levels of CO2. This effect is called “photosynthetic acclimation,” attributed to five mechanisms at the cellular level, reported by Ramírez and Kallarackal (2015): (1) gene repression and sugar accumulation; (2) insufficient nitrogen uptake by the plant; (3) a link of carbohydrate accumulation with inorganic phosphate and, consequently, a limitation in the renewing capacity of RuBP; (4) accumulation of starch in the chloroplast; and (5) capability of triose phosphate utilization. Photosynthetic acclimation with e-CO2 is a critical topic that must be assessed in detail because it would indicate that the advantage of e-CO2 can be lost over time. Therefore, new studies must involve several growing cycles.
Since e-CO2 generates higher photosynthesis rates, a more significant amount of assimilates is available to be channeled towards biosynthetic pathways of different types (Treutter, 2010), resulting in higher levels of secondary metabolites due to the greater availability of precursor molecules (Becker & Kläring, 2016). Furthermore, in e-CO2 environments, because of the greater number of growing sink organs, there is an increase in the demand for photo- assimilates, which stimulate the net assimilation rates of carbon in the form of sucrose and starch (Bhargava & Mitra, 2021). e-CO2 (750 ± 30 μmol/mol) can increase photosynthesis rates without affecting stomatal conductance and dark respiration. Nevertheless, ABA and 1- aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid levels cannot do this without a stressful condition such as salinity (reported in the tomato), where the intermediates of the Krebs cycle in e-CO2 can also be increased to reduce the harmful effect of salinity (Brito et al., 2020). However, e-CO2 can also decrease the respiratory rate (Kochhar & Gujral, 2020). Cytochrome pathway respiration may be affected, and respiration may be increased through the alternative oxidase pathway due to a decrease in O2, an aspect that also deserves more attention.
Bitter orange trees planted in open-top chambers with transparent plastic for 17 years at 300 ppm CO2 higher than the ambient concentration (table 1) showed a 70 % increase in the total biomass of the orange tree compared to the control tree (Kimball et al., 2007). This improvement came from the more significant number of fruits produced, mainly by numerous branches, an increase in the thickness of the trunk and branches, and an increase in the length of the fine roots in 64.5 % and 57.2 % at soil depths of 0-15 and 15-30 cm, respectively (Prior et al., 2012). These advantages can considerably improve the productivity of fruit trees.
Young lemon (Citrus limon) plants exposed to 650 and 850 ppm CO2 and a 1-month drought maintained their growth. However, at 400 ppm it decreased (table 1) due to the down- regulation of the stomata by which the foliar transpiration and the daytime use of water of the plants decreased by 13 % - 46 %, although the photosynthesis was 15 % - 25 % higher compared to environmental CO2 (Paudel et al., 2018). The authors concluded that e-CO2 partially offset the effects of drought on plant development and thus diminished some of the effects of anthropogenic climate change.
In the Satsuma mandarin with e-CO2, up to 500 ppm increases the gross photosynthetic rate of the fruit peel, but at higher concentrations, the rate decreases, a reaction similar to C4 photosynthesis (Hiratsuka et al., 2015). The authors find that foliar photosynthesis constantly increases between 50 and 1,000 ppm CO2 (table 1). Interestingly, the photosynthesis of the fruit was higher than the foliar at a low photosynthetic photon flux density (PPFD) of 13.5 to 68 µmol m-2 s-1; for this reason, Hiratsuka et al. (2015) characterized the species as an intermediate state between C3, C4, and shade plants.
Viticulture regions are confined to unique climatic niches; climate change affects them significantly due to changes in precipitation and temperature. The changes can destabilize the balance between climate, soil, and plant, with profound effects on the production of high- quality wines (Moriondo et al., 2013), meaning global warming will shift for new regions towards the poles and in the tropics to the increased altitude that may potentially become more suitable for growing and producing high-quality wines (Jones et al., 2005). This situation is critical in Colombia, where grapevines are grown above 2,200 m a.s.l.
The greenhouse and FACE studies (table 1) showed an increase in photosynthetic yield and thus a higher production of grapes (Martínez-Lüscher et al., 2015; Wohlfahrt et al., 2018). Bindi et al. (2001) observed a 45–50 % increase in grape biomass production when the CO2 concentration rose to 700 μmol/mol without adverse effects on the quality of the grape or wine. However, when e-CO2 was accompanied by drought or thermal shocks due to supra- optimal temperatures, induced burns and a considerable loss of the berries greatly affected the yield (table 1) (Kizildeniz et al., 2018).
Performance is highly dependent on photosynthesis, and CO2 is one of the essential constituents of this process (Li et al., 2020). In strawberries, e-CO2 of 720 ppm and high temperatures (25/20 °C day/night) decreased the yield due to the lower number of inflorescences induced at these temperatures, while low temperatures (20/15 °C) increased their production and quality (table 1) (Sun et al., 2012). These authors warned that the optimal temperatures for flower induction must be considered for e-CO2, which must be low since global warming can affect strawberry production.
Effects on the quality of strawberries occur when e-CO2 (300 and 600 ppm higher than ambient CO2) increases the concentrations of flavonoids and anthocyanins in fruits (Wang et al., 2003). The authors found that plants grown in e-CO2 showed higher oxygen-free radical absorbance activity in the fruit (Wang et al., 2003). Two studies of the effect of e-CO2 on strawberry leaves showed an increase in leaf size, photosynthesis, and light saturation (table 1) (Li et al., 2020). These results confirmed what was observed by Keutgen et al. (1997) in which an e-CO2 of 600 ppm promoted net foliar photosynthesis, while at a higher concentration, it led to a decrease in net assimilation.
Cactaceous fruits such as yellow pitaya (Selenicereus megalanthus), characterized by the acid metabolism of Crassulaceae (CAM), reacted to an e-CO2 of 1,000 ppm (vs. 380 ppm environmental) with a tremendous increase in the daily intake of CO2 and vegetative and reproductive growth factors (table 1) compared to the red pitaya (Hylocereus undatus) that also showed a considerable increase in vegetative growth, but only a 7 % increase in the fresh weight of fruits, compared to 63 % of yellow pitaya (Weiss et al., 2010). The authors attributed the response to a differential adaptation of these two species to humid conditions (Weiss et al., 2010). Rajan et al. (2020) classified pitayas (dragon fruits) as very suitable for climate change conditions due to their lower demand for soil moisture and reduced transpiration rate (figure 1).
CO2 fixation occurs mainly at night in CAM plants, catalyzed by the cytosolic enzyme phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) to produce malate or aspartate, stored in vacuoles (Mishra et al., 2019; Nobel, 1999). Decarboxylation occurs during the day and results in the release of CO2 from malic or aspartic acid and its conversion to carbohydrates in the Calvin cycle (Taiz et al., 2017). Due to their transpiration efficiency (three to five times higher than C3 or C4 plants), these plants are more suitable in places with water scarcity (Mishra et al., 2019).
Cruz et al. (2016) found that for papaya seedlings, e-CO2 at 750 ppm increased not only the assimilation rate but also the instantaneous efficiency of water use (table 1), especially at the higher level of N applied (52% at 8 mM N), compared to the lowest (16% at 3 mM N). The e-CO2 stimulated the accumulation of dry mass in the plants, especially for plants cultivated with lower levels of N. However, e-CO2 decreased N concentrations in all plant organs (figure 1), regardless of the level of N used (Cruz et al., 2016).
Unfortunately, neither Colombia nor other countries have studied CO2 on important fruits for export, e.g., cape gooseberry, purple passionfruit, and sweet granadilla. In Colombia, no studies have been carried out with different concentrations of CO2 in fruit trees.
Aspects of mitigating the adverse effect of CO2 on fruit trees
Despite the increase in atmospheric CO2, considering global warming and altered rainfall, food production is uncertain for the future (Haokip et al., 2020). For the profitable production of fruit trees, climate change, especially e-CO2, is a tremendous challenge for the producer needing to find possible solutions to mediate these effects (Fischer et al., 2016). Therefore, fruit growers must achieve high efficiency in the use of nutrients (particularly nitrogen) and water, while guaranteeing a sufficient entry of light (Ramírez & Kallarackal, 2015), e.g., through greater distances between trees, so that plant conduction and pruning achieve optimal leaf growth and development (Casierra-Posada & Fischer, 2012).
Fruit growers must guarantee adequate “soil fertilization with CO2” to increase soil respiration (Fischer et al., 2016). In Italy, organically managed vineyards that apply manure and bury pruning residues showed higher soil respiration rates than conventional orchards (Brunori et al., 2016). Thus, a 2/3 increase in soil CO2 production is seen for microorganisms and 1/3 for root respiration when fertilizers are applied organically (Fischer & Orduz-Rodríguez, 2012).
Likewise, producers must mitigate climate change by selecting more adapted cultivars that respond to e-CO2 and are capable of tolerating drought or waterlogging conditions (Fischer et al., 2016). The plant’s response capacity to e-CO2 is related to the sink’s intrinsic capacity, adaptive plasticity, and good progress. These aspects could be achieved with plant breeding programs or genetic engineering (Dingkuhn et al., 2020). Also, Mishra et al. (2019), with a view to prolonged e-CO2 levels (the reality of climate change), underline the species and varieties with high sink strength to accumulate carbohydrates. These plants do not react with suppression of photosynthesis, unlike the plants that accumulate carbohydrates excessively in leaf tissues (figure 1). In this regard, exploring the genomic basis of local adaptation is essential for evaluating the conditions under which fruit trees will successfully adapt in situ to global climate change (Cortés et al., 2020).
Because e-CO2 is accompanied by an increase in temperature and, in many cases, by more intense dry seasons, new orchards should be established at higher altitudes and latitudes (Fischer & Melgarejo, 2020; Houston et al., 2018) where there is sufficient availability of water for irrigation. Preferably irrigation systems should be used, which reduce GHG emissions (CO2 and N2O), such as underground drip irrigation (Jackson et al., 2011) or deficit irrigation that saves much water without damaging the quality of fruits (Vélez-Sánchez et al., 2019, 2021). An increase in altitude decreases CO2 partial pressure and H2O vapor (Nobel, 1999). However, in the case of deciduous fruit trees in the inner tropics, it is not sure that an increase in altitude for the plantations will guarantee sufficient chilling hours to break bud rest so that the growers continue defoliating and applying chemicals to trees to break dormancy (Luedeling et al., 2011).
Based on observations of farmers’ performance in the face of extreme climatic events, resilience is highly related to the high biodiversity of farms, typical in traditional agricultural systems, especially in combination with agroecological methods that are the only viable methods for maintaining productivity and sustainability of peasant agriculture under climate change (Altieri & Nicholls, 2017; Pérez et al., 2010). However, further studies are required under the new scenarios to evaluate the impacts of climate change, as they may serve as tools in decision-making for the management of fruit species and their productivity.
To avoid losses in fruit production due to e-CO2, Haokip et al. (2020) proposed implementing a plan based on a strategic scientific impact assessment with the adaptations and mitigation necessary. Sharma et al. (2021) confirmed that sustainable fruit production systems could mitigate emissions and sequester carbon within the atmosphere. Besides the shallow soil tillage, which preserves the soil organic matter, the structural characteristics of orchards and vineyards, including their long-life cycle, permanent organs (trunk, branches, roots), and high yields, force them to accumulate a considerable amount of carbon (Sharma et al., 2021). Also, Marín et al. (2016) reported high carbon fixation rates (17.7 t year-1) in agroforestry systems with citrus species.
Conclusions
Due to human activity, the concentration of CO2 is constantly increasing and stands out as one of the major causes of global warming. Generally, e-CO2 positively affects fruit trees, such as increased photosynthesis, water use efficiency, and growth. Therefore, in many cases, the yield and the quality of fruits also increase.
The increased growth of fruit trees due to e-CO2 requires more nutrients and water, so selecting genotypes that benefit from e-CO2, make highly efficient use of nitrogen and water, and have a high sink strength, is very important. More importantly, fruit growers should select cultivars adapted to climate change that respond to e-CO2 and tolerate drought or waterlogging conditions.
Thanks to their permanent organs, sustainable fruit production systems can minimize emissions and sequester carbon within the atmosphere. Also, to fulfill the requirement of sufficient CO2 fertilization, especially of the lower plant part, increased production of soil CO2 through organic fertilizer application is a good strategy.
The authors conclude that there is unquestionably a “fertilization effect of CO2” on fruit species that increases with the progress of climate change. However, much research lacks fruit trees compared to many other field crops. Further studies are required to address the direct effects of atmospheric e-CO2 and its interactions with environmental variables such as rainfall, temperature, soil moisture, nutrient availability, and the vapor pressure deficit with altitude.