1. Introduction
Software tools are conceived with the purpose of solving a problem or speeding up a process. It is necessary to apply the use of software applications in any field; Tasks are made easier thanks to them; this applies directly to the case study: the parking establishments.
In some parking establishments there are software tools used to improve the business management, tools allocated to simple tasks, such as billing or client management.
For these reasons, it is necessary to implement a complete solution, one which takes into account many of the activities that are executed in this kind of establishments; revenue management, expenses, customers, vehicles, monthly installments, employees, complaints, logbook, audit, and parameterization in a single tool.
Throughout this document, the reader will find the different processes applied to the development of software, particularly applied to a parking management software.
Initially the analysis stage will be covered, along with the used techniques, going through the software design, built diagrams, and finishing with the development stage.
In section 2 Methodology the description and justification of the problem “administration system, parking management” is carried out, plus, the development platform is chosen; in section 3 Results and Discussion, the user stories are used for requirements gathering, for the purpose of design, a Model-View-Controller architecture is used 1 for software quality 2 and its scalability, as well as describing the functionalities of each software module (Attachment, Audit, Logbook, Block, Warehouse, Client, Configuration, Spot, Employee, Income, Inventory, Line, Monthly Installment, Loan, Complaints, Vehicle, Voucher, Notes)
In section 4 Development, the agile methodology SCRUM 3 was used for the development of the project, which conceives the development of the software with the use of Sprints, or cycles; and having roles within the project’s team. The agile methodology 4+1 is used, tools used for the project development include the French IDE WINDEV, the programming language WLANGUAGE and the HFSQL database engine, using a Client-Server architecture, and the MVC: Model-View-Controller methodology, the screenshots of the application are also displayed.
In section 5 the project conclusions, advantages and disadvantages of using a French development tool are presented.
2. Methodology
2.1. Problem description
This project is being developed at the Technological University of Pereira, located in the southeast of the city of Pereira, Risaralda (within the metropolitan area of the central west). Parking establishments usually do not have an administration system, which makes the management of income, money, customers and other activities a bit problematic. The analysis, design and development of a software for parking management is proposed.
2.2. Problem statement
In Bogotá, on January 23, 2015, there are between 1,700 to 3,000 parking lots 4. In this regard, considering the population of the 20 main cities of Colombia, with a factor of one parking lot for every 2654 people, we can assume that in Colombia there are approximately 8,209 parking lots. The administration of a parking lot includes several aspects, such as; billing, monthly installments management, spot verification and management, and reports, among other aspects. In many of the establishments, this process is done manually. This can mean a considerable loss of time, that affects the execution of the tasks of the administrator. It is intended to implement a software that facilitates the administration of a parking establishment; allowing billing, automatic allocation of spots, verification of remaining spots, reports generation, informs, and control of monthly installments, in a way that the tasks accomplished by the establishment manager can be assisted with the use of said software, allowing considerable time savings in his tasks. It is also intended to create additional modules that handle the concurrence in parking spots.
2.3. Platform choice
The number of users of the different versions of Windows is shown in Table 1 5.
Table 1 Windows versions usage
| Source | Net Market Share | W3Counter | Global Stats |
|---|---|---|---|
| Date | May 2016 | May 2016 | May 2016 |
| Total | 89.68% | 38.55% | 72.27% |
| Windows 7 | 48.57% | 21.57% | 38.95% |
| Windows 10 | 17.43% | 9.18% | 19.33% |
| Windows 8.x | 11.39% | 4.78% | 8.08% |
| Windows XP | 10.09% | 3.02% | 5.91% |
| Windows Vista | 1.35% |
From the previous table, the base version of Windows is chosen, Windows 7, since it is the version with the most users, even so, the software can be used in the other Windows versions, starting with Windows XP.
3. Results and Discussion
The Model-View-Controller architectural pattern was used for this project 6. The MVC pattern defines the model as the access to the database, the view as the user or system interfaces, and the controller as the one that interacts between the view and the model, managing the project workflow 7.
3.1. Requirements gathering
The requirements gathering was made using user stories (Table 2). A user story is a representation of a requirement written in one or two sentences using the user's common language. User stories are used in agile development methodologies for specifying requirements (together with discussions with users and validation tests) 3.
3.2. Design
3.2.1. Used tools
The following tools, methodologies and techniques were used in the project design:
3.2.2. Function types
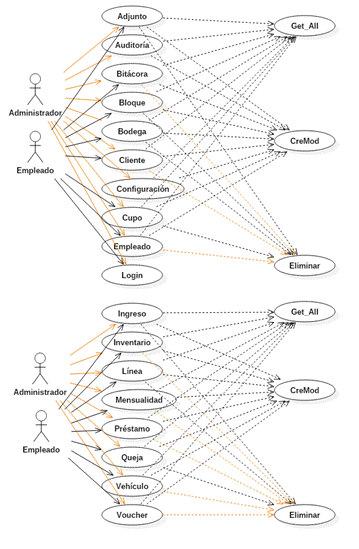
In Figure 1 three main functions can be highlighted that coincide with most classes; Next, their use is detailed:
Get_All_x: The Get_All function is the function that is responsible for obtaining the data from the database, and returning them in a structure array, which has the same class name. This function obtains the data from dynamic queries, built from the sent parameters.
CreMod_x: The CreMod function is the function that is responsible for creating or modifying the data, in the database, returning a 1 as a success response, or 0 as an error message.
Delete_x: The Delete function is the function responsible for deleting (logically, in most cases) the rows of the database.
Attachment: the function allows the user to upload attachments of bills, documents, registration forms and others; in the form of images, so that the user can make a diagnosis or follow-up on this data.
Logbook: The function allows communication between employees by means of book entries, as well as keeping a record of the novelties of the establishment. The employee can write messages that the other employees will see when they enter the module
Block: the function is the software, of the physical spaces that make up the establishment. A block, normally represents a floor, destined to the parking of vehicles.
Warehouse: The function to create warehouses in the software, to manage the physical warehouses, and the storage in them.
3.3. Class diagram description
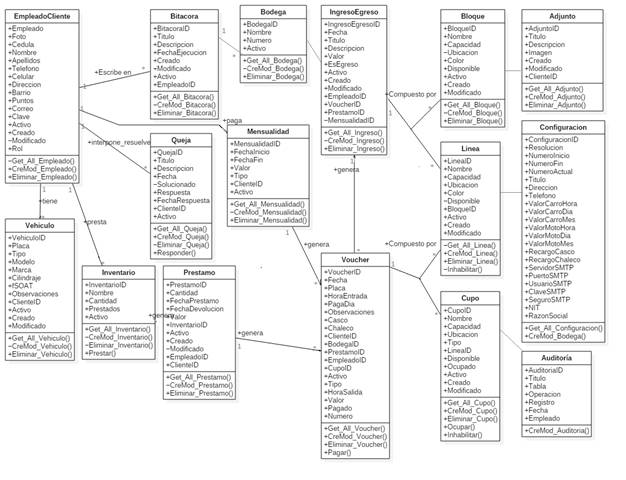
These schemes incorporate a structure and the behavior of each of the system’s objects and their relationships with the other objects, the classes and their associations between each other.
The general design of the class diagram of the parking management system is presented below. Figure 2 shows the entire class system of the program to be implemented
3.3.1. Attachment
The attachment class is the class that allows the user to upload attachments of bills, documents, registration forms and others; in the form of images, so that the user can make a diagnosis or follow-up on this data. The attachment class has the following fields: id, title, description, image, created, modified, and clientID.
The class Attachment has the following methods
Get_All_Attachment: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields
CreMod_Attachment: it is the method that allows to create or modify attachments
Delete_Attachment: it is the method that allows to delete attachments from the database
Notes: Attachments can only be deleted by the administrator user.
3.4. Audit
The audit class is the class that keeps track of any write operation in the database performed by employees, or users of the software, so that responsibilities can be monitored on the system.
The audit class has the following fields: id, title, table, operation, record, date and employeeID.
The audit class has the following methods
Get_All_Audit: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields
CreMod_Audit: it is the method that allows to create audit records
Notes: Audit records cannot be modified or deleted by any user.
3.5. Logbook
The logbook class is the function that allows communication between employees by means of book entries, as well as keeping a record of the novelties of the establishment. The employee can write messages that the other employees will see when they enter the module
The logbook class has the following fields: id, title, execution date, description, employeeID, created, modified and active.
The logbook class has the following methods
Get_All_Logbook: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields
CreMod_Logbook: it is the method that allows to create or modify the records of the logbook.
Delete_Logbook: it is the method that allows to delete the entries from the logbook, from the database.
Notes: The logbook can only be modified or deleted by the administrator user.
3.6. Block
The block class is the way that the physical spaces that make up the establishment are represented in the software. A block, normally represents a floor, destined to the parking of vehicles.
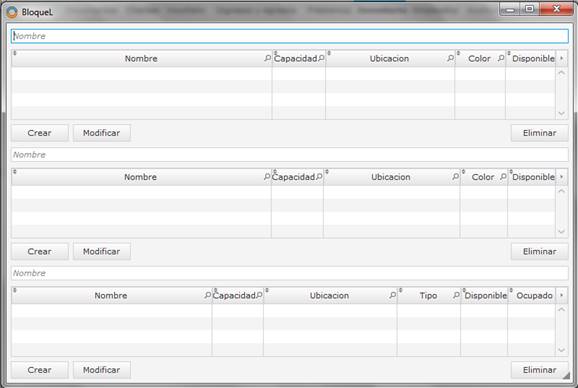
The block class has the following fields: id, name, capacity, location, color, available, active, created, modified.
The block class has the following methods
Get_All_Block: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Block: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Block: it is the method that allows to delete the blocks from the database.
Disable: it is the method that allows to disable the block, in case of damages or incidents.
3.7. Warehouse
The warehouse class is the class that allows to create warehouses in the software, to manage the physical warehouses, and the storage in them. The warehouse class has the following fields: id, name, number, and active.
The warehouse class has the following methods
3.8. Client
The client class is the class that allows to create clients, relate them to vehicles, monthly installments, and to keep track of them. The client class has the following fields: id, photo, ID card, name, surnames, telephone, cellphone, address, neighborhood, points, active, created, modified, email, and password.
The client class has the following methods
Get_All_Client: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Client: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Client: it is the method that allows to delete the clients from the database.
Notes: Clients can only be deleted by the administrator user.
3.9. Configuration
The configuration class is the class that allows to configure all the prices to be used in the system; hour, day or month, of motorcycles or cars; surcharges for vest or helmet and SMTP parameters used for sending email
The configuration class has the following fields: id, resolution, start number, end number, current number, title, address, telephone, car value (time, day, month), motorcycle value (time, day, month), helmet surcharge, vest surcharge, SMTP server, SMTP port, SMTP user, SMTP password, and SMTP secure server; in addition to the NIT and the corporate name of the establishment.
The configuration class has the following methods
Get_All_Configuration: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Configuration: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Configuration: it is the method that allows to delete the configuration from the database.
Notes: The configuration can only be modified by the administrator user.
3.10. Spot
The spot class is the class that allows to create parking spots in the system. Each block has one or more lines, and each line has one or more spots, which are where the customers will leave their vehicles.
The spot class has the following fields: id, name, capacity, location, type, available, occupied, active, created, modified, and lineID.
The spot class has the following methods
3.11. Employee
The employee class is the class that allows to manage the user data of each employee, their password, and the class that enables the audit. The class employed has the following fields: id, photo, ID card, name, surnames, telephone, cellphone, address, neighborhood, points, active, created, modified, email, password, and role.
The class employed has the following methods
Get_All_Employee: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields
CreMod_Employee: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Employee: it is the method that allows to delete the employees from the database.
PasswordRecovery: it is the method that allows to recover the user’s password.
Notes: Employees can only be deleted by the administrator user.
Only the users can change their own password.
3.12. Income
The income class is the class that allows to keep track of all the incomes and expenses of the system, as well as bills, loans, monthly installments, and both incomes and expenses created manually. The income class has the following fields: id, date, title, description, value, isExpense, active, created, modified, employeeID, voucherID, loanID, and monthlyinstallmentID.
The income class has the following methods
Get_All_Income: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Income: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Income: it is the method that allows to delete the incomes from the database.
Notes: incomes or expenses can only be deleted by the administrator user.
3.13. Inventory
The inventory class is the class that allows to create items for loan purposes in the database. The inventory class has the following fields: id, name, amount, borrowed, and active.
The inventory class has the following methods
Get_All_Inventory: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Inventory: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Inventory: it is the method that allows to delete the items from the database.
Borrow: it is the method that increases or decreases the number of borrowed ones.
Notes: Items can only be modified and deleted by the administrator user.
3.14. Line
The line class is the class that allows to create parking lines, dependent on the blocks, which will contain spots, which will be used by the clients. The line class has the following fields: id, name, capacity, location, color, available, active, created, modified, and blockID.
The line class has the following methods
Get_All_Line: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Line: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Line: it is the method that allows to delete the lines from the database.
Notes: For a line to be deleted, it must not have any active spots.
3.15. Monthly installment
The monthly installment class is the class that allows to create monthly installments in the system, assigning them to a client and verifying the active monthly installments at the time of billing. The monthly installment class has the following fields: id, start date, end date, value, type, clientID, and active.
The monthly installment class has the following methods.
Get_All_MonthlyInstallment: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_MonthlyInstallment: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_MonthlyInstallment: it is the method that allows to delete the monthly installments from the database.
Expire: automatic procedure that verifies overdue monthly installments and disables them.
Notes: Monthly installments can only be modified and deleted by the administrator user.
3.16. Loan
The loan class is the class that allows to create loans from the current inventory of the establishment. The loan class has the following fields: id, amount, loan date, return date, value, active, created, modified, inventoryID, employeeID, and clientID.
The loan class has the following methods
Get_All_Loan: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Loan: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Loan: it is the method that allows to delete the loans from the database.
Pay: It is the method that allows to pay the value of a loan and close it.
Notes: loans can only be modified or deleted by the administrator user.
3.17. Complaint
The complaint class is the class that allows to create complaints about the establishment's service and respond to them. The complaint class has the following fields: id, title, description, date, solved, response, response date, clientID, and active.
The complaint class has the following methods
Get_All_Complaint: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Complaint: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Complaint: it is the method that allows to delete the complaints from the database.
Solve: it is the method that allows to respond to complaints.
3.18. Vehicle
The vehicle class is the class that allows to create vehicles and relate them to the clients. The vehicle class has the following fields: id, license plate, type, model, brand, displacement, soat’s date, observations, active, created, modified, and clientID.
The vehicle class has the following methods
Get_All_Vehicle: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Vehicle: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Vehicle: it is the method that allows to delete the vehicles from the database.
Notes: vehicles can only be modified or deleted by the administrator user.
3.19. Voucher
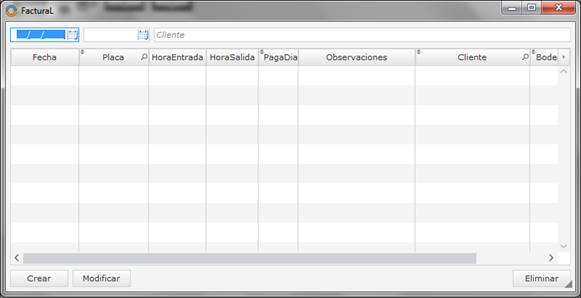
The voucher class is the class that allows generating logical receipts in the system, to keep track of the supplied services. The voucher class has the following fields: id, date, license plate, entry time, day pay, observations, helmet, vest, clientID, warehouseID, loanID, employeeID, active, spotID, type, departure time, value, paid, and number.
The voucher class has the following methods
Get_All_Voucher: it is the method that allows to obtain the rows of the database, with or without filters on their fields.
CreMod_Voucher: it is the method that allows to create or modify records.
Delete_Voucher: it is the method that allows to delete the vouchers from the database.
Pay: it is the method that allows payments to be made on the generated vouchers.
Notes: vouchers can only be modified or deleted by the administrator user.
4. Development
4.1. Methodology
The agile methodology SCRUM 8,9, was used for the development of the project, which conceives the development of the software with the use of Sprints, or cycles; and having roles within the project’s team.
4.2. Used tools
The French IDE WINDEV 10 was used for the project development as well as the programming language WLANGUAGE 11, the HFSQL as the database engine, a Client-Server architecture 12), and the MVC: Model-View-Controller methodology.
4.3. Prototype
Some screen designs implemented by ParqueApp are shown in Figures 3, 4, 5 and 6. The design for each module is shown below.
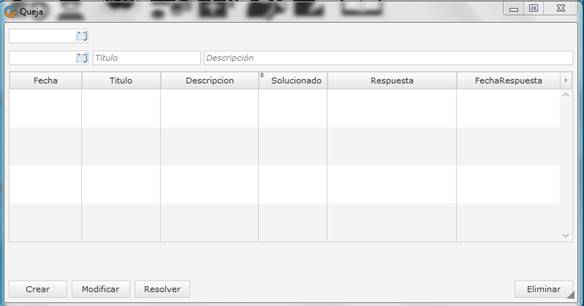
Figure 3 is the complaint’s module that allows the creation of client’s complaints, as well as a response to the complaint. This is done as a way for the establishment to keep track of the complaints.
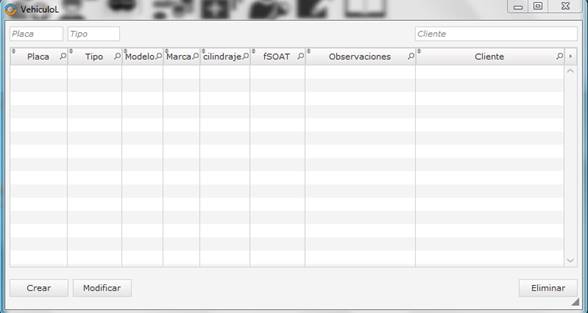
Figure 4 shows the vehicle’s module that allows the management of the client’s vehicles.
Figure 5 shows the parking module that allows the creation of floors, blocks, lines and parking spots. Figure 6 shows the module of vouchers/bills that allows the creation of bills of the parking service in the system.
5. Conclusions
Thanks to the realization of the project, it was possible to create a software that allows the management of a parking establishment, making the executed activities simpler and faster.
Data collection was done through interviews and observations to some parking lots in the city of Pereira, geographically separated by more than 100 meters.
As a result of the statistical investigation it is concluded that the most used platforms in these establishments are laptops with Windows 7 as the operating system.
Through the user stories the characteristics that the software should have were defined, to meet the needs of the administrators and employees; with the requirements being gathered through these user stories.
Through the selected methodologies, techniques, and tools, it was possible to perform the analysis, and the software design, in accordance with the gathered requirements, giving stability and scalability to the solution.
Thanks to the realization of the project, some methodologies, techniques and tools were discovered and will serve as the basis for future projects.
6. Recommendations
A second stage of the software includes the development of the application in a WEB environment, in order for its distribution to be carried out as SaaS (software as a service).
Web services or an API Rest, based on the web software, must be developed to scale the software to a mobile platform.
A third stage of the software includes the development of a mobile application connected to the main system.
An image processing system must be developed for reading license plates through mobile devices.