Artículos
Data from the study of CdS:Al thin films grown by the method of chemical bath deposition after aging
Datos del estudio de películas delgadas de CdS:Al crecidas por el método de deposición de baño químico después del envejecido
Edgar Mosquera1
Jesús Diosa1
Arturo Fernández-Pérez2
1 Universidad del Valle, Departamento de Física & Centro de Excelencia en Nuevos Materiales, Facultad de Ciencias Naturales y Exactas, Cali, Colombia. Correo electrónico: Edgar.mosquera@correounivalle.edu.co, jesus.diosa@correounivalle.edu.co.
2 Universidad del Bío-Bío, Departamento de Física, Facultad de Ciencias, Concepción, Chile. Correo electrónico: arturofe@ubiobio.cl.
Abstract
This article present the data of the study of the structural, optical and vibrational properties of CdS:Al thin films synthesized by chemical bath deposition (CBD) method after aging. The samples were characterized by X-ray diffraction, UV-vis and photoluminescence spectroscopy, and Raman spectroscopy. X-ray diffraction pattern of the samples disclosed hexagonal crystalline structure of CdS. The crystallite size was estimated for each thin film. The energy band gap was calculate using the Tau plot method. The samples present defects in their structure. A detailed study on the structure was carry out in the region of 200 to 800 cm-1, where the 1LO and 2LO phonon modes are presents. The data have not been reported nor discussed for now.
Keywords : CdS:Al; Chemical bath deposition; Optical properties; Structure; Thin films
Resumen
Este artículo presenta los datos del estudio de las propiedades estructurales, ópticas y vibracional de películas delgadas de CdS:Al sintetizadas por el método de deposición de baño químico (DBQ) después del envejecido. Las muestras fueron caracterizadas por difracción de rayos X, espectroscopia UV-visible y fotoluminiscencia, y espectroscopia Raman. El patrón de difracción de rayos X de las muestras presenta una estructura cristalina hexagonal de CdS. El tamaño del cristalito fue estimado para cada película delgada. La brecha de banda de energía fue calculada empleando el método de Tau. Las muestras presentan defectos en su estructura. Un estudio detallado sobre la estructura fue llevado a cabo en el rango de 200 a 800 cm-1, donde los modos vibracionales 1LO y 2LO están presentes. Los datos no han sido reportados o discutidos por ahora.
Palabras claves: CdS:Al; Deposición de baño químico; Estructura; Películas delgadas; Propiedades ópticas
1. Introduction
The data presented in this paper is related to a research article entitled “Characterization of chemically-deposited aluminum-doped CdS thin films with post-deposition thermal annealing” 1. The data contain a description on characterization of undoped and aluminum-doped CdS thin films synthesized by chemical bath deposition method. The aged samples were characterized to know if their properties have been modified for use in solar cells 2. Their characterization was carried out using various analytical techniques. All corresponding Table and Figures are provided with this article.
2. Methodology
Here, we describe the measurement to determine the properties of the thin films 3-5 after aging. Several sets of aluminum-doped CdS thin films were grown by chemical bath deposition (CBD) on glass substrates (25 mm x 75 mm x 1 mm) using bath solutions with different concentrations of Al. The recipe to prepare undoped and doped CdS thin films is described in 1 and 4, respectively. The samples were characterized by using a X ray PANnalytical X´pert Pro diffractometer, the absorbance measurements were analyzed using a Chromtech spectrophotometer CT-8600, and photoluminescence (PL) measurements were performed at RT in a Perkin Elmer Spectrofluorometer LS55. Finally, Raman spectra were recorded at room temperature using a DXR Raman spectrometer ThermoFisher Scientific. Radiation of 532 nm (2.33 eV) from diode laser was focused on the samples in a backscattering geometry.
3. Results y discussion
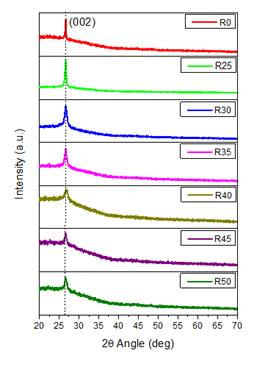
Figure 1 shows the XRD patterns for all synthesized samples whit different Al content. The principal (002) plane corresponds to the hexagonal crystalline phase of CdS and no other peaks have been observed, which indicates that the Al ions do not change the crystal structure of the CdS films. In addition, the crystallite size was estimated using the Scherrer´s formula 1, D = 0.9( (( cos ()-1, and reported in Table 1.
Table 1 Crystallite size and energy band gap of CdS:Al thin films after aging.
| Sample |
Crystallite size (nm) |
Energy band gap (eV) |
| 0.00 |
14.09(1) |
2.38(6) |
| 0.25 |
16.83(1) |
2.52(8) |
| 0.30 |
10.62(2) |
2.55(7) |
| 0.35 |
14.55(4) |
2.58(6) |
| 0.40 |
12.08(1) |
2.58(3) |
| 0.45 |
21.25(3) |
2.55(6) |
| 0.50 |
33.25(9) |
2.55(2) |
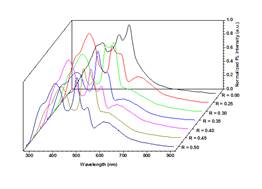
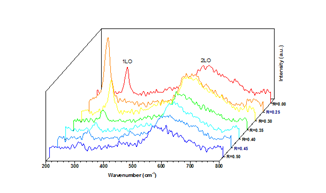
The energy band gap (Eg) was calculate using the Tau plot method and reported in Table 1. Here, we observed an increase in Eg with Al content with respect to the CdS thin film. Figure 2 shows PL measurements of the thin films. The samples present emission bands that could be attributed to defect luminescence. The Raman spectra of CdS and CdS:Al thin films grown by CBD are shown in Figure 3. Here, the 1LO and 2LO phonon modes are presents.
4. Value of the Data
The data provide structural and optical information about aluminum-doped thin films after aging of the samples.
Method and data will be advantageous for solar cell applications.
The data can be used for quantitative comparison with data from other studies of similar materials exposed to different experimental conditions.
5. Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Universidad del Valle, C.I. 71152, and DIUBB Grant 184423/2R.
6. References
1. Fernández-Pérez A, Navarrete C, Valenzuela P, Gacitúa W, Mosquera E, Fernandez H. Characterization of chemically-deposited aluminum-doped CdS thin films with post-deposition thermal annealing. Thin Solid Films. 2017; 623:127-34. Doi: 10.1016/j.tsf. 2016.12.036.
[ Links ]
2. Repins I, Contreras B, Egaas C, Dehart J, Scharf C, Perkins B, Nou B. 19.9%-efficient ZnO/CdS/CuInGaSe2 solar cell with 81.2% fill factor. Prog Photovoltaics: Res Appl. 2008; 16(3):235-239. Doi: 10.1002/pip.822.
[ Links ]
3. Khallaf H, Chai G, Lupan O, Chow L, Park S, Schulte A. Investigation of aluminium and indium in situ doping of chemical bath deposited CdS thin films. J Phys D Appl Phys. 2008; 41: 185304. Doi: 10.1088/0022-3727/41/18/185304.
[ Links ]
4. Fernández-Pérez A, Sandoval-Paz M G, Saavedra R. Photoacoustic study on the optical properties of Aluminium-doped Cadmium Sulphide thin-films. Chalcogenide Letters. 2016; 13(11): 507-514.
[ Links ]
5. Khan M J I, Kanwal Z. First principle calculations of optical properties of CdS:Al system (A DFT + U study). Mater Res Express. 2019; 6: 035905. Doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/aaf5a8
[ Links ]