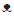Ahigh sodium consumption diet is associated with elevated blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) in developed and developing countries 1,2. In 2010, the cause of 1.65 million CVD deaths was associated with a sodium intake above the 2.0 g/day level recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) 1,3. Therefore, one of the priorities of international and local agencies is to make people reduce the sodium intake in order to decrease CVD occurrence rates and the burden this disease represents for health systems. However, such initiatives have been limited in part by the lack of reliable and comparable data on sodium intake 4.
Ecuador, a medium-income country, has experienced important socioeconomic and demographic changes over the last decades that have resulted in longer life expectancy rates, urbanization, a substantial economic growth, and a reduction regarding the transmission of communicable diseases 5,6. As a result, eating changes in the population have occurred as people have changed from traditional and non-processed food diets to those in which refined sugars, animal products, and highly processed foods levels are high 7. Currently, CVD and diabetes are the leading causes of mortality in Ecuador 8. According to the 2012 National health and nutrition survey of Ecuador (ENSANUT-ECU), the prevalence of pre-hypertension and hypertension in adult population aged from 18 to 59 years is 37.2% and 9.3%, respectively 9.
Despite dramatic increases in both the prevalence of hypertension and unhealthy dietary patterns in Ecuador have been reported 5,9, there are no data on sodium consumption by the population in this country by using a not diet-based method. To address this knowledge gap, a pilot study was conducted with the following objective: i) to provide preliminary data regarding sodium intake in an urban sample of adults aged 25-64 years, and ii) to explore the feasibility to determine population-level sodium intake by using 24-hr urine samples.
METHODS
Study design
A cross-sectional study was conducted in a sample of young and middle-aged adults living in an urban setting located in the highlands of Ecuador. The 2.0 grams per day sodium consumption level recommended by the WHO 3 was used to differentiate between normal and high sodium intake groups . Based on the methodology of the WHO for population-level sodium intake determination in 24-hr urine samples 10, subjects meeting one or more of the following criterion were excluded from the study: those who were not able to provide informed consent and a 24-hr urine excretion sample; those with a known history of heart or kidney failure, stroke, and liver disease; those who had used diuretics, or multivitamins, NSADS, and prostaglandins within two weeks prior to the study, and being pregnant. For the assessment of the feasibility a 120 subjects minimum value of 24-hr urine samples was established as the enrollment objective.
Study sample and setting
Based on a WHO/PAHO expert group that recommends a minimum sample of 120 subjects per age and sex stratum for a national survey 10, it was assumed that this sample size (n=120) would be enough for a pilot study. In order to account for the attrition rate, which may be as high as 50%, 180 individuals 10 were invited to participate. The study sample consisted of a convenience sample made up of employees of a higher education institution (Universidad San Francisco de Quito [USFQ]) and its main teaching hospital. A broad spectrum of employees (including health care workers, professors, and janitorial staff) from both institutions was asked to take part in the study.
Prior to data collection, participants were informed about the purpose and protocol of the study, and requested to sign an informed consent, in which the methodology of the pilot study was thoroughly explained. Likewise, the interviewer emphasized the scientific importance of the information to be obtained, while ensuring confidentiality of participants' data. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the USFQ.
Data collection
The WHO STEPS instrument was administered to those participants whose informed consent was obtained in order to collect data on demographics, medical history, and anthropometric measurements 11. In order to obtain 24-hr urine samples each subject was given a kit to collect the sample, besides the research team provided participants with a detailed explanation on how to collect the sample properly. On the day of collection, all subjects were trained to discard the first morning urine, and to collect the subsequent urine samples for a 24-hr period. Furthermore, to ensure the estimation of sodium intake from a regular diet, participants were not allowed to collect urine samples on weekends or holidays.
Urinary sodium and potassium were measured by using an ISE (ion-selective electrodes) indirect Na-K-Cl for Gen.2 module (Roche Diagnostic, Switzerland). The laboratory in charge of analyzing the samples reported a final 24-hr sodium excretion value in mmol/day for each subject. Finally, by multiplying each of the final results by a 23 factor, the conversion from sodium mmol to sodium mg was made, while the conversion from sodium (mg) to salt (1g NaCl) was achieved by dividing said result by 390 12. Data were collected from March 2015 to October 2016.
Statistical analysis
Descriptive statistics were used to summarize the baseline characteristics of the study participants. Continuous variables are described as mean ± SD or median (IQR), and categorical variables, as counts and percentages. Based on the available literature, which has reported higher sodium consumption in men than in women 4, data were separately analyzed by sex. Differences between normal and high-sodium consumers were assessed by means of parametric and non-parametric tests as appropriate. P-values <0.05 from two-sided tests were considered as statistically significant. All analyses were performed using R v 3.3.2 software for MacTm OS.
RESULTS
Figure 1 shows that the final study population of this cross-sectional analysis was 129 subjects (~72% of the total subjects that were invited to participate). The median age of the sample was 39 years; 91% participants identified themselves as belonging to the mestizo race; 60% were female, and 53% of the final sample had <12 years of schooling. Table 1 shows that males had a less favorable risk factor profile than females.
Table 1 Demographic and clinical characteristics of the study population
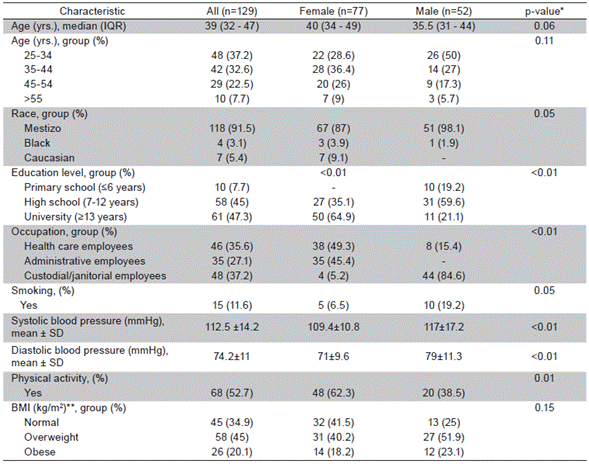
IQR: interquartile range; SD: standard deviation; BMI: body mass index. *All continuous variables were analyzed by using t-test and Wilcoxon Rank Sum test; all categorical data were analyzed through Chi-squared or Fisher's exact tests as appropriate; **BMI groups: Normal <24.9 kg/m2; Overweight 25-29.9 kg/m2; Obese >30 kg/m2
Overall, sodium intake in the study population was 2 655(±1 185) mg/d (range: 1 725 to 3 404), which is equivalent to a dietary salt intake of 6.8 g/d (range: 4.4 to 8.7). Sodium intake in males was significantly higher than in females: 3 175(±1 202) mg/d vs. 2 304 (±1 042) mg/d, respectively, (p<.01). On the other hand, the mean potassium intake was 1 224(±550) mg/d (range: 858 to 1 521). Furthermore, the median creatinine value was 1 079 mg/dl (range: 880 to 1 333) per day.
Based on the 2.0 g per day sodium intake value recommended by the WHO 1,3, a higher sodium consumption than this reference value was observed in 63% of the participants. In Table 2 the following results are depicted: subjects with higher sodium intake levels were more likely to be males with a lower level of education (custodial/ janitorial employees) and higher urine potassium levels, although none of them had the ≥3.5 g/d potassium value recommended by the WHO 13. There were no differences regarding age, BMI, and perception of salt consumption between normal and high sodium intake groups.
DISCUSSION
Results obtained in this cross-sectional study based on a 24-hr urinary excretion collection allow to say that approximately two-thirds (63%) of the participants had sodium intake levels higher than the who recommended value 1,3. In addition, this higher consumption of sodium was most prevalent in males and janitorial employees.
The present pilot study provides a reliable preliminary value sodium intake and how it varies based on a 24-hr urinary sodium excretion basis in a sample of urban population in Ecuador. During the writing of this paper, an abstract reported that subjects aged between 15 and 65 years and who were living in urban settings of the coast and highlands of Ecuador had an average sodium intake of 4901.9 mg/d 14. However, said values were obtained through a diet-based method (24-hr recall surveys), which has been reported to have larger measurement errors when estimating habitual dietary intake in comparison with the use of urinary markers 15,16.
Table 2 Differences between participants with normal and high-salt intake levels
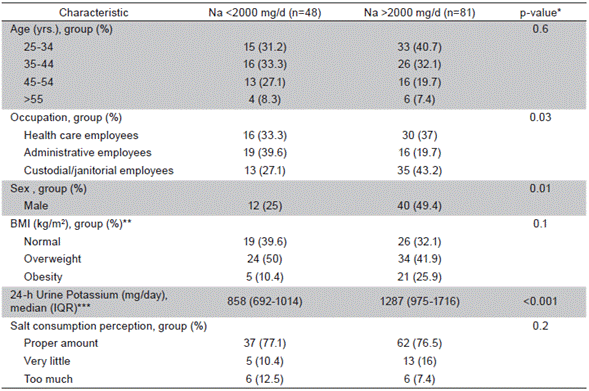
***IQR: interquartile range; BMI: body mass index. *All continuous variables were analyzed by using t-test and Wilcoxon Rank Sum test; all categorical data were analyzed through Chi-squared or Fisher's exact tests as appropriate.**BMI groups: Normal <24.9 kg/m2; Overweight 2529.9 kg/m2; Obese >30 kg/m2. The WHO recommended potassium intake value is 3,510 mg per day
The high consumption of sodium found in this study could be explained by several factors. For example, high sodium intake among people with low levels of schooling and income has been associated with the possibilities this type of population has regarding acquiring knowledge on healthy dietary practices and affordability constraints 17. Overall, population groups with a lower socioeconomic level are more prone to consume high-sodium, high-fat and high-sugar food 18. Also, this could reflect the widespread accessibility to cheap ultra-processed high-sodium products due to the lack or weak policies promoting healthy eating habits in the country 19,20.
In addition, these high sodium intake levels could be explained by cultural preferences towards fast food consumption instead of fruits and vegetables consumption as reflected by the consistent low potassium values found in the study population 13. These results are in agreement with the findings of the ENSANUT-ECU, where it was reported that the recommended 400 mg of fruit/vegetables per day consumption level was not observed in the Ecuadorian population 9.
This pilot study provides enough evidence and rationale to support the execution of a national sodium intake survey to understand, at a country-level, which are the population's most common eating habits and what types of food they eat, and how sodium levels vary by age, sex, and geographical location. This information will help both medical providers and key stakeholders to successfully influence or change Ecuadorian's choices, attitudes, beliefs, and behaviors towards sodium daily consumption, which ultimately will help to prevent the development of CVD and hypertension in the country.
Based on the findings and experience of this study, 72% of the subjects recruited initially completed their participation in it. Although the recommended sample size for a specific age and sex stratum for a national survey was obtained 10, a more comprehensive study will require the recruitment, retention, and follow-up strategies to be reconsidered and adapted towards the rural population of Ecuador. In terms of acceptability, enrolled participants showed high satisfaction and perceived it as appropriate to be aware of the consequences of a diet high in sodium (although this was not quantitatively assessed, but based on what the subjects told the researchers personally). In light of these results, it's possible to conclude that this project is highly feasible to be scaled at a national-level.
To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study that provides data on the distribution of sodium intake in an Ecuadorian population using 24-hr urinary excretion samples, and that it reported less measurement errors compared with diet-based methods 15,16. In addition, the results obtained here are not adjusted for non-urinary losses such as sweat. This guarantees its comparability with prior unadjusted reports of 24-hr urinary sodium excretion 4. Thus, the final sodium estimates reported here can be considered as the most reliable value of sodium consumption for the study sample. The main limitation of this study is the lack of generalizability of the findings at a country-level. Therefore, the estimated sodium intake might be a lower estimate of the true value due to heterogeneity in sex, age, cooking styles, and socio-demo-graphic variables across the country.
In summary, the sodium consumption in 129 young and middle-aged adults was estimated based on 24-hr urinary excretion samples. Sodium intake was higher than the who recommended level 1,3 in nearly two-thirds of the participants. These results should contribute supporting the execution of a national sodium intake survey that, in turn, would provide information to guide and plan public health strategies seeking to decrease cardiovascular diseases occurrence rates in Ecuador