Introduction
Most osteoarticular infections in childhood have an acute course, being S. aureus the most frequent causal germ. In the face of a subacute course in which there is no response to the usual antibiotic treatment, the possibility that it is caused by an anaerobic microorganism should be considered 1; the genus Fusobacterium is the most frequent.2
Clinical case
A 10-year-old healthy boy is brought to the emergency room due to right gonalgia (knee pain) for the last 3 weeks. The patient denies antecedents of trauma and remains afebrile all the time. The articular exploration of the hip and the knee shows no limitation of mobility or inflammatory signs. X-rays of the hip and the knee are performed, without alterations, and the patient is discharged with antiinflammatory treatment.
14 days later (5 weeks of evolution) he comes due to worsening of the pain, antalgic position of the right lower limb and limitation of mobility of the right hip. The patient remains afebrile. Laboratory analyses were requested, showing mild leukocytosis and neutrophilia (13.6 x 109 leukocytes/l, 66.1% neutrophils) and C reactive protein of 15.15 mg/dl. A joint ultrasound scan is performed, which shows joint effusion in the right hip; an ultrasound-guide arthrocentesis is carried out and joint fluid of opaque appearance is extracted with 114,840 cells/mm3 (92.7% PMN) and 0mg/dl of glucose.
Given the suspicion of septic arthritis of the right hip, traumatology indicates arthroscopy for drainage and joint lavage; in addition, intravenous cloxacillin and cefotaxime are started.
On the second day after admission, a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is performed, which reveals osteomyelitis in the acetabulum and myositis of the external obturator muscle and the adductor muscles (Fig. 1).
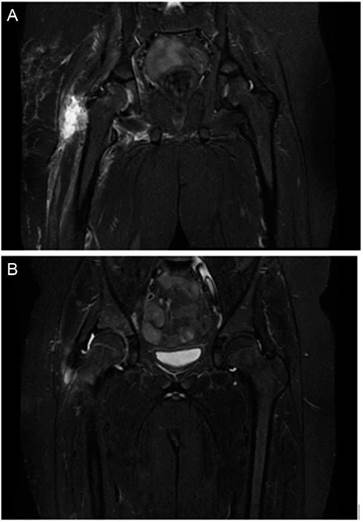
Figure 1 A) Acetabular osteomyelitis and myositis of the external obturator muscle and adductor muscles. B) Significant improvement in acetabular bone edema. Important decrease in muscle edema.
During the first days after admission, the clinical course was torpid, with onset of fever, worsening of pain and increase in the acute phase reactants (maximum CRP of 26.75 mg/dl and ESR of 99mm/h), requiring, on the fifth and the seventh day after admission, arthrotomy for drainage and joint lavage.
The PCR for Kingella kingae in the joint fluid is negative and no growth is detected in the cultures thereof until the seventh day, when they notify the isolation of Fusobacterium nucleatum, for which the treatment is changed to ampicillin and metronidazole awaiting the antibiogram. After verifying sensitivity, it is changed to intravenous.
Discussion and conclusions
With this case we want to highlight that, even though osteoarticular infections due to anaerobic agents are infrequent in childhood,2 there is a need to think about these infections when the clinical course is atypical (subacute condition, absence of fever or poor clinical evolution with the usual antibiotic treatment).1,3 The microbiological identification by conventional methods results difficult, so if there is a high suspicion of bacterial infection and the cultures are sterile, molecular identification by 16S rRNA sequencing could be carried out. (3
It is recommended that the initial treatment includes a beta-lactam antibiotic together with clindamycin or metronidazole, since the proportion of beta-lactamase-producing Fusobacterium spp is increasing. A study has also reported up to 9% of clindamycin-resistant Fusobacterium. ( 1 In general, with adequate treatment, the prognosis is very good. (2,4,5
Although this clinical picture has been related to oral cavity disease or immunosuppression, (3-5 the majority do not present these antecedents, (1,2 as in our case.











 text in
text in 


